Product Description
HYRL-1739 High Speed Rapier Loom
Type HYRL-1739 High Speed Rapier Loom,as a leading weaving machine, following market demands and development, is designed to weave high quality, high value-added fabric,with the features of advanced technology, reliable structure, easy maintenance, high-speed and high-grade.
This machine is adopted with modular design, high degree of mechanical and electrical integration.And it is equipped with advanced rotary electronic dobby and electronic color selection device.And it can achieve to weave all types of fabrics such as plain weave, twill, satin, jacquard etc by changing the program.of electronic control box.
Main specification:
| Reed width | 190cm,210cm,230cm,280cm | ||
| Machine Speed | 460RPM–600RPM | ||
| Main Drive | Directly driven by variable speed motor (patent) | ||
| Shedding Motion | Staubli 2658 electronic dobby, up to pages of heald frame | Electronic heald leveling time setting | Dobby pattern edited by the eclectric cabinet |
| Let-off Motion | Driven by independent servo motor, warp tendion detected by sensor, double back rest structure | Disc diameter:φ805mm,φ1000mm | |
| Take-up Motion | Driven by independent servo motor,double rollers pressurized device | Max cloth roller diameter φ600mm |
|
| Color Selection | Independence motor driven, 4-6 colors, up to 8 colors | Color selection time and pattern edit set in the electric cabinet | |
| Weft Accumulators | High speed drum weft feeder, coaxial tensioner to adjust tension, standard 4, up to 8 moveable assembly accumulator frame | ||
| Selvage | Double sides, each driven by independent motor, selvage time is controlled by electric control cabinet | ||
| Pick finding | Aumatic pick finding, full leveling or semi-leveling stop | ||
| Lubrication | Forced circulation lubrication device driven by independent oil pump motor | With oil temperature, oil pressure,jam protection | |
| Control | 10 inches true color touch screen HMI,six color indicator light | 32-bit master control system, fully enclosed cabinet | Both sides push button design |
Fabrics Made By this Machine
Exhibition/Show
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Rapier Loom |
|---|---|
| Voltage: | 380V |
| Computerized: | Computerized |
| Precision: | High Precision |
| Certification: | CE, ISO9001: 2000 |
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What are the signs that indicate a need for tensioner roller replacement, and how can they be diagnosed?
Identifying the signs that indicate a need for tensioner roller replacement is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and reliability of a belt drive system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the signs and diagnostic methods for determining when tensioner roller replacement is necessary:
1. Excessive Belt Slack:
If the tensioner roller has worn out or lost its tensioning capability, it may result in excessive belt slack. Excessive belt slack can be observed visually by noticing sagging or drooping of the belt between pulleys. To diagnose this, visually inspect the belt and check for any significant slack or looseness. Excessive belt slack indicates that the tensioner roller is no longer providing adequate tension and should be replaced.
2. Belt Misalignment:
A failing tensioner roller can lead to belt misalignment, causing the belt to deviate from its intended path. Belt misalignment can be diagnosed by observing the belt’s position in relation to the pulleys. Signs of misalignment include the belt running off-center, making contact with adjacent components, or riding too close to the edge of the pulleys. If belt misalignment is detected, it is essential to inspect the tensioner roller for any wear, damage, or misalignment and replace it if necessary.
3. Unusual Noise or Vibration:
A failing tensioner roller can generate unusual noise or vibrations in the belt drive system. This can be caused by worn bearings, misalignment, or other internal damages within the tensioner roller. To diagnose this, carefully listen for any abnormal noises such as grinding, squeaking, or rattling coming from the tensioner roller area while the system is in operation. Additionally, pay attention to any excessive vibrations or shaking of the belt drive system. If unusual noise or vibration is present, it indicates a potential issue with the tensioner roller that may require replacement.
4. Visible Wear or Damage:
Inspecting the tensioner roller for visible wear or damage is an essential diagnostic method. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks, grooves, or uneven surface texture on the roller. Additionally, check for any signs of physical damage, such as dents or deformation. If the tensioner roller shows visible signs of wear or damage, it is an indication that it has reached the end of its service life and should be replaced.
5. Inadequate Tension:
If the tensioner roller fails to provide sufficient tension to the belt, it can lead to belt slippage, reduced power transfer, and decreased overall system performance. Insufficient tension can be diagnosed by observing belt slippage or excessive wear on the belt’s contact surfaces with the pulleys. Check the tension of the belt by applying moderate pressure to it with your finger. If the belt deflects significantly, it indicates inadequate tension provided by the tensioner roller. In such cases, the tensioner roller should be inspected and replaced if necessary.
6. Maintenance Schedule:
Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is an important aspect of diagnosing the need for tensioner roller replacement. Manufacturers often provide guidelines on the expected service life or recommended replacement intervals for tensioner rollers. It is essential to consult the maintenance schedule specific to the belt drive system and adhere to the recommended replacement intervals. This proactive approach helps prevent potential failures or performance issues associated with worn or damaged tensioner rollers.
7. Professional Inspection:
In complex or critical applications, it may be necessary to seek the expertise of a professional technician or engineer to diagnose the need for tensioner roller replacement. Professionals can perform comprehensive inspections using specialized tools and techniques, such as laser alignment or vibration analysis, to assess the condition of the tensioner roller accurately. They can identify any underlying issues or potential risks and provide recommendations for replacement based on the specific requirements of the belt drive system.
In summary, the signs that indicate a need for tensioner roller replacement include excessive belt slack, belt misalignment, unusual noise or vibration, visible wear or damage, inadequate tension, adherence to maintenance schedules, and professional inspections. By regularly inspecting the tensioner roller and promptly addressing any signs of wear or malfunction, operators can ensure the reliable and efficient operation of their belt drive systems.

How do tensioner rollers contribute to reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of belts?
Tensioner rollers play a vital role in reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of belts in various applications. They offer several key contributions in achieving these objectives:
1. Maintaining Proper Belt Tension:
Tensioner rollers help maintain the optimal tension in belts throughout their operation. Proper tension is crucial for efficient power transmission and preventing belt slippage. When belts operate under inadequate tension, slippage can occur, leading to increased wear on the belt and associated components. Tensioner rollers ensure that the belts remain appropriately tensioned, reducing wear and extending their lifespan.
2. Absorbing Belt Vibrations:
Vibrations can occur in belt drive systems due to imbalances, misalignments, or variations in load. These vibrations can accelerate belt wear by causing friction and excessive flexing. Tensioner rollers are designed to absorb and dampen vibrations, minimizing their impact on the belt. By reducing vibrations, tensioner rollers help to decrease wear and prolong the life of the belt.
