Product Description
Wire Rope Double Drum Crane for Shaft Lifting
Introduction:
Mine hoist can be divided into 2 kinds; 1 kind is JKE series single rope mining hoist and the other is Multi-rope friction hoist.
This series mine hoist including 2m-5m single tubular and double tubular types, and can be used for mining hoist, personnel lifting and material and equipment descending from vertical shafts or inclined shafts of coal, metal and nonmetal ores.
JK mine hoist is mainly used in inclined roadways and wells of coal mines, metal mines and non-metal mines to hoist or lower personnel and materials.
Technical parameters:
| Model | Drum | Tension PF |
Tension Differe |
Rope Diameter |
Lift height (m) | Max Speed |
Reduce speed ratio |
Motor Speed |
||||||
| Number | Dia | Width | 1-layer | 2-layer | 3-layer |
|||||||||
| m | KN | mm | m | m/s | r/min | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.5/20 | 1 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 62 | 24 | 305 | 650 | 1571 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 1000 | |||
| JK-2×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/20 | 1.80 | 375 | 797 | 1246 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2/20 | 2.5 | 2.00 | 83 | 28 | 448 | 945 | 1475 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 750 | ||||
| JK-2.5×2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/20 | 2.30 | 525 | 1100 | 1712 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-3×2.2/20 | 3.0 | 2.20 | 135 | 36 | 458 | 966 | 1513 | 6.0 | 20.0 | |||||
| 2JK-2×1/11.2 | 2 | 2.0 | 1.00 | 62 | 40 | 24 | 182 | 406 | 652 | 7.0 | 11.2 | |||
| 2JK-2×1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/11.2 | 1.25 | 242 | 528 | 838 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.20 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 843 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.50 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 319 | 685 | 1080 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/11.2 | 3.0 | 135 | 90 | 36 | 289 | 624 | 994 | 10.5 | 11.2 | |||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/11.2 | 1.80 | 362 | 770 | 1217 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/11.2 | 3.5 | 1.70 | 170 | 115 | 40 | 349 | 746 | – | 12.6 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 2.10 | 450 | 950 | – | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/10 | 4.0 | 245 | 160 | 48 | 421 | 891 | – | 12.6 | 10.0 | 600 | ||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/11.2 | 11.2 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-5×2.3/10 | 5.0 | 2.30 | 280 | 180 | 52 | 533 | – | – | 12 | 10.0 | 500 | |||
| 2JK-5×2.3/11.2 | ||||||||||||||
Possible defects:
| Defect | Causes |
| Unfilled sections | Insufficient material Low pouring temperature |
| Porosity | Melt temperature is too high Non-uniform cooling rate Sand has low permeability |
| Hot tearing | Non-uniform cooling rate |
| Surface projections | Erosion of sand mold interior A crack in the sand mold Mold halves shift |
FAQ
Q: How about the quality of your products?
A: Our machines are manufactured strictly according to national and international standards, and we take a test on each equipment before delivery.
Q: How about the price?
A: We are manufactory, and we can give you lower price than those trade companies. Besides, customers from Made in China can get a discount.
Q: Do you provide after-sale service?
A: Yes. The warranty period of our machines is 1 year, and we have a professional after-sale team to promptly and thoroughly solve your problems.
Q: Do you provide equipment operation training?
A: Yes. We can send professional engineers to the working site for equipment installation, adjustment, and operation training. All of our engineers have passports.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, ISO 9001:2008 |
|---|---|
| Standard: | ASME, BS, ANSI, GB, ASTM, DIN |
| Surface Treatment: | Sand Blast |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
| Name: | Shaft Lifting |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What is the impact of tensioner rollers on the noise level and vibration in a belt drive system?
Tensioner rollers play a significant role in managing the tension and alignment of belts in a belt drive system, and they can have a notable impact on the noise level and vibration of the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the impact of tensioner rollers on noise and vibration in a belt drive system:
1. Noise Reduction:
Tensioner rollers help reduce noise in a belt drive system by maintaining proper belt tension and alignment. When the tensioner roller is properly adjusted, it ensures that the belt remains in contact with the pulleys without excessive slack or tension. This helps minimize belt slippage, which is a common source of noise in belt drive systems. Additionally, tensioner rollers with damping mechanisms or optimized designs can further reduce noise by absorbing vibrations and minimizing the transmission of sound waves through the system.
