Product Description
Dear friends!
My name is Irina Mamoshina. Please pay a moment of your attention : -).
Our company HangZhou CHINAMFG International Trade Co., Ltd is engaged in the production and sale of auto parts for Chinese special equipment, engines and equipment assembly. We also produce metal parts ourselves, such as gears, fingers, filters, etc.
Our products include:
ZL30G, ZL40G, ZL50G, ZL50GL, ZL60G, LW3
| After-sales Service: | No |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | No |
| Condition: | New |
| Certification: | CE, RoHS, GS, ISO9001 |
| Standard: | DIN, ASTM, GOST, GB, JIS, ANSI, BS |
| Customized: | Non-Customized |

How do tensioner rollers contribute to the adaptability and versatility of machinery in different settings?
Tensioner rollers play a crucial role in enhancing the adaptability and versatility of machinery in various settings. Here’s a detailed explanation of how tensioner rollers contribute to the adaptability and versatility of machinery:
1. Tension Adjustment:
Tensioner rollers allow for easy adjustment of belt tension. In different operating conditions or applications, the required belt tension may vary. Tensioner rollers provide a means to quickly and accurately adjust the tension to suit the specific requirements of the machinery. This adaptability enables the machinery to accommodate different loads, speeds, or operating conditions without the need for significant modifications or replacements.
2. Belt Length Compensation:
In some situations, machinery may require the use of belts with different lengths or sizes. Tensioner rollers can compensate for variations in belt length by accommodating the necessary slack or tension adjustments. This flexibility allows machinery to be easily adapted to different belt lengths or sizes, facilitating the use of belts with varying specifications without the need for extensive modifications to the system.
3. Belt Type Compatibility:
Tensioner rollers are designed to accommodate different types of belts, such as V-belts, timing belts, flat belts, or ribbed belts. This versatility enables machinery to utilize various belt types based on the specific requirements of the application. Tensioner rollers can be configured or adjusted to suit the specific belt profile, ensuring proper tension and alignment regardless of the belt type used. This adaptability allows machinery to be versatile in accommodating different belt types for different applications.
4. Misalignment Compensation:
Tensioner rollers can compensate for minor belt misalignment. In real-world operational scenarios, belt misalignment can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, component wear, or external forces. Tensioner rollers with self-aligning or adjustable features can help mitigate the effects of misalignment by automatically adapting to the belt’s position. This adaptability ensures that the belt remains properly tensioned and aligned, reducing wear, improving performance, and extending the life of the machinery.
5. Installation Flexibility:
Tensioner rollers provide flexibility during the installation process. They can be easily positioned or adjusted to suit the available space, layout, or specific constraints of the machinery or system. This adaptability simplifies the installation process and allows for the efficient integration of tensioner rollers into different machinery configurations or designs. The ability to accommodate varying installation requirements enhances the versatility of the machinery in different settings.
6. Noise and Vibration Control:
Tensioner rollers contribute to noise and vibration control in machinery. They help maintain proper belt tension and alignment, reducing the risk of belt slippage, flutter, or excessive vibrations. By minimizing these issues, tensioner rollers contribute to a quieter and smoother operation of the machinery, enhancing its adaptability in noise-sensitive environments or applications that require precise control and stability.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability:
Tensioner rollers facilitate maintenance and service tasks, enhancing the adaptability of machinery in different settings. They are designed for easy access and adjustment, simplifying routine inspections, tension adjustments, or replacement of belts. The ease of maintenance and serviceability allows for efficient and timely adjustments or repairs, minimizing downtime and ensuring the machinery can quickly adapt to changing operational requirements.
In summary, tensioner rollers significantly contribute to the adaptability and versatility of machinery in different settings. They enable easy tension adjustment, accommodate variations in belt length or size, support various belt types, compensate for misalignment, provide installation flexibility, contribute to noise and vibration control, and facilitate maintenance and serviceability. By incorporating tensioner rollers into machinery design and operation, manufacturers and operators can enhance the adaptability and versatility of their equipment, allowing for efficient and reliable performance across a range of applications and operating conditions.