3. Distributing Tension Evenly:
Tensioner rollers distribute tension more evenly along the length of the belt. They help prevent localized areas of excessive tension, which can lead to premature wear and belt failure. By ensuring a more uniform distribution of tension, tensioner rollers contribute to reducing wear and extending the lifespan of belts.
4. Compensating for Belt Stretch:
Over time, belts can stretch due to the mechanical stresses they experience during operation. Belt stretch can result in reduced tension and compromised power transmission. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt stretch by applying additional tension to maintain the desired level of belt tension. This compensation helps to prevent belt slippage, wear, and premature failure, thereby increasing the lifespan of the belt.
5. Reducing Belt Misalignment:
Proper belt alignment is essential for minimizing wear and optimizing belt life. Tensioner rollers assist in maintaining belt alignment by exerting consistent pressure on the belt and guiding it along the desired path. By reducing belt misalignment, tensioner rollers help prevent edge wear, side-loading, and premature belt failure.
6. Providing Belt Support:
Tensioner rollers provide support to the belt, especially in longer spans or applications with heavy loads. They help prevent belt sagging and excessive flexing, which can lead to accelerated wear and reduced belt life. By offering support, tensioner rollers contribute to minimizing wear and increasing the durability of the belt.
7. Facilitating Belt Tracking:
Proper belt tracking is crucial for belt longevity and performance. Tensioner rollers aid in maintaining belt tracking by applying controlled pressure and guiding the belt along the intended path. By promoting accurate belt tracking, tensioner rollers help prevent edge wear, rubbing, and premature belt failure.
8. Minimizing Belt Slippage:
Belt slippage can occur when there is insufficient tension or excessive loads in the system. Tensioner rollers help maintain the necessary tension in the belt, ensuring a secure grip between the belt and the pulleys. By minimizing belt slippage, tensioner rollers reduce wear, heat generation, and premature belt failure.
In summary, tensioner rollers contribute significantly to reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of belts by maintaining proper tension, absorbing vibrations, distributing tension evenly, compensating for belt stretch, reducing belt misalignment, providing belt support, facilitating belt tracking, and minimizing belt slippage. These contributions help optimize the performance, efficiency, and longevity of belt drive systems in various applications.

How do tensioner rollers differ from other components in a vehicle’s belt drive system?
Tensioner rollers in a vehicle’s belt drive system have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how tensioner rollers differ from other components in a vehicle’s belt drive system:
1. Function:
Tensioner rollers are specifically designed to maintain proper tension in belts within the vehicle’s belt drive system. Their primary function is to apply the necessary force to keep the belts properly tensioned, ensuring efficient power transmission and preventing slippage. Other components in the belt drive system, such as pulleys or idler pulleys, have different functions like redirecting the belt’s path or guiding it around various engine accessories.
2. Design:
Tensioner rollers, also known as belt tensioners or idler pulleys, typically consist of a pulley-like structure mounted on a spring-loaded arm or bracket. They have a smooth or grooved surface that comes into contact with the belt. The design allows the tensioner roller to rotate freely on bearings or bushings, accommodating the movement of the belt and maintaining the desired tension. In contrast, other components in the belt drive system, such as crankshaft pulleys or accessory pulleys, have different shapes and configurations depending on their specific tasks.
3. Tension Adjustment:
Tensioner rollers are designed to automatically adjust the tension in the belts. They can compensate for belt stretch or wear by adapting their position and maintaining the desired tension level. This self-adjusting feature ensures consistent belt tension throughout the vehicle’s operation. In contrast, other components in the belt drive system usually have a fixed position and do not actively contribute to tension adjustment.
4. Location:
Tensioner rollers are typically positioned at strategic locations within the belt drive system to optimize tensioning. They are often placed in locations where the belt’s tension tends to decrease due to the movement of different engine accessories. This placement allows the tensioner rollers to provide the necessary tension and prevent belt slippage. Other components, such as crankshaft pulleys or accessory pulleys, have specific positions based on their roles in driving the various engine accessories.
5. Maintenance and Replacement:
Tensioner rollers require regular maintenance and inspection to ensure their proper functioning. They may need lubrication, and their condition should be checked for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If a tensioner roller is found to be faulty or no longer providing adequate tension, it should be promptly replaced to prevent belt-related issues. Other components in the belt drive system may have their maintenance requirements and replacement intervals based on their specific design and usage.
6. Impact on Belt Performance:
Tensioner rollers have a direct impact on belt performance by maintaining the correct tension. They help prevent belt slippage, ensure optimal power transmission, and contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of the belt drive system. Other components, although crucial for the system’s operation, may not have the same direct influence on belt tension and performance.
In summary, tensioner rollers differ from other components in a vehicle’s belt drive system in terms of their function, design, tension adjustment capabilities, location, maintenance requirements, and impact on belt performance. Understanding these differences is important for effectively maintaining and optimizing the performance of the belt drive system in a vehicle.


editor by Dream 2024-04-24
China Custom Wholesale High Quality Factory Textile Machine Spare Part Coil Winding Ceramic Eyelet wholesaler
Product Description
Wholesale High Quality Factory Textile Machine Spare Part Coil Winding Ceramic Eyelet
Product Description
1. Ceramic eyelet guides (Ceramic ring ) and zirconia ceramic eyelet are applied to the coiling machine and spinning and weaving machinery, it is in common use fault silk another piece.
2. Silk thread slides when the job, in China eye outside, for reducing friction, must raise material hardness, smoothness and form.
3. Our company selects and uses 99%’s Al2O3, hardness greater than HRa88, density 3.85, surpasses essence throwing Ra0.2.
4. The alumia ceramic (Textile ceramic eyelet) Zirconia ceramic eyelet is used to set less (friction is also less) location of pressure right.
5. For cost reduction, according to using a request, smoothness polishing handicraft is allotted being (0.8 throw Ra) roughly, is throw (Ra accurate 0.4), surpasses essence throwing (Ra0.2).
The alumina ceramic eyelet(zirconia ceramic eyelet) is 1 of our feature products with competitive price.
Product Name: Ceramic Eyelet Xihu (West Lake) Dis.
|
Brand Name: |
DEFULI |
|
Material: |
99%AL2O3 |
|
Application: |
Ceramic CZPT for wire |
|
Polish: |
Fine Polish degree Ra0.2 |
|
Hardness: |
≥HRA85 |
|
Volume Density: |
≥3.60 |
|
Bending Strength: |
≥280 Mpa |
|
Basic Tolerance: |
+/-1% |
|
Color: |
Pink, White, Light Pink, Black, Dark Red |
|
Molding Method: |
LOW PRESSURE IN JECTION |
Detailed Product Description
Ceramic eyelet applicable for wire or silk rolling of various winding machines and textile machinery. It is made of precise ceramic and polished up to Ra0.2, high hardness and smooth surface enable the enameled wire free from hurt during surface sliding.