2. Vibration Damping:
Tensioner rollers can also contribute to the damping of vibrations in a belt drive system. Vibrations can occur due to various factors, such as belt misalignment, inconsistent tension, or irregularities in the pulley surfaces. By maintaining proper tension and alignment, tensioner rollers help reduce these vibrations. Additionally, tensioner rollers with damping mechanisms or advanced bearing systems can absorb and dissipate vibrations, further reducing the overall vibration levels in the system.
3. Belt Slap and Flutter Prevention:
Tensioner rollers play a crucial role in preventing belt slap and flutter, which are sources of noise and vibration in belt drive systems. Belt slap occurs when the belt tension is insufficient, causing the belt to oscillate and slap against nearby components. Flutter refers to the rapid vibration or flapping of the belt due to irregular tension or misalignment. Tensioner rollers help maintain proper tension and alignment, preventing belt slap and flutter and consequently reducing the associated noise and vibration.
4. Improved Belt Contact:
Proper tension and alignment provided by tensioner rollers ensure improved belt contact with the pulleys. When the belt is correctly tensioned, it maintains consistent and optimal contact with the pulley surfaces. This results in smoother power transmission and reduced belt slip, which in turn leads to reduced noise and vibration. Tensioner rollers help maintain this optimal belt contact, contributing to quieter and smoother operation of the belt drive system.
5. Reduced Wear and Tear:
By maintaining proper tension and alignment, tensioner rollers help minimize excessive wear and tear on the belt and other components in the drive system. When the belt is properly tensioned, it experiences less stress and friction, reducing the likelihood of noise and vibration-inducing issues such as belt stretching, slipping, or premature wear. By minimizing these factors, tensioner rollers contribute to a quieter and smoother-running belt drive system.
6. System Stability:
Optimal tension and alignment provided by tensioner rollers contribute to the overall stability of the belt drive system. When the belt operates with consistent tension and alignment, it reduces the chances of sudden changes or fluctuations that can lead to noise and vibration. The stability provided by tensioner rollers helps maintain a more controlled and balanced operation, resulting in reduced noise and vibration levels.
7. Maintenance of Performance Over Time:
Tensioner rollers help maintain the performance of the belt drive system over time. As belts naturally wear and stretch over their lifespan, tensioner rollers can compensate for these changes by continuously adjusting the tension. This ensures that the belt remains properly tensioned and aligned, minimizing the risk of noise and vibration issues that can arise from belt deterioration. By maintaining consistent performance, tensioner rollers contribute to a quieter and smoother-running belt drive system throughout its service life.
In summary, tensioner rollers have a significant impact on the noise level and vibration in a belt drive system. They help reduce noise by maintaining proper tension and alignment, absorbing vibrations, preventing belt slap and flutter, and improving belt contact. Tensioner rollers also contribute to smoother operation, reduced wear, increased system stability, and long-term performance maintenance. By ensuring optimal functionality, tensioner rollers help create a quieter and more vibration-free environment in belt drive systems.
What role do tensioner rollers play in ensuring proper alignment and tension in belt systems?
Tensioner rollers play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and tension in belt systems. They perform several key functions that contribute to the overall performance and reliability of belt-driven systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Maintaining Proper Belt Tension:
Tensioner rollers help maintain the optimal tension in belts. Proper tension is essential for efficient power transmission and preventing belt slippage. Tensioner rollers exert a controlled amount of pressure on the belt, ensuring it remains tensioned within the desired range. By maintaining proper belt tension, tensioner rollers help prevent power loss, slippage, and premature wear of the belt.
2. Absorbing Belt Vibrations:
Vibrations can occur in belt systems due to imbalances, misalignments, or variations in load. These vibrations can lead to increased wear, noise, and reduced belt life. Tensioner rollers are designed to absorb and dampen vibrations, minimizing their impact on the belt. By reducing vibrations, tensioner rollers help maintain proper alignment and tension, enhancing the performance and longevity of the belt system.
3. Reducing Belt Misalignment:
Proper belt alignment is critical for optimal performance and longevity. Tensioner rollers play a role in maintaining belt alignment by exerting consistent pressure on the belt and guiding it along the intended path. They help prevent lateral movement and ensure that the belt remains centered on the pulleys. By minimizing belt misalignment, tensioner rollers reduce wear, noise, and the risk of premature belt failure.
4. Compensating for Belt Stretch:
Belts can experience stretch over time due to the mechanical stresses they undergo during operation. Belt stretch can result in reduced tension and compromised power transmission. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt stretch by applying additional tension to maintain the desired level of belt tension. This compensation helps prevent belt slippage, excessive wear, and premature failure, ensuring proper alignment and tension in the belt system.