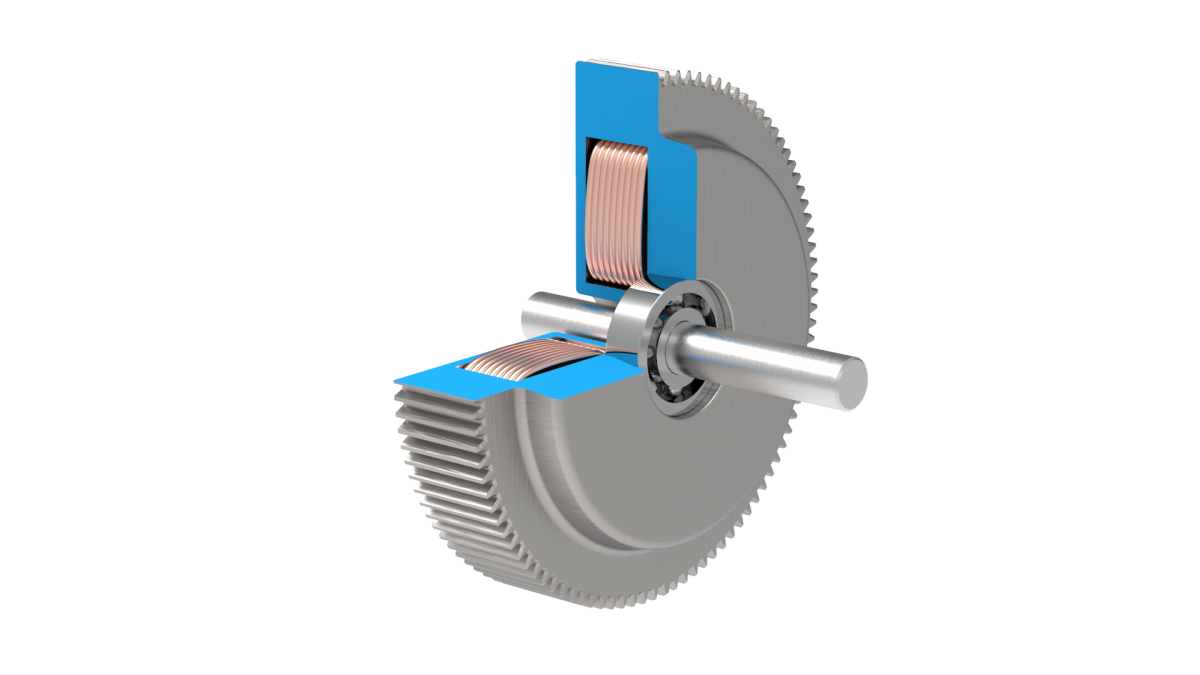
What role do tensioner rollers play in ensuring proper alignment and tension in belt systems?
Tensioner rollers play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and tension in belt systems. They perform several key functions that contribute to the overall performance and reliability of belt-driven systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Maintaining Proper Belt Tension:
Tensioner rollers help maintain the optimal tension in belts. Proper tension is essential for efficient power transmission and preventing belt slippage. Tensioner rollers exert a controlled amount of pressure on the belt, ensuring it remains tensioned within the desired range. By maintaining proper belt tension, tensioner rollers help prevent power loss, slippage, and premature wear of the belt.
2. Absorbing Belt Vibrations:
Vibrations can occur in belt systems due to imbalances, misalignments, or variations in load. These vibrations can lead to increased wear, noise, and reduced belt life. Tensioner rollers are designed to absorb and dampen vibrations, minimizing their impact on the belt. By reducing vibrations, tensioner rollers help maintain proper alignment and tension, enhancing the performance and longevity of the belt system.
3. Reducing Belt Misalignment:
Proper belt alignment is critical for optimal performance and longevity. Tensioner rollers play a role in maintaining belt alignment by exerting consistent pressure on the belt and guiding it along the intended path. They help prevent lateral movement and ensure that the belt remains centered on the pulleys. By minimizing belt misalignment, tensioner rollers reduce wear, noise, and the risk of premature belt failure.
4. Compensating for Belt Stretch:
Belts can experience stretch over time due to the mechanical stresses they undergo during operation. Belt stretch can result in reduced tension and compromised power transmission. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt stretch by applying additional tension to maintain the desired level of belt tension. This compensation helps prevent belt slippage, excessive wear, and premature failure, ensuring proper alignment and tension in the belt system.
5. Facilitating Belt Tracking:
Proper belt tracking is essential for smooth operation and longevity of the belt system. Tensioner rollers aid in maintaining belt tracking by exerting controlled pressure and guiding the belt along the intended path. They help prevent the belt from wandering or rubbing against the pulleys or other components. By facilitating accurate belt tracking, tensioner rollers contribute to proper alignment, reduced wear, and extended belt life.
6. Supporting Belt Span:
In longer belt spans or applications with heavy loads, tensioner rollers provide support to the belt. They help prevent sagging and excessive flexing of the belt, which can lead to accelerated wear and reduced belt life. By offering support, tensioner rollers contribute to maintaining proper alignment and tension throughout the belt system.