The ceramic eyelet is used to set less (friction is also less) location of pressure right. For cost reduction , according to using a request, smoothness polishing handicraft is allotted being (0.8 throw Ra) roughly , is throw (Ra accurate 0.4), surpasses essence throwing (Ra0.2). Be that single face is super-accurate at the same time mark throw and two-sided super-accurate throw. Specification of china eye many, select and use specification listing in common use in support a customer the day after tomorrow now, also may demand making to order according to the customer.We dedicate ourselves to making products that enable industry to run more efficiently and productively through the application of leading-edge materials. We differentiate ourselves by offering not just products, but a partnership with each client to create solutions of real value to meet specific challenges. KEIR’s product solutions are focused on continuous process improvement, energy savings, and longer operating life.We can duplicate most any item, making prototypes from 99.8% pure Alumina ceramic to replace parts made from metal, plastic, ceramic, or other materials. Our proprietary production process provides the versatility to make this wide range of parts without tooling charges.
Display Of Product
Company profile
HARTAI TECHNOLOGYLIMITED was founded in 2001, the factory is located in HangZhou city. ZheJiang province.
We specialized in the manufacture and RD of the component which is used in coil of wire and tension systems. textile machinery and electrical industry precision ceramics. Such as: coil winding nozzle, coil winding tensioner, tension meter, ceramic eyelets, ceramic coating pulley. etc.
We produce high quality coil winding nozzle which include tungsten carbide nozzle, ruby nozzle and ceramic nozzle. We adopt the excellent raw material and technology to ensure best quality which exceed our customer’s expection. Our main customer Mitsubishi, ABB, SVM, YKK. etc, We expect long term relationship with you!
FAQ
1. How can I get a quotation?
You can find our contact information below this page and some detail information will be very helpful to get an exact quotation. We will give quotation within 24hours, if urgent, please tell us and we will regard your inquiry priority.
2. How can I get a sample?
As the price confirmed, you can require for samples.
3. Can you do the design for us?
Yes, we have our factory and we can make OEM order.
4. How long can I expect to get the sample?
Normally it takes 7-15days to produce the sample.
5. What about the lead time for mass production?
It depends on what kind of products you ordered. Generally, 15-25days for mass order.
We sincerely hope to get your inquiry of this voice coil actuator! If any questions, please feel free to contact us. Thanks for visiting our website!O(∩_∩)O
How to Repair a Timing Belt Tensioner
Your timing belt tensioner is a critical component of your vehicle’s drivetrain. Too little tension, for example, will cause the belt to slip, and too much tension can overload shaft bearings, leading to premature failure. If you notice that your belt tensioner is not working properly, you should immediately visit a mechanic. Corrosion from road splash, dirt, mud, or other debris can jam the tensioner housing. To avoid this, make sure that you replace your timing belt tensioner as soon as possible.
Symptoms of a bad belt tensioner
If you’ve ever wondered what signs indicate a bad belt tensioner, look no further than your vehicle’s engine. Worn belts or a broken tensioner can cause an irritating squealing noise, as well as the belt to slip. Even worse, a bad tensioner can cause water to enter the belt and pulley, resulting in water damage. A worn tensioner is usually the culprit of the noise, but there are also other warning signs that a belt is in trouble.
Your vehicle’s engine may start to run poorly or even squeal when you turn the key. Similarly, your engine may fail to start at all, or the check engine light may illuminate. The belt may also start to wear out in an unusual pattern. These signs indicate that the tensioner is in need of replacement. If you notice 1 or more of these signs, get your car checked right away.
To check the condition of the tensioner, remove the drive belt and observe the pulley. You may notice rust dripping or bleeding at the mounting bolts, which are the most common signs of a bad tensioner. If you can’t remove the drive belt, check the pulley by rotating it. If you feel resistance, the pulley is likely worn or slack.
Failure of the belt tensioner will also cause other parts of the car to fail. If a bad belt tensioner isn’t fixed quickly, you might not be able to use the vehicle properly. You could end up breaking your car’s engine, losing power steering, and possibly even the water pump. If your car is not running right, you could be stuck in the middle of nowhere. Even if the alternator doesn’t work, you’ll still have a malfunctioning power steering system and a dead AC system.
A broken timing belt tensioner can cause strange noises or a no-start condition. These noises and symptoms are signs of a bad belt tensioner, and you’ll have to replace it ASAP. If you don’t know what symptoms mean, don’t hesitate to take your car to a mechanic. You’ll be surprised how easy it is to check this vital component and save yourself a bunch of money.
Components of a belt tensioner
The components of a belt tensioner assembly consist of 4 key components. The clearance between the pulley and the base is critical to the tensioner’s operation. If the tensioner is installed incorrectly, the spring can break and cause severe injury. The spring’s preload and powerful force make it difficult to service the unit safely. These parts are non-serviceable. If you are unsure of how to repair your tensioner, contact an authorized mechanic.
The components of a belt tensioner drive are shown in FIG. 2. The rotor shaft is connected to the drive screw, while the second transmission is connected to the gear shaft. The rotor and gear shaft are in parallel with each other. The gear shaft and worm wheel are connected to the belt tensioner drive. In other words, the belt tensioner drive is located in the B-pillar of the motor vehicle.
A belt tensioner may be equipped with a drive shaft and electric motor. The drive shaft may also contain a worm gear or worm wheel. The drive shaft also has an intermediate gearbox. Once the tensioner is set, it is ready to move to its safe-position position. It is a relatively simple and inexpensive replacement for your belt. When replacing a multi-ribbed belt, be sure to replace the tensioner along with the belt. Gates recommends replacing all wear parts at once.
In the event of a faulty drive belt tensioner, the belt will not stay taut. The pulley can wobble and cause the belt to fray. In addition to this, the bearings can cause a loud squealing noise. In this case, the accessory motors will continue to run, while the belt itself will not. Therefore, replacing the timing belt tensioner is an important part of maintaining the car.