5. Facilitating Belt Tracking:
Proper belt tracking is essential for smooth operation and longevity of the belt system. Tensioner rollers aid in maintaining belt tracking by exerting controlled pressure and guiding the belt along the intended path. They help prevent the belt from wandering or rubbing against the pulleys or other components. By facilitating accurate belt tracking, tensioner rollers contribute to proper alignment, reduced wear, and extended belt life.
6. Supporting Belt Span:
In longer belt spans or applications with heavy loads, tensioner rollers provide support to the belt. They help prevent sagging and excessive flexing of the belt, which can lead to accelerated wear and reduced belt life. By offering support, tensioner rollers contribute to maintaining proper alignment and tension throughout the belt system.
7. Allowing Tension Adjustment:
Tensioner rollers often incorporate mechanisms that allow for tension adjustment. This feature enables fine-tuning of the belt tension to suit specific operating conditions or accommodate changes in load or temperature. Tension adjustment capability ensures that the belt system can be properly tensioned, optimizing performance, and reducing the risk of wear or slippage.
In summary, tensioner rollers play a vital role in ensuring proper alignment and tension in belt systems. They maintain proper belt tension, absorb vibrations, reduce belt misalignment, compensate for belt stretch, facilitate belt tracking, provide belt support, and allow tension adjustment. By performing these functions, tensioner rollers contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability, and longevity of belt-driven systems.

What is a tensioner roller, and what role does it play in mechanical systems?
A tensioner roller, also known as a belt tensioner or idler pulley, is a component commonly used in mechanical systems to maintain proper tension in belts or chains. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of various systems that rely on the power transmission provided by belts or chains. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a tensioner roller is and the role it plays in mechanical systems:
1. Definition and Construction:
A tensioner roller is a pulley-like component that is typically mounted on a spring-loaded arm or bracket. It consists of a smooth or grooved surface that comes into contact with the belt or chain. The tensioner roller is designed to rotate freely on bearings or bushings, allowing it to accommodate the movement of the belt or chain and maintain the desired tension.
2. Tension Maintenance:
The primary role of a tensioner roller is to maintain the appropriate tension in belts or chains. Tension is crucial for the proper functioning of power transmission systems. If the tension is too loose, the belt or chain may slip, resulting in a loss of power transfer and potential damage to the system. On the other hand, excessive tension can cause increased wear on the belt or chain, as well as strain on other components. The tensioner roller applies the necessary force to keep the belt or chain properly tensioned, ensuring optimal power transmission efficiency and preventing premature wear or failure.
3. Compensation for Belt or Chain Stretch:
Over time, belts and chains can experience stretching due to normal wear and tear or changes in operating conditions. This stretching can lead to a decrease in tension and affect the performance of the mechanical system. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt or chain stretch by automatically adjusting their position to maintain the desired tension. The spring-loaded arm or bracket allows the tensioner roller to move and adapt to the changing length of the belt or chain, ensuring consistent tension throughout the system’s operation.
4. Noise and Vibration Dampening:
Tensioner rollers also contribute to reducing noise and vibration in mechanical systems. The smooth rotation of the tensioner roller on its bearings or bushings helps absorb and dampen the vibrations generated during the operation of the belt or chain. This reduces the overall noise level and improves the smoothness of the system’s operation, enhancing user comfort and minimizing potential damage caused by excessive vibrations.
5. Maintenance and Replacement:
Proper maintenance of tensioner rollers is essential to ensure their continued functionality. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If a tensioner roller is found to be worn, damaged, or no longer providing adequate tension, it should be promptly replaced to prevent further complications and maintain the optimal operation of the mechanical system.
6. Applications:
Tensioner rollers are used in a wide range of mechanical systems that rely on belts or chains for power transmission. They can be found in automotive engines, industrial machinery, HVAC systems, printing equipment, and many other applications. The specific design and size of tensioner rollers may vary depending on the requirements of the system in which they are used.
In summary, a tensioner roller is a crucial component in mechanical systems that rely on belts or chains for power transmission. It ensures the proper tension of the belt or chain, compensates for stretch, reduces noise and vibration, and contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of tensioner rollers are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues in mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-03-26
China best Wire Rope Double Drum Crane for Shaft Lifting near me manufacturer
Product Description
Wire Rope Double Drum Crane for Shaft Lifting
Introduction:
Mine hoist can be divided into 2 kinds; 1 kind is JKE series single rope mining hoist and the other is Multi-rope friction hoist.
This series mine hoist including 2m-5m single tubular and double tubular types, and can be used for mining hoist, personnel lifting and material and equipment descending from vertical shafts or inclined shafts of coal, metal and nonmetal ores.