7. Allowing Tension Adjustment:
Tensioner rollers often incorporate mechanisms that allow for tension adjustment. This feature enables fine-tuning of the belt tension to suit specific operating conditions or accommodate changes in load or temperature. Tension adjustment capability ensures that the belt system can be properly tensioned, optimizing performance, and reducing the risk of wear or slippage.
In summary, tensioner rollers play a vital role in ensuring proper alignment and tension in belt systems. They maintain proper belt tension, absorb vibrations, reduce belt misalignment, compensate for belt stretch, facilitate belt tracking, provide belt support, and allow tension adjustment. By performing these functions, tensioner rollers contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability, and longevity of belt-driven systems.

Can you explain the importance of tensioner rollers in maintaining belt tension in engines?
Tensioner rollers play a crucial role in maintaining belt tension in engines, and their importance cannot be overstated. Here’s a detailed explanation of why tensioner rollers are essential in ensuring proper belt tension in engines:
1. Reliable Power Transmission:
In engines, belts are used to drive various components such as the alternator, water pump, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. These belts need to maintain the correct tension to ensure efficient power transfer from the engine to these accessories. Tensioner rollers provide the necessary force to keep the belts properly tensioned, allowing them to transmit power reliably. By maintaining optimal belt tension, tensioner rollers help prevent slippage or disengagement of the belts, ensuring that the engine accessories operate smoothly and consistently.
2. Compensation for Belt Stretch and Wear:
Belts in engines can experience stretching over time due to regular use and exposure to heat. Additionally, belts can wear out and lose their original tensioning properties. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for these factors by automatically adjusting their position to maintain the desired tension. As belts stretch or wear, the tensioner roller adapts to the changes and ensures that the belts remain properly tensioned. This compensatory function helps maintain optimal belt performance and extends their lifespan.
3. Preventing Belt Noise and Vibrations:
Correct belt tension is crucial for minimizing noise and vibrations in engines. Insufficient tension can lead to belt slippage, causing squealing or chirping noises. On the other hand, excessive tension can cause increased friction and vibrations, resulting in a noisy and uncomfortable engine operation. Tensioner rollers help maintain the ideal tension, reducing the risk of belt slippage and excessive vibrations. By promoting smooth belt operation, tensioner rollers contribute to a quieter and more comfortable engine experience.
4. Enhancing Engine Safety and Reliability:
Proper belt tension is essential for the safe and reliable operation of engines. If the belt tension is too loose, the belts may disengage from their pulleys, resulting in a loss of power to critical engine components. This can lead to engine overheating, loss of electrical power, or compromised steering functionality. On the other hand, excessive tension can put excessive stress on the belts and other engine components, potentially causing premature wear or failure. Tensioner rollers help maintain the correct tension, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the engine and its accessories.
5. Maintenance and Longevity:
Tensioner rollers require regular maintenance and inspection to ensure their continued functionality. Proper lubrication, alignment, and visual inspections are necessary to identify any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If a tensioner roller is found to be faulty or no longer providing adequate tension, it should be promptly replaced to prevent belt-related issues and ensure the longevity of the engine and its components.
In summary, tensioner rollers are of utmost importance in maintaining proper belt tension in engines. They enable reliable power transmission, compensate for belt stretch and wear, reduce noise and vibrations, and enhance engine safety and reliability. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of tensioner rollers are essential for ensuring optimal engine performance and preventing potential belt-related problems.


editor by CX 2023-12-04
China OEM Power Cage Pulley 8 Inch Pulleys Single Fitness Motor Small Metal Wheel Exercise Equipment Meat Grinder Exercise Meat Grinder Alternator Belt Tensioner near me shop
Product Description
Power cage pulley 8 inch pulleys single fitness motor small metal wheel exercise equipment meat grinder exercise meat grinder alternator belt tensioner
How to Tell If Your Timing Belt is Worn Out
The timing belt is a component of your engine that consists of special materials that coordinate the rotational movement of your camshaft and crankshaft. This synchronization is vital for sustainable combustion. In addition to being vital for the proper operation of your engine, the belt is also responsible for setting the pace at which it will turn. Timing belts must be extremely strong and resilient, able to maintain a high degree of synchronicity, and operate effectively even in the most severe conditions.
Problems caused by a worn-out timing belt
A worn-out timing belt can cause misfiring. Because the belt controls the movement of the pistons in the engine, it’s critical that it’s functioning properly. Misfires can cause serious engine damage and should be fixed as soon as possible. But how do you know if your timing belt is worn out? Here are 3 of the most common symptoms of a worn-out belt.