In some systems, the belt tensioner uses a worm gear as the first gear. This results in rolling engagement of the screw’s teeth. This reduces noise and vibrations, while maximizing the efficiency of the belt tensioner drive. Additionally, a worm gear can eliminate the need for additional parts in belt tensioners. While this may not be practical in all instances, it is a good choice for space-constrained environments.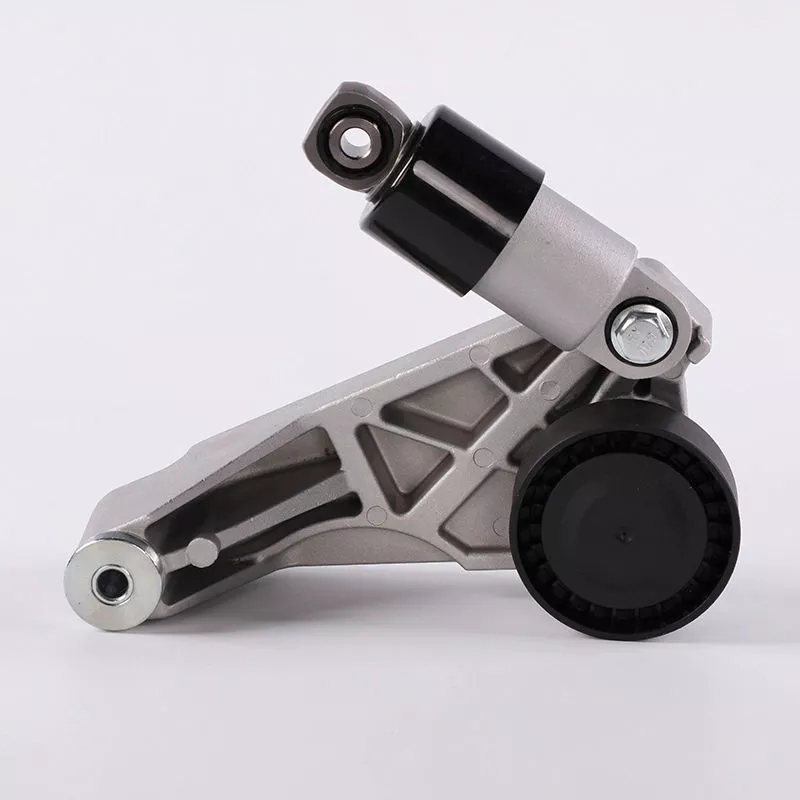
Repair options for a timing belt tensioner
A timing belt tensioner is an essential part of an automobile’s timing chain and is responsible for ensuring proper timing. Proper alignment of timing marks is essential to the proper operation of the engine, and improper alignment may lead to damage to the engine. To repair a timing belt tensioner, there are several repair options available. First, you need to remove the engine cover. You can then remove the timing belt tensioner by loosening the pulley using a ratchet or breaker bar.
When the timing belt isn’t properly tensioned, the engine will misfire. The engine misfires when the valve opens and the pistons rise at the wrong time. When this happens, the timing belt cannot properly grip the gears and the engine will not function. If this part fails, you’ll have to replace the whole timing chain. However, if you are handy with tools, you can easily replace the entire timing belt tensioner yourself.
If your timing belt tensioner is out of alignment, you should replace it. If you’re not sure whether it needs to be replaced, check it with a professional and learn the details of the repair. The timing belt tensioner is the most critical part of the engine, so it’s important to know about it. Otherwise, your car won’t run as well as it could. Repair options for a timing belt tensioner will vary depending on the severity of the problem and how much damage it has done.
While there are several repair options for a timing belt tensioner, the average cost of replacement is $364 to $457, and this doesn’t take into account any tax or fee you may be charged. DIY repair methods will usually cost you $50 to $150, and you’ll likely save a lot of money in the process. However, you need to remember that you may be unable to do the job yourself because you don’t know how to use the proper tools and equipment.
While it is not difficult to replace a timing belt tensioner on your own, you should know that you’ll need to remove other parts of the engine as well as special tools to make the repair properly. This is an advanced repair job and requires a great deal of skill. If you’re new to home car repair, you may not want to attempt it yourself. There are many other options, such as hiring a mechanic.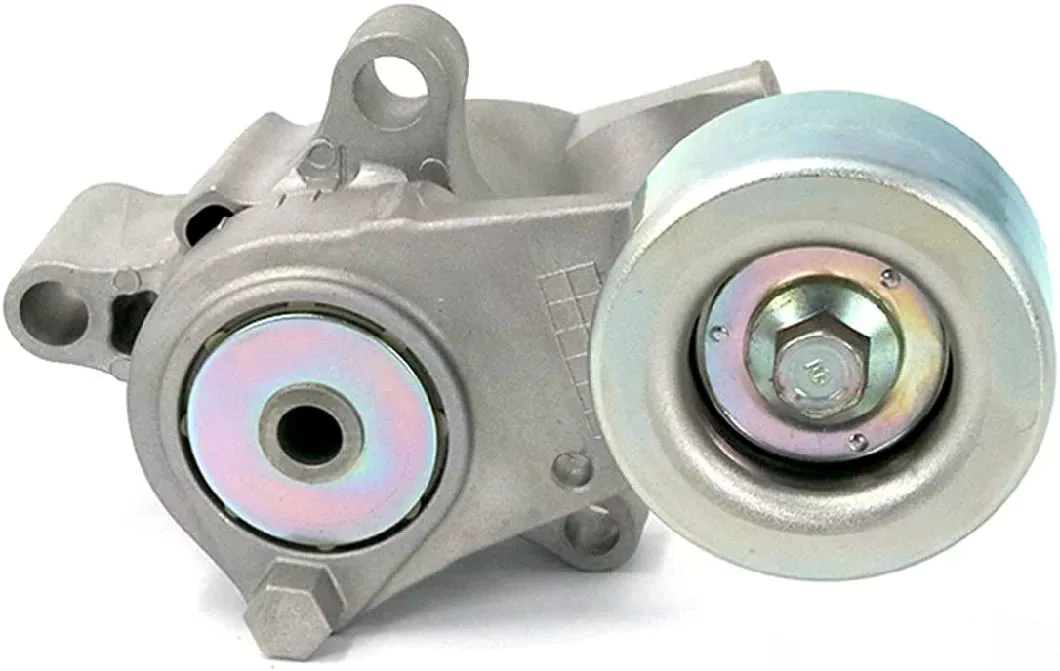
Installation instructions
While there are no universal installation instructions for belt tensioners, the manufacturer of your car may provide detailed instructions. Before attempting to replace your tensioner, read the manufacturer’s recommended procedures carefully. To install a new tensioner properly, unload the old 1 and take a picture or sketch of how the belt should be routed. Once the old tensioner is out, follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications. Make sure to unload and remove the belt from the tensioner, and follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications to install the new one.
If your car comes with a manual belt tensioner, you can follow the instructions. The manual will have a corresponding guide for installation. When installing a belt tensioner, make sure the manual clearly states the static tension for your particular model. Check that it is in line with the engine relief to ensure proper belt tension. You can then use a 6mm allen key to turn the tensioner clockwise and counterclockwise. Once it is in position, release the tensioner to operate. The belt tensioner should now apply the proper tension to your belt.
Before installing a new belt tensioner, make sure you read the manual completely. You should follow these steps carefully to avoid any problems with the tensioner. If the tensioner has failed, you must replace it immediately. A new belt tensioner will help you ensure proper performance of your accessory belt drive system. If you are installing a new multi-ribbed belt, you should replace the tensioner as well. However, it is important to note that replacing the belt tensioner is a complicated process and requires a mechanic to be able to safely remove the belt from the engine.