JK mine hoist is mainly used in inclined roadways and wells of coal mines, metal mines and non-metal mines to hoist or lower personnel and materials.
Technical parameters:
| Model | Drum | Tension PF |
Tension Differe |
Rope Diameter |
Lift height (m) | Max Speed |
Reduce speed ratio |
Motor Speed |
||||||
| Number | Dia | Width | 1-layer | 2-layer | 3-layer |
|||||||||
| m | KN | mm | m | m/s | r/min | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.5/20 | 1 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 62 | 24 | 305 | 650 | 1571 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 1000 | |||
| JK-2×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/20 | 1.80 | 375 | 797 | 1246 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2/20 | 2.5 | 2.00 | 83 | 28 | 448 | 945 | 1475 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 750 | ||||
| JK-2.5×2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/20 | 2.30 | 525 | 1100 | 1712 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-3×2.2/20 | 3.0 | 2.20 | 135 | 36 | 458 | 966 | 1513 | 6.0 | 20.0 | |||||
| 2JK-2×1/11.2 | 2 | 2.0 | 1.00 | 62 | 40 | 24 | 182 | 406 | 652 | 7.0 | 11.2 | |||
| 2JK-2×1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/11.2 | 1.25 | 242 | 528 | 838 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.20 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 843 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.50 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 319 | 685 | 1080 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/11.2 | 3.0 | 135 | 90 | 36 | 289 | 624 | 994 | 10.5 | 11.2 | |||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/11.2 | 1.80 | 362 | 770 | 1217 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/11.2 | 3.5 | 1.70 | 170 | 115 | 40 | 349 | 746 | – | 12.6 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 2.10 | 450 | 950 | – | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/10 | 4.0 | 245 | 160 | 48 | 421 | 891 | – | 12.6 | 10.0 | 600 | ||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/11.2 | 11.2 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-5×2.3/10 | 5.0 | 2.30 | 280 | 180 | 52 | 533 | – | – | 12 | 10.0 | 500 | |||
| 2JK-5×2.3/11.2 | ||||||||||||||
Possible defects:
| Defect | Causes |
| Unfilled sections | Insufficient material Low pouring temperature |
| Porosity | Melt temperature is too high Non-uniform cooling rate Sand has low permeability |
| Hot tearing | Non-uniform cooling rate |
| Surface projections | Erosion of sand mold interior A crack in the sand mold Mold halves shift |
FAQ
Q: How about the quality of your products?
A: Our machines are manufactured strictly according to national and international standards, and we take a test on each equipment before delivery.
Q: How about the price?
A: We are manufactory, and we can give you lower price than those trade companies. Besides, customers from Made in China can get a discount.
Q: Do you provide after-sale service?
A: Yes. The warranty period of our machines is 1 year, and we have a professional after-sale team to promptly and thoroughly solve your problems.
Q: Do you provide equipment operation training?
A: Yes. We can send professional engineers to the working site for equipment installation, adjustment, and operation training. All of our engineers have passports.
How to Repair a Timing Belt Tensioner
Your timing belt tensioner is a critical component of your vehicle’s drivetrain. Too little tension, for example, will cause the belt to slip, and too much tension can overload shaft bearings, leading to premature failure. If you notice that your belt tensioner is not working properly, you should immediately visit a mechanic. Corrosion from road splash, dirt, mud, or other debris can jam the tensioner housing. To avoid this, make sure that you replace your timing belt tensioner as soon as possible.
Symptoms of a bad belt tensioner
If you’ve ever wondered what signs indicate a bad belt tensioner, look no further than your vehicle’s engine. Worn belts or a broken tensioner can cause an irritating squealing noise, as well as the belt to slip. Even worse, a bad tensioner can cause water to enter the belt and pulley, resulting in water damage. A worn tensioner is usually the culprit of the noise, but there are also other warning signs that a belt is in trouble.
Your vehicle’s engine may start to run poorly or even squeal when you turn the key. Similarly, your engine may fail to start at all, or the check engine light may illuminate. The belt may also start to wear out in an unusual pattern. These signs indicate that the tensioner is in need of replacement. If you notice 1 or more of these signs, get your car checked right away.
To check the condition of the tensioner, remove the drive belt and observe the pulley. You may notice rust dripping or bleeding at the mounting bolts, which are the most common signs of a bad tensioner. If you can’t remove the drive belt, check the pulley by rotating it. If you feel resistance, the pulley is likely worn or slack.