A car engine will misfire if the timing belt is broken, which could lead to severe damage. A broken belt may also cause excessive smoke to be produced by the exhaust system. If these symptoms are present, it’s time to take the car in for a timing belt replacement. A worn-out belt will affect the performance of your car. It will also affect the engine’s starting speed. When it’s time to replace it, you should do it now to avoid future problems.
Misfiring and premature cylinder closing are 2 of the most common symptoms of a worn-out timing belt. A worn-out belt can cause permanent engine damage. Because the timing belt contains teeth that grip the gears, it can slip. If the timing belt slips, the teeth can fall into the gears, causing the engine to misfire. Worn-out timing belts can also cause the engine to stall.
Engine ticking is another common sign of a worn-out timing belt. It can also be caused by low oil pressure. When oil pressure drops, the timing belt will become loose and cause a ticking sound. You should replace the timing belt as soon as it’s damaged. But it’s not enough if you don’t notice any of these signs right away. If the ticking sound continues, you’ll probably have an engine-related problem.
Types of timing belts
Timing belts are made of special materials that help the engine synchronize the crankshaft’s rotation with the camshaft’s. This precision is vital for the combustion process, as it ensures the proper opening and closing of the valves within the combustion chamber. The belts control the engine’s pace, which is why they must be strong enough to maintain synchronicity and operate at high speeds. However, timing belts do not come cheap, so there are several factors that you should be aware of before buying one.
First, timing belts come in different pitch sizes. A typical metric pitch is 5 millimeters, but some manufacturers use a higher or lower pitch. The pitch determines how much tension the belt will be able to carry and whether or not it will wear out prematurely. Other pitch sizes are more common. Timing belts come in 3 different widths, and they all have different tooth profiles. To find the right 1 for your engine, you need to know the pitch.
Modified curvilinear belts are made of 2 different types of materials. They combine the strengths of trapezoidal and curvilinear belts. The outer surface of these belts has a steeper angle than the belt’s teeth, which means that the power transmitted by the motor is much higher. Consequently, they are the primary choice for high-performance industrial applications. A synchronous timing belt is ideal for applications where precise synchronization of the driven and driver shafts is important.
Spliced and welded timing belts are used in many general applications. These belts typically have no joints or weak points and are more durable. These types of timing belts are also made with a smooth back and sealed edges. If you need a custom length or shape, these can also be manufactured. Then, you can order them for your exact measurements. When you need a new timing belt, you can simply ask for a quote and order 1 online.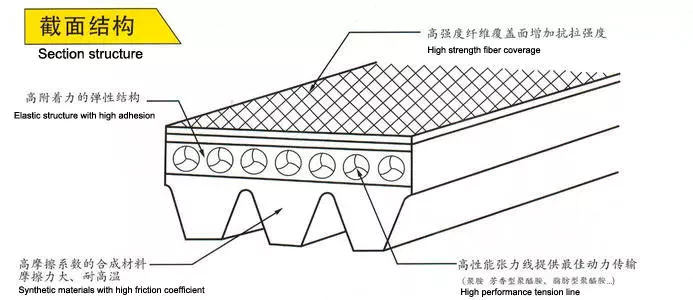
Common problems
Timing belts are a crucial part of your car’s drive system, and improper installation can cause a whole host of issues. It is also susceptible to crimping and premature wear. In either case, it is vital to take action early to prevent excessive engine wear and extend the life of the timing belt. Here are some common problems with timing belts. You may be surprised to learn that these problems are often caused by common car maintenance practices.
Regardless of the cause of the problem, a worn or faulty timing belt will affect the engine’s timing. This may result in misfires or excessive exhaust release. Engine misfiring is a serious sign that something is amiss. Depending on the extent of the problem, it could even lead to engine damage. If you experience erratic performance or excessive smoke, it’s likely the timing belt is faulty. Here are some common problems with timing belts and their causes.
Engine misfire is a common warning sign that your timing belt is wearing. This occurs when the timing belt slips off the gears or camshaft, causing the cylinder to open too early. If you notice this problem, take immediate action by visiting your mechanic immediately. Moreover, timing belt failures can cause a large amount of damage to your car’s engine, so it is essential to have your timing belt replaced in time.
Improperly adjusting the tension of your timing belt can also lead to serious problems. This can cause excessive wear on your engine’s pistons and valves, and damage the engine. Ultimately, a damaged timing belt may result in an expensive engine rebuild. While this might seem like a good option, it is not always the most practical solution. Ultimately, your car’s timing belt will wear down if you don’t fix these problems immediately.