To install a second stage drive belt, walk the belt onto the input drive and generator. Ensure that the belt is seated properly in the grooves of the pulleys. Next, replace the input drive belt and right and left Drive Disk covers. Test the machine to ensure that it is working properly. If it doesn’t, replace the original drive belt. After installing the new belt, you may want to read the manual again to make sure it is in perfect condition.


China supplier Hot Selling High Quality Auto Machine Spare Part Textile Auto Machine Tungsten Carbide Nozzle with Free Design Custom
Product Description
Hot Selling High Quality Auto Machine Spare Part Textile Auto Machine Tungsten Carbide Nozzle
Product description
Coil winding wire CZPT Nozzles(TungstenCarbide nozzle)also call wire CZPT tubes, wire CZPT eyelets, wire CZPT needles.
it is used on coil winding machine. It is made precisely of hard alloy and enjoys the hardness up to HRA90.
Two terminals and innerle are all receive mirror surface treatment to ensure enameled wire makes no scrape. High hardness, resistance to flexure, block and impact.
Product Features:
1. High Wear Resistance
This is assured by the choice of materials for wear elements possessing. Hardness Value: 1800 ~ 2200Vickers, or 3times that of case hardened steel. Body material is stainless steel for structural supports, not wear-bearing.
2. Scratch-Proofing
Eliminate wire insulation film damage, low friction resistance, stable wire tension. The wire-guiding surfaces are mirror finished by CZPT lapping to a surface roughness of 2 -4 micro inches Ra or better, material permit.
3. Straightness and Stiffness
Straightness and Stiffness are defined by the wire exit being concentric and inflexible with respect to the nozzle locating? . In plain terms, the wire should exit from the nozzle concentric to the locating? To within 0.02 mm, with or without load. A geometric characteristic presentation is shown at upper left. Concentricity to within 0.01mm.
4. Precise Exit Radii
Because the coil winding nozzle’s Exit Radii governs the angle of the wire exit from 1 coil to the next, it should be monitored to + / – 0.571 mm. This is done by digital measurement, shown at upper right.
Prodict Specification:
Measurements:
Customize available by requested, outside diameter is governed by nozzle wall thickness. See the measurements drawing to confirm your nozzles measurements according to your winding machine and coil products.
Processing limit: D1≥ 0.2mm, D1≥ 0.7mm
| NO | Model | L | L1 | D | D1 | d | d1 | H |
| 1 | W5710-0.8-0602 | 20 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| 2 | W571-1.5-1007 | 30 | 7 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 3 | W571-2-1007 | 30 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 4 | W571-2-1210 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 5 | W571-2-1007 | 35 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| 6 | W0330-2-0808 | 30 | 8 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 8 | W0326-2-1007 | 26 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 9 | W571-2-1571 | 30 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 11 | W835-2.5-2011 | 35 | 11 | 2.5 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 12 | W0330-2-1006 | 30 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 13 | W 0571 -2-1215 | 35 | 15 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 15 | W571-3-1571 | 30 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 16 | W0630-3-1008 | 30 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 17 | W03303-0807 | 30 | 7 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 19 | W0630-3-1309 | 30 | 9 | 3 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 21 | W0614-3-1509p | 14 | 9 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 5 |
| 22 | W1014-3-1509p | 14 | 9 | 3 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 23 | W571-3-1009p | 14 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 5 |
| 24 | W1030-3 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 25 | W0326-3-0808 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 29 | W0626-3-1208 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 30 | W1030-3-2014 | 30 | 14 | 3 | 2 | 12 | 12 | |
| 31 | W1230-3-2514 | 30 | 14 | 3 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| 33 | W0330-3-0502 | 30 | 2 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 34 | W0626-3-1208 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 36 | W0330-3-0504 | 30 | 4 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 37 | W0823-3 | 25 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |||
| 38 | W571-1211 | 35 | 11 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| 39 | W5715-3-0811 | 35 | 11 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.35 | 0.35 | |
| 41 | W1571-3-1608 | 25 | 8 | 3 | 1.6 | 1 | 1 | |
| 42 | W0845-3-2017 | 45 | 17 | 3 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 43 | W1535-3 | 35 | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |||
| 44 | W1036-3-2016 | 36 | 16 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| 45 | W0630-3-1212 | 30 | 12 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 46 | W 0571 -4-2015 | 30 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 47 | W1243-4-2515p | 43 | 15 | 4 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 20 |
| 48 | W0843-4-2015p | 32 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 20 |
| 49 | W1232-4.5 | 43 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |||
| 50 | W1543-4-2512p | 43 | 12 | 4 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 20 |
| 51 | W0843-3.9-2019p | 20 | 19 | 3.9 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 19 |
| 52 | W2571-5 | 20 | 5 | 2 | 2 |
Display of Product
Information of our company
HARTAI Technology Industry Co., Ltd , found in 2001, is located in the beautiful city of China’s manufacturing industry HangZhou City. It is committed to nozzle, ruby products, tungsten carbide products, ceramic products, plastic crochet hook and precision machinery manufacturing .Our main products are nozzle, ceramic roller, jump wire preventer, various sizes of ceramic eyes, combination wire roller, ceramic wheel and non-standard parts, all kinds of tension and so on.
FAQ
1. How can I get a quotation?
You can find our contact information below this page and some detail information will be very helpful to get an exact quotation. We will give quotation within 24hours, if urgent, please tell us and we will regard your inquiry priority.
2. How can I get a sample?
As the price confirmed, you can require for samples.
3. Can you do the design for us?
Yes, we have our factory and we can make OEM order.
4. How long can I expect to get the sample?
Normally it takes 7-15days to produce the sample.
5. What about the lead time for mass production?
It depends on what kind of products you ordered. Generally, 15-25days for mass order.
We sincerely hope to get your inquiry of this voice coil actuator! If any questions, please feel free to contact us. Thanks for visiting our website!O(∩_∩)O
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Neoprene Timing Belts
The timing belt is an important component of an automobile engine. Made of special materials, this belt coordinates the rotational motion of the crankshaft with the camshaft. The coordinated precision is essential for sustainable combustion, and ensures that the valves in the combustion chamber open at the right times. Timing belts determine the engine’s pace, so it is essential that they perform at high synchronicity and strong enough to operate in extreme conditions.
Fabric timing belt
A timing belt is made of a yarn that has been crimped and woven into a mating surface, called the engagement surface. This yarn, known as the warp, must be able to stretch from a substantially flat state along irregularities in the mold. It must be flexible enough to stretch by several tens of percent under low load conditions. The warp yarn of a timing belt is made of synthetic fiber and is crimped into the right shape to be stretched easily.