Symptoms of a worn-out timing belt
If your car’s engine makes a high-pitched squeal when you start or run it, you may be experiencing a worn-out timing belt. You can check the belt by opening the hood and listening closely to the noise. You may also notice uneven RPM counts. The squealing sound can be caused by a number of factors, such as low oil pressure, engine lubrication problems, or even the timing belt.
If your car is exhibiting these symptoms, then it’s time for a replacement. A timing belt breaks down while your engine is running, and this can cause major engine damage. The timing belt is connected to the crankshaft and camshaft by a belt that keeps the 2 parts in sync rotation. When the timing belt wears out, it may cause a jump in the belt’s tooth, causing cylinders to open and close randomly, resulting in blow-by.
A timing belt is crucial to the functioning of your car’s engine. It synchronizes the engine rotation system and opens and closes the valves at the right time. Because it is subject to great forces inside the engine, the belt must be replaced at some point. Every vehicle needs a new timing belt at least once in its lifecycle. But what are the symptoms of a worn-out timing belt?
The timing belt is crucial to your car’s performance, so if you notice any of these signs in your vehicle, you should make an appointment with a qualified mechanic. The best way to tell if your timing belt needs to be replaced is to visually inspect the belt. You can visually inspect the belt while the engine is off, and if you notice it’s sagging, you should replace it.
When to replace a timing belt
A timing belt is an essential part of your vehicle’s engine and is responsible for synchronizing the rotation system, allowing the valves to open and close at the correct time. Due to its constant use and great forces inside the engine, timing belts must be replaced at some point. The recommended interval for timing belt replacement is anywhere from 60,000 to 150,000 miles. In most cases, timing belt replacement is recommended for vehicles between 6 and 10 years old.
Costs for a timing belt replacement can vary widely depending on the make and model of your vehicle. The labour and parts used for timing belt replacement are relatively inexpensive, but you’ll have to remove several parts of your engine to access them. Timing belt replacement also involves replacing the water pump, which is driven by the timing belt. These other parts will be replaced with new ones, but the overall cost of the repair depends on the type of car you drive.
A timing belt is a thin, rubber piece that runs along the front of the engine. It’s responsible for synchronizing the valves and camshafts and is an important component of an engine. The belt’s custom teeth make it easy to see when it’s time to replace your car’s timing belt. Oftentimes, car manufacturers recommend timing belt replacement every 2 to 4 years or 50,000 miles, and they’re not the only ones who recommend it.
A professional mechanic can replace the timing belt and water pump in 1 service, saving you both time and money. Timing belt replacement is an intricate task and can last anywhere between 4 and 8 hours, depending on the make and model of your car. However, it is worth it if you can get your vehicle into a garage or repair shop sooner rather than later. You can save a lot of money on labor costs by replacing your timing belt and water pump yourself.


China high quality Power Cage Pulley 8 Inch Pulleys Single Fitness Motor Small Metal Wheel Exercise Equipment Meat Grinder Exercise Meat Grinder Alternator Belt Tensioner wholesaler
Product Description
Power cage pulley 8 inch pulleys single fitness motor small metal wheel exercise equipment meat grinder exercise meat grinder alternator belt tensioner
Why You Should Get a New Timing Belt
A timing belt is a rubber belt with teeth that transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley. It prevents the piston from striking the valves at a critical level. Unfortunately, these belts cost a lot to replace. Here are some reasons why you should consider getting a new one. If you’re not sure whether a new timing belt is necessary, read on. You can also save money by avoiding unnecessary repairs and replacements by choosing an aftermarket timing belt.
Timing belts are rubber belts with hard teeth
While it’s true that timing belts are commonly known as “drive belts,” there are several different types of belts that are used in engines. Despite their commonity, timing belts are made of different materials. The material used to make them is important because it can either negatively impact performance or negatively affect its life span. Whether it’s a car, truck, or motorcycle, timing belts are an essential part of your engine.
Among their many advantages, timing and drive belts are designed to reduce friction, increase speed, and transmit torque more efficiently. In fact, the design of timing belts is similar to that of a cam belt. Both belts work in conjunction with each other to increase the torque and speed of a vehicle. In both types, the teeth of the belt are aligned at the same angle. In a small-scale drive system, this elongation is minimal, but if the load is too high, the teeth of the belt will begin to jump or cog over the pulley’s teeth, causing the noise.
Timing belts are used to synchronize the movement of the crankshaft and camshaft. Timing belts have hard teeth on the inner side of the belt and interlock with the cogwheels on the crankshaft and camshafts. Because of this, they make it easier for the exhaust and intake valves to open and close at the proper time. Timing belts are made of high-10sile rubber, but they may also be polyurethane, welded urethane, or moulded polyurethane.
When a timing belt is worn, it may degrade. The teeth will gradually lose their shape over time and the belt will begin to slip. If the teeth become rounded, the belt may still work, but its timing will be off. Hence, it is vital to replace the timing belt if you notice these signs. If you find any damage, contact a qualified mechanic for repair. If the teeth are worn or damaged, consider replacing the entire belt.
When it comes to a car’s engine, timing is vital. Timing belts connect the internal moving parts of the engine. In addition to timing, they can also power water, oil, and injection pumps. And it’s vital to make sure your timing belt doesn’t get damaged because it will not function properly. So don’t neglect timing belts unless you’re certain they’re damaged.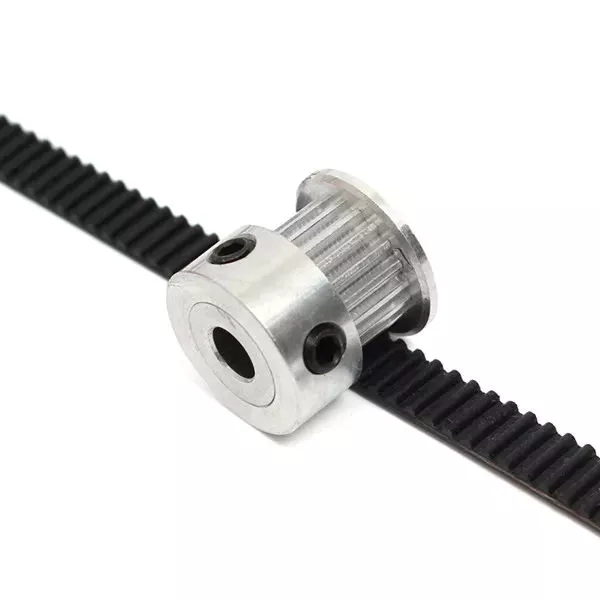
They transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley
A timing belt is a mechanical device that transfers rotary motion from a central motor to a drive pulley through a chain. The belt must be wide enough to accommodate the torque that will be produced by the design. The belt must be wider than the size selected for the drive pulley. In order to determine the correct belt width, the center-to-center distance between the drive pulley and the central motor is measured.
Unlike the elastic belt, which tends to stretch when pressed against a large load, the timing belt does not suffer from this problem. Instead, it exhibits low torsional stiffness, which allows it to transfer rotary motion efficiently. The timing belt also reduces the likelihood of slippage. This is because the cord material is very strong compared to the loads that it must handle.
The most common type of timing belt pulley is made of nylon. The advantage of nylon is that it has a natural lubrication surface and is relatively low-maintenance. It is also durable, malleable, and low-melting point. It is also highly resistant to wear and tear and is suitable for applications that are exposed to high temperatures. However, the belt must be cleaned and maintained on a regular basis.
A Timing belt can be used in a variety of applications. For instance, the timing belt is used in automotive engines. However, the timing belt is also found in stationary power generators, marine engines, and aviation engines. Additionally, it is used in conveyors, winches, treadmills, and washing machines. It also plays a crucial role in the curtain at a theater hall.
The timing belt can be flat, V-shaped, or trapezoidal. The latter is usually made of rubber. The distance between the 2 pulleys is between 5 and 10 meters. The flat belts transmit power through friction between the belt and the pulley. The efficiency of flat belts is approximately 98% and it makes very little noise. However, it must be used in conjunction with the appropriate motor drive. Ultimately, the engineers must choose the best 1 that can deliver the torque that the drive pulley needs to generate.
They prevent pistons from striking the valves on a critical level
In an interference engine, the valves and pistons share the same space in the cylinder, but they move at different rates. While 1 or more of the valves may open into the piston’s travel area, the other is closed and never makes contact with the piston. Timing belts prevent this critical collision from occurring and prevent the piston from damaging the engine. Most timing belts fail at start-up and shutdown. Check the car owner’s manual for recommended replacement intervals.
The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. The timing belt allows the piston to move without striking the valves, allowing the engine to perform its essential functions. The camshaft is used to push fuel and air into the cylinder. The valves close and open as the engine moves forward. When the engine is running, the timing belt prevents the piston from striking the valves on a critical level.
Because of their critical role in the engine, timing belts are often an overlooked component. Without proper timing, an engine will not work properly, and valve damage can be costly. If timing fails, the piston will strike the valves on a critical level, which will damage the engine. Timing belts are a vital automotive component, so make sure yours is in good condition.