This fabric can be used without thickening the base cloth. It can contain a large number of warp threads, and its wear resistance can be enhanced over time. The timing belt of the present invention does not crack or wear out after a long time of use. The base cloth does not wear out, which allows the timing belt to last for a long time. This makes it an extremely durable material. To learn more, read on.
The teeth of a timing belt are made of tough rubber and a nylon fabric facing. The fabric is coated with a plastic compound that gives it its shape and covers the cord. The materials used to make these belts vary, but all are strong and durable. They are also suitable for high-load applications. In addition to nylon timing belts, strongbelt premiums are also available. In addition to nylon and neoprene timing belts, they are also compatible with RPP and HTD pulleys.
The teeth of timing belts are made of high-strength polychloroprene elastomer. The teeth are made of a special manufacturing process that ensures good adhesion. The facing fabric is made of low-elongation glass cord and is covered by a polyamide fabric that has a low coefficient of friction. If you need an exact fit, you can buy a high-quality belt from TransDev.
Neoprene timing belt
When it comes to dependable drive belts, neoprene is hard to beat. It’s widely used in insulated clothing and weather stripping, and has been a key component in the development of timing belts since the late 1970s. And because it’s so hardy, neoprene timing belts are incredibly reliable. Here are a few reasons why. Neoprene is the most durable synthetic material for timing belts, and these 3 reasons should not discourage you from purchasing a new neoprene timing belt.
Neoprene timing belts are made of a high-quality chloroprene compound with a hardness of 74 Shore A. The high-strength glass fiber strands in the belt’s body transmit high power while enhancing its flexural strength. In addition, it’s covered with a high-strength polyamide fabric to reduce friction and protect contact surfaces from wear and tear.
Unlike neoprene, polyurethane synchronous belts are resistant to temperature and abrasion. Polyurethane timing belts are resistant to acids and chlorides, and exhibit excellent abrasion resistance. A neoprene belt can be used in high-speed applications, and can withstand extreme temperatures. However, the resistance of polyurethane to abrasion is not as good as that of neoprene.
The 2 most common types of timing belts are rubber and urethane. Rubber is the least expensive and quietest, and is the least flexible of the two. Neoprene is also highly elastic and does not retain its shape when it’s stretched, making it a popular choice for applications in manufacturing, agriculture, and robotics. They are also great for applications where precision and motion control are important. These properties make timing belts extremely effective in leading the industry toward its goals.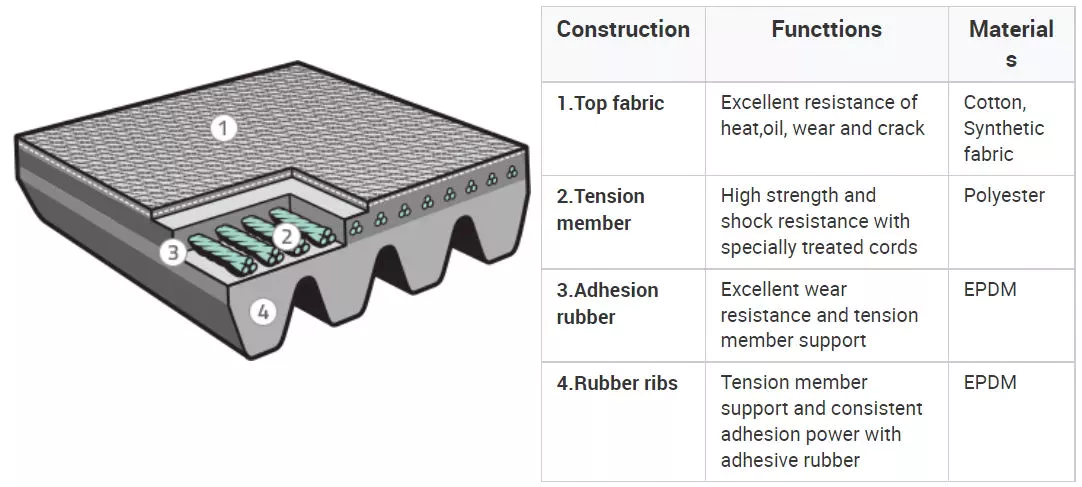
Chain timing belt
Traditionally, a vehicle’s timing system consists of a timing belt or chain. These components keep the engine’s intake and exhaust valves in the proper order. When these components go bad, it can ruin the engine in seconds. But there are advantages and disadvantages to each of them. Read on to learn about the pros and cons of each type of timing system. Here are some examples. Chain: A timing belt is generally made of reinforced rubber.
Chain: A timing chain is generally found in heavy-duty vehicles with higher torque. This type of timing belt is also found on many cars and SUVs with 4 cylinder engines that do not require a lot of torque. Unlike timing belts, timing chains are more durable and will last longer than their rubber counterparts. But there are certain things to keep in mind when replacing a timing belt. Make sure to change the oil regularly to avoid premature wear.
Chain: A chain is easier to maintain than a timing belt. It does not change length in response to temperature. And it requires a smaller tensioner. However, this also means that the timing belt is more prone to breaking. It can jump out of place if oil is flowing along it, causing an engine malfunction. If this happens, you’ll have to replace the entire timing belt and the engine will not work correctly. That’s why replacing a chain is so important.
A timing belt is a critical part of an engine. A failed timing belt can cause catastrophic engine damage. It can slip and break, colliding with the piston and valves. Fortunately, there are a variety of ways to check your timing belt. But a good rule of thumb is to replace it as soon as possible. You’ll also need to remove the front engine cover and any other components that may be in the way. In some cases, the engine might even have to be moved.
Trapezoid shaped teeth
In terms of tooth profile, there are 2 main types of timing belts: the curvilinear and trapezoidal types. Curvilinear timing belts are more rounded and less likely to result in excessive tension loss. These types of timing belts are also more prone to backlash and reduce accuracy. Here’s how they differ from each other. These 2 types of belts share similarities but differ in important ways.
Older timing belts generally have trapezoidal-shaped teeth, but newer types use curved teeth. Curved teeth are less prone to wear out quickly and last longer than straight ones. The trapezoidal teeth also tend to wear out more quickly at higher speeds. As a result, they’re only suitable for cars that get very little use. If you’re planning on using your timing belt frequently, you may want to choose a new 1 with curved teeth.
Curvilinear teeth are designed to alleviate the stress concentrations caused by trapezoidal tooth profiles. They also have a greater depth and reduce ratcheting. In addition to their efficiency, curvilinear timing belts are quieter than their trapezoidal counterparts. And they’re a little bit more expensive than their trapezoidal counterparts. So, what’s the difference between these 2 types of teeth?