A timing belt is a necessary part of your Subaru’s engine. It synchronizes the crankshaft and camshaft to prevent problems with the engine. If a timing belt breaks, the pistons will strike the open valves and cause massive engine damage. Timing belts must be replaced when recommended in your owner’s manual. If it breaks, the engine will shut down.
They cost a lot to replace
Timing belts are expensive to replace, with the average car owner paying $1,200 to have them replaced. Most cars have transverse engines, where the cam cover rests against the driver’s side of the engine. These specialty cars are notoriously difficult to service and require the services of a specialist mechanic. Timing belts are a complex system with a series of idler bearings and tensioner bushes to guide and drive the belt. These components are often replaced at the same time as other routine maintenance work, and they may cost you a bundle.
If you have a car that’s been in the shop for a while, timing belt replacement may be the only option. A timing belt that’s popped isn’t going to make the car run, so you’ll need to get it replaced. If you need the belt replaced, you can use a car service, or you can try to replace the timing belt yourself. It’s a good idea to get several quotes before making the decision to replace the belt.
Depending on the make and model of your car, timing belt replacement costs may range from $250 to more than $1,000. Prices will vary according to vehicle type, labor hours, and the brand of parts and labor. If you don’t have a mechanic handy, you can always use a free online tool like CZPT to get an estimate for timing belt replacement and find a mechanic near you. This will help you save money and avoid the hassle of spending a lot of money on an unnecessary repair.
While timing belts typically last between 60,000 and 100 thousand miles, you may only need to replace them once in your car’s lifetime. Timing belts may seem cheap at first, but if you’re planning on selling your car, you’ll want to avoid the expense of replacing your timing belt. If you don’t, your car’s engine may run poorly and cause your car to use more fuel than it should.


China manufacturer Wheel Loader Spare Parts Tension Roller Tension Pulley for CZPT Wp12 Diesel Engine Parts Belt Tensioner for Jeep and Dodge Engine Wp10 Wd615 Diesel Engine with Good quality
Product Description
Dear friends!
My name is Irina Mamoshina. Please pay a moment of your attention : -).
Our company HangZhou CZPT International Trade Co., Ltd is engaged in the production and sale of auto parts for Chinese special equipment, engines and equipment assembly. We also produce metal parts ourselves, such as gears, fingers, filters, etc.
Our products include:
ZL30G, ZL40G, ZL50G, ZL50GL, ZL60G, LW3
Types of V-Belts and Their Properties
A v-belt’s inside length and pitch are determined by measuring along the bottom side. The included angle of a v-belt is measured from its flanks when it is extended. Most v-belt sections are 40 degrees. There are different types of v-belts, and the dimensions of each are standardized by different organizations. This article will introduce the different types of v-belts and their properties.
Notched v-belts reduce bending stress
Notched V-belts reduce bending stress by reducing the axial length of the belt by 2 or more notches. These notches are characterized by different profiles, which differ in the pitch angle and the inside length. ISO and DIN standards are followed by the manufacturers of these belts. Notched v-belts are used on industrial machinery in countries other than the US.
Compared to the standard V-belts, notched ones are designed to resist bending stress better and offer better heat dissipation. They also last longer and run cooler than standard V-belts. Furthermore, they are about 2 percent more energy efficient than their standard counterparts. Therefore, notched V-belts are a viable replacement for standard V-belts.
Notched V-belts are commonly used in industrial applications because of their low price, ease of installation, and availability of many sizes. Another advantage of notched V-belts is that they provide more wedging force and higher load capacity. Notched V-belts have a wider v-groove than flat ones, which makes them more effective for heavy-duty applications.
Notched V-belts also provide better traction. They reduce bending stress, which is beneficial for preventing fatigue and tearing of v-belts. Additionally, v-belts can be installed in an existing equipment to add more performance. And with proper maintenance and installation, notched V-belts will provide trouble-free service for many years to come.
Ribbed v-belts reduce heat dissipation
Various kinds of v-belts are available for varying applications. The more popular types are the fractional horsepower and the double-V. Fractional horsepower v-belts are designed for light-duty applications, such as machine shop equipment and household appliances. The common sectional names are 2L, 3L, 4L, and 5L. The L in each of these belts refers to the top width of the belt, multiplied by 1 eighth inch.
Unlike conventional belts, ribbed v-belts are flexible, making them ideal for use in vibrating loads. They reduce heat dissipation and can be ordered in single or multiple sets to match your application. However, ribbed v-belts should not be mounted on deep-groove sheaves, as this can cause the belt to turn over. If you use deep-groove sheaves, the risk of rupture is very high. Deep-groove sheaves can also cut banded belts. Extremely worn sheaves can also cause the belt to rip.
The 2 types of ribbed v-belts differ in their construction and application. While both types have trapezium cross-sections, they are similar in that they are made of polyurethane or other durable materials. Ribbed v-belts have an additional layer of fabric on the elastomer core for reduced noise and better heat dissipation.
Ribbed v-belts are available in a variety of sizes, including trough v-belts. Their cross-sections are categorized by their top and bottom widths and depths. The included angle of most v-belt sections is approximately 40 degrees. Different types of v-belts have different cross-sections, and these cross-sections are standardized by various organizations.
As the load increases, a ribbed v-belt will wedge into the groove and decrease the amount of friction needed to maintain the correct torque. Flat belts can track off the pulleys due to friction. However, V-belts are more stable and require less width than flat belts. The main advantage of ribbed v-belts is their increased efficiency.
The global-local finite-element model is also used to calculate the maximum and minimum J-integrals during a belt’s running cycle. The data is then used to evaluate the durability of ribbed v-belts in various applications. The numerical models used for the calculations involve a ribbed V-belt with 5 full ribs.
Cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip
Cogged v-belts are designed for maximum performance and durability on even the harshest drive systems. These belts are made from high-modulus polyester cords that resist hardening and stretch and provide superior balance and strength. They also feature raw-edge sidewalls to reduce slip and drive vibration. In addition, they have specially-formulated rubber compounds for oil resistance. CZPT Cog-Belt offers substantial savings in downtime, energy consumption and horsepower.
A double cogged v-belt combines the benefits of cogged and double vee-belts. Its bonded reinforced tie band offers enhanced flexibility and reduces belt whipping in multiple-belt drives. Double cogged v-belt dimensions vary depending on the standards of the manufacturer. Regardless of the type, you’ll want to use a belt that is aligned correctly.
Standard v-belts are also known as wrapped or raw edge v-belts. Wrapped V-belts feature fabric covers above and beneath the cord to increase lateral rigidity and reduce belt whip. Cogged V-belts also have fabric covers to prevent wear on the core and increase the belt’s operating temperature. They’re ideally suited for applications that require high-temperature operation.
Cogged V-belts can significantly decrease energy consumption and improve power transmission capabilities. They also have a bias-cut cover stock that provides axial and lateral stability while preserving the cord integrity. A fiber loaded cogged construction offers optimum flexibility while minimizing heat buildup. It can be installed on any type of drive, including chain conveyors and industrial-grade machines.
The two-layer tie-band permanently bonds multiple belts together. This provides maximum cord support, heavy shock absorption, and stability. The belts are also engineered with patented banding processes that eliminate belt turnover and distribute load evenly across the drive. CZPT Cog-Band Belts minimize belt whip and provide stability. They also minimize belt turnover and rollover in heavy-duty industrial applications.
A classic v-belt is the most common and economical belt. Its nominal dimensions are 1/2″ to 1-11/2″ wide and 16″ to 400 inches long. The width is usually 40 degrees. Different organizations use different cross-sections to classify v-belts. The following table provides a general comparison of the 2 types. The Cogged V-Belt is designed to reduce belt whip by increasing the lateral rigidity of the belt.
Cogged v-belts provide superior environmental resistance
The patented design of the Dayco V-Belt provides maximum power transmission while combining the benefits of a cogged belt and raw-edge construction. The belt’s top cogged design helps increase air flow around it, preventing deterioration and extending its useful life. The belt’s three-ply design features neoprene impregnated fabric for superior durability and a specially-formulated polyester cord for increased strength and stability.
A variety of v-belts are available, with cogged and notched versions presenting unique characteristics. Cogged V-belts are more flexible than uncogged versions and feature ‘X’-shaped grooves for enhanced heat dissipation. Cogged V-belts are interchangeable with conventional v-belts, although their ‘X’ design is most common. Hexagonal v-belts are a popular option for applications where traction is needed.
Another type of Cogged V-belt is designed specifically for outdoor power equipment. This v-belt is brown, with smooth clutching covers. Its aramid cord is very strong and provides superior durability in adverse conditions. Cogged V-belts can withstand severe shock loads and are therefore ideal for outdoor power equipment. Furthermore, they offer superior environmental resistance, minimal stretch, and a long service life.
A Cogged V-belt is composed of tensile cords that are supported by a rubber stock. Different manufacturers use different synthetic rubber stocks for this purpose. These materials help to extend the belt’s operating temperature range and resist premature failure. In addition to tensile cords, the belt’s body is covered with a fabric cover. The fabric is treated to form a chemical bond with the core materials, which allows it to withstand constant bending.