Timing belts have a tendency to favor the tracking of an “S”-shaped twist. As a result, a trapezoid-shaped timing belt is more likely to keep the engine in sync. A good quality timing belt will help you achieve this. If you don’t, consider replacing your timing belt with a metric-styled one. That way, you’ll get the best performance out of your belt.
Other types of timing belts
Timing belts are essential for operating your vehicle’s engine. These belts connect the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft. The belts synchronize the timing of the engine’s valves and pistons to prevent damage. Previously, the belt was referred to as the “gilmer drive belt.”
There are 3 basic designs for timing belts. Some are shaped like a trapezoid, while others have a curvy tooth shape. Timing belts with this tooth design are generally more efficient for force transmission, although they suffer from backlash. These teeth also wear quickly at high speeds, which can make them prone to noise. In order to solve these issues, manufacturers now offer belts with curved teeth.
Another popular type is polyurethane. These are resistant to oil and high temperatures, and are energy-efficient solutions. Polyurethane timing belts offer increased elasticity and load capacity, which are important for optimal torque production. These belts are favored by a variety of industries because of their ease of cleaning and maintenance. They can be used for power transmission systems, as well as in roller conveyor systems. However, fabric timing belts are best used when acceleration forces are high.
Other types of timing belts are not always as durable. V-Belts have teeth-like structures on their surfaces and work under constant speed. They are typically a lighter option, but have similar disadvantages. They are more expensive than chains and lack the flexibility of customizing. Unlike chains, timing belts are sold in predetermined length loops. Their pitch is easily identified. It is a key indicator of whether or not they are suitable for a specific application.


China Custom High Performance Eco Friendly China Machine Spare Part Coil Winding Tungsten Carbide Nozzle with Great quality
Product Description
High Performance Eco Friendly China Machine Spare Part Coil Winding Tungsten Carbide Nozzle
Product description
Coil winding wire CZPT Nozzles(TungstenCarbide nozzle)also call wire CZPT tubes, wire CZPT eyelets, wire CZPT needles.
it is used on coil winding machine. It is made precisely of hard alloy and enjoys the hardness up to HRA90.
Two terminals and innerle are all receive mirror surface treatment to ensure enameled wire makes no scrape. High hardness, resistance to flexure, block and impact.
Product Features:
1. High Wear Resistance
This is assured by the choice of materials for wear elements possessing. Hardness Value: 1800 ~ 2200Vickers, or 3times that of case hardened steel. Body material is stainless steel for structural supports, not wear-bearing.
2. Scratch-Proofing
Eliminate wire insulation film damage, low friction resistance, stable wire tension. The wire-guiding surfaces are mirror finished by CZPT lapping to a surface roughness of 2 -4 micro inches Ra or better, material permit.
3. Straightness and Stiffness
Straightness and Stiffness are defined by the wire exit being concentric and inflexible with respect to the nozzle locating? . In plain terms, the wire should exit from the nozzle concentric to the locating? To within 0.02 mm, with or without load. A geometric characteristic presentation is shown at upper left. Concentricity to within 0.01mm.
4. Precise Exit Radii
Because the coil winding nozzle’s Exit Radii governs the angle of the wire exit from 1 coil to the next, it should be monitored to + / – 0.571 mm. This is done by digital measurement, shown at upper right.
Prodict Specification:
Measurements:
Customize available by requested, outside diameter is governed by nozzle wall thickness. See the measurements drawing to confirm your nozzles measurements according to your winding machine and coil products.
Processing limit: D1≥ 0.2mm, D1≥ 0.7mm
| NO | Model | L | L1 | D | D1 | d | d1 | H |
| 1 | W5710-0.8-0602 | 20 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| 2 | W571-1.5-1007 | 30 | 7 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 3 | W571-2-1007 | 30 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 4 | W571-2-1210 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 5 | W571-2-1007 | 35 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| 6 | W0330-2-0808 | 30 | 8 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 8 | W0326-2-1007 | 26 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 9 | W571-2-1571 | 30 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 11 | W835-2.5-2011 | 35 | 11 | 2.5 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 12 | W0330-2-1006 | 30 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 13 | W 0571 -2-1215 | 35 | 15 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 15 | W571-3-1571 | 30 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 16 | W0630-3-1008 | 30 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 17 | W03303-0807 | 30 | 7 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 19 | W0630-3-1309 | 30 | 9 | 3 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 21 | W0614-3-1509p | 14 | 9 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 5 |
| 22 | W1014-3-1509p | 14 | 9 | 3 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 23 | W571-3-1009p | 14 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 5 |
| 24 | W1030-3 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 25 | W0326-3-0808 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 29 | W0626-3-1208 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 30 | W1030-3-2014 | 30 | 14 | 3 | 2 | 12 | 12 | |
| 31 | W1230-3-2514 | 30 | 14 | 3 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| 33 | W0330-3-0502 | 30 | 2 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 34 | W0626-3-1208 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 36 | W0330-3-0504 | 30 | 4 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 37 | W0823-3 | 25 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |||
| 38 | W571-1211 | 35 | 11 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| 39 | W5715-3-0811 | 35 | 11 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.35 | 0.35 | |
| 41 | W1571-3-1608 | 25 | 8 | 3 | 1.6 | 1 | 1 | |
| 42 | W0845-3-2017 | 45 | 17 | 3 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 43 | W1535-3 | 35 | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |||
| 44 | W1036-3-2016 | 36 | 16 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| 45 | W0630-3-1212 | 30 | 12 | 3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 46 | W 0571 -4-2015 | 30 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| 47 | W1243-4-2515p | 43 | 15 | 4 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 20 |
| 48 | W0843-4-2015p | 32 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 20 |
| 49 | W1232-4.5 | 43 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |||
| 50 | W1543-4-2512p | 43 | 12 | 4 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 20 |
| 51 | W0843-3.9-2019p | 20 | 19 | 3.9 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 19 |
| 52 | W2571-5 | 20 | 5 | 2 | 2 |
Display of Product
Information of our company
HARTAI Technology Industry Co., Ltd , found in 2001, is located in the beautiful city of China’s manufacturing industry HangZhou City. It is committed to nozzle, ruby products, tungsten carbide products, ceramic products, plastic crochet hook and precision machinery manufacturing .Our main products are nozzle, ceramic roller, jump wire preventer, various sizes of ceramic eyes, combination wire roller, ceramic wheel and non-standard parts, all kinds of tension and so on.
FAQ
1. How can I get a quotation?
You can find our contact information below this page and some detail information will be very helpful to get an exact quotation. We will give quotation within 24hours, if urgent, please tell us and we will regard your inquiry priority.
2. How can I get a sample?
As the price confirmed, you can require for samples.
3. Can you do the design for us?
Yes, we have our factory and we can make OEM order.
4. How long can I expect to get the sample?
Normally it takes 7-15days to produce the sample.
5. What about the lead time for mass production?
It depends on what kind of products you ordered. Generally, 15-25days for mass order.
We sincerely hope to get your inquiry of this voice coil actuator! If any questions, please feel free to contact us. Thanks for visiting our website!O(∩_∩)O
What Is a V-Belt?
A v-belt is a type of belt that provides a continuous motion to the vehicle’s wheels. This type of belt is made of several different components. They usually have a trapezium-shaped cross-section because of its elastomer core. Elastomers are often made of polyurethane or a synthetic rubber with good shock resistance. Sometimes, a v-belt will have 2 sections – cushion rubber and compression rubber.
Link-type V-belt
A laminated link-type V-belt is 1 embodiment of the present invention. The belt comprises individual lamina sections connected longitudinally by studs and tubes, each of which has at least 1 connecting means. The slots in the links allow for a full share of the load to be transferred through the belt, and they also reduce substantially all internal mechanical stresses. The belt is preferably designed to extend substantially the entire width of the machine being driven.
Conventional link-type V-belts are installed between 2 pulleys on the tight side of the V-drive. A wide end of a link moves in the direction of rotation, while the stud of a second, smaller link pulls the nose end of the third link forward. The shank of the stud pivots on a solid fabric located in hole 2 of the third link below. The bottom link, however, curls over the stud and the belt is assembled.
The present invention offers an improved method of forming a link-type V-belt. The belt is manufactured using links and does not have to be fitted as tightly as conventional link-type V-belts. This belt is flexible and strong enough to handle normal tension loads in a well-designed drive. In addition, the belts made using the present invention will have a longer life, thereby extending the drive’s load-carrying capacity.
Classical V-belt
A classical trapezoidal belt profile makes the VB Classical V-belt ideal for various industrial applications. Available in small sizes from 5mm to 3mm, these belts are available with cogged or raw edges. Their highly engineered construction makes them ideal for a variety of uses. These belts are commonly used in motors, compressors, milling machines, mixers, and other mechanical devices. To determine the right belt for your application, consider the following factors.
The classic v-belt is the most common and economically-priced type of v-belt. They are manufactured using special formulated rubber reinforced with polyester cords. These belts can span from 16 inches to 400 inches in length. The classic V-belt is also very easy to replace. The belt’s outer diameter and pitch can be measured. The length is typically standardized by the Association for Rubber Product Manufacturers.
Typically, classical V-belts are used in single-belt drives. Because they don’t require lubrication or maintenance, these belts are often available in sizes A and B. However, larger belt sizes are rarely used for single-belt drives. In such cases, multiple A or B belts are an economical alternative to single-belt C. In addition, narrower-profile V-belts provide higher power ratings than conventional V-belts because of their higher depth-to-width ratio. These belts are ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Narrow V-belt
The narrow v-belt is the same as a conventional v-belt, but it has a smaller top and bottom width. This makes it suitable for higher horsepower applications, and it is used in high-end sports cars. Narrow v-belts are generally characterized by a letter “v” on the top side and a length of outside dimensions of 1.6:1.
The steel wires that comprise the core of the v-belt are endless and are free of joints. This provides the strength required for torque transmission. A base rubber compound is placed around the steel wire and acts as a medium of compression and shock absorption during power transmission. A plastic layer acts as a protective cover, and provides the rubber with a degree of temperature tolerance. While choosing a narrow v-belt, it is important to keep in mind that there are some disadvantages to a narrow V-belt.
For example, a narrow V-belt is suitable for high-power applications, and may be used in a small assembly space. Its narrow profile also allows it to be space-saving in layout and allows high-speed drives without additional belts. Furthermore, it reduces operating and maintenance costs. It is ideal for applications where space is limited, and a high torque is required. The benefits of a narrow V-belt are plentiful.
Banded belt
Identifying a banded v-belt can be tricky, but there are a few signs that can indicate a possible problem. Cracked belts can be difficult to spot, but they can be an early indicator of a more serious problem. Look for cracked underside edges, worn covers, and misplaced slack. If 1 or more of these factors applies to your belt, you may want to seek a replacement.
Banded v-belts are made with an elastomer core. The main component of this belt is the elastomer, which is used for the band’s flexural strength and shock resistance. It’s sometimes separated into 2 sections, with each section connected to the other by a tension cord. This gives the belt its trapezium cross-section, which increases tensile strength.
The 2 main types of banded v-belts are wrapped or raw edge. Wrapped v-belts have a fiber-covered body while raw edge belts are uncovered. Banded v-belts are often classified by their cross-section, and include: standard v-belt, wedge v-belt, narrow versus double v-belt, cogged v-belt, and double t-belt.
Banded v-belts are popular with commercial applications. Whether you’re looking for a 2V-belt or a large 8V-belt, V-Belt Guys has what you need. We also stock a wide variety of different banded v-belts and can help you find 1 that fits your needs and budget. Take a look at our selection today!
Traditional V-belt
Although a traditional V-belt may be a glorified rubber band, modern variations reflect advances in engineering. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for trouble-free service. When you are replacing a traditional V-belt, be sure to follow these simple steps to ensure its longevity. Read on to learn more. Listed below are the features of each type of V-belt. Identify the type of belt you need by measuring its top width, circumference, and dimensions.
TEC Traditional V-belts have an exceptionally low slip rate and are resistant to high operating temperatures. These types of belts do not experience early belt aging. They are also highly resistant to poor operating conditions. However, the maintenance is more extensive than other types of belts. A typical V-belt part number is B50, which is the cross-section size of a 50-inch belt. The belt’s lifespan is greatly increased because of this feature.
A ribbed V-belt is another option. It has a deeper V than a traditional V-belt. The ribs in this type are narrower and more flexible. These ribs are smaller than the classic V-belt, but they can transmit 3 times as much horsepower. Because they are thinner, these belts are more flexible than traditional V-belts. The thickness of the ribs is less critical.
Metric V-belt
Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.
Metric V-belts are generally more durable than their equivalents made of standard American-sized belts. Metric V-belts are available in many different sizes to fit different machineries. In addition to offering superior load-carrying capacity, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are known for their exceptional flex and stretch characteristics. For optimum performance in textile mills, food processing, and machine tool applications, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are manufactured using a proprietary construction that combines a higher load-carrying capacity with superior flex and stretch.
Metric belts can generate 50% to 100% more horsepower than conventional and classic sectioned belts. This is achieved through improved construction and placement of the cord line. These belts also have unique wedge designs that help them support the cord in motion. However, you must ensure the proper tension when buying a Metric V-belt, because improper tension may damage the belt. They are compatible with both U.S. and international standards.