Failure of the belt tensioner will also cause other parts of the car to fail. If a bad belt tensioner isn’t fixed quickly, you might not be able to use the vehicle properly. You could end up breaking your car’s engine, losing power steering, and possibly even the water pump. If your car is not running right, you could be stuck in the middle of nowhere. Even if the alternator doesn’t work, you’ll still have a malfunctioning power steering system and a dead AC system.
A broken timing belt tensioner can cause strange noises or a no-start condition. These noises and symptoms are signs of a bad belt tensioner, and you’ll have to replace it ASAP. If you don’t know what symptoms mean, don’t hesitate to take your car to a mechanic. You’ll be surprised how easy it is to check this vital component and save yourself a bunch of money.
Components of a belt tensioner
The components of a belt tensioner assembly consist of 4 key components. The clearance between the pulley and the base is critical to the tensioner’s operation. If the tensioner is installed incorrectly, the spring can break and cause severe injury. The spring’s preload and powerful force make it difficult to service the unit safely. These parts are non-serviceable. If you are unsure of how to repair your tensioner, contact an authorized mechanic.
The components of a belt tensioner drive are shown in FIG. 2. The rotor shaft is connected to the drive screw, while the second transmission is connected to the gear shaft. The rotor and gear shaft are in parallel with each other. The gear shaft and worm wheel are connected to the belt tensioner drive. In other words, the belt tensioner drive is located in the B-pillar of the motor vehicle.
A belt tensioner may be equipped with a drive shaft and electric motor. The drive shaft may also contain a worm gear or worm wheel. The drive shaft also has an intermediate gearbox. Once the tensioner is set, it is ready to move to its safe-position position. It is a relatively simple and inexpensive replacement for your belt. When replacing a multi-ribbed belt, be sure to replace the tensioner along with the belt. Gates recommends replacing all wear parts at once.
In the event of a faulty drive belt tensioner, the belt will not stay taut. The pulley can wobble and cause the belt to fray. In addition to this, the bearings can cause a loud squealing noise. In this case, the accessory motors will continue to run, while the belt itself will not. Therefore, replacing the timing belt tensioner is an important part of maintaining the car.
In some systems, the belt tensioner uses a worm gear as the first gear. This results in rolling engagement of the screw’s teeth. This reduces noise and vibrations, while maximizing the efficiency of the belt tensioner drive. Additionally, a worm gear can eliminate the need for additional parts in belt tensioners. While this may not be practical in all instances, it is a good choice for space-constrained environments.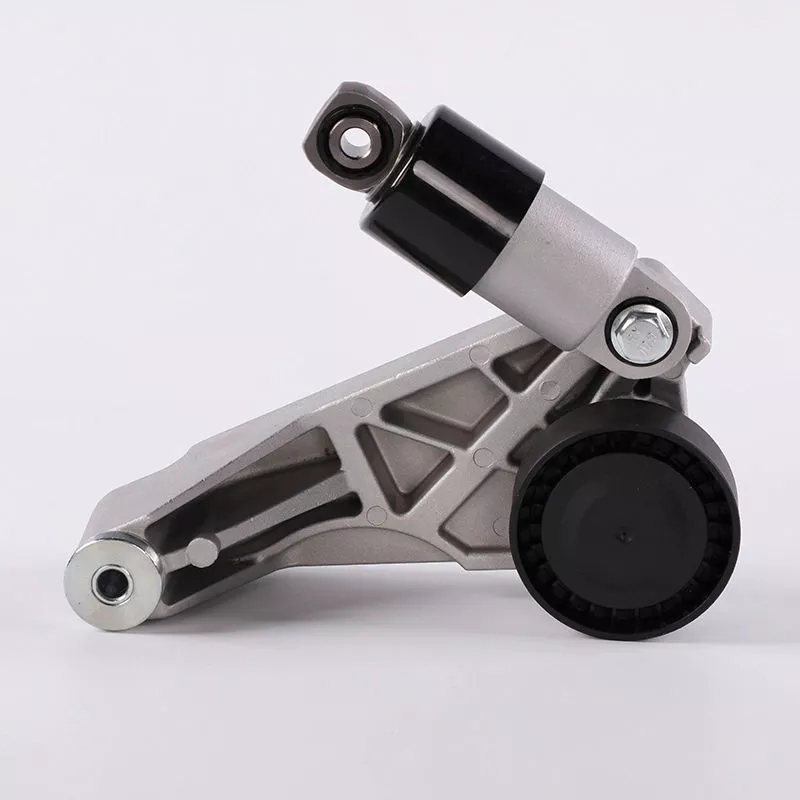
Repair options for a timing belt tensioner
A timing belt tensioner is an essential part of an automobile’s timing chain and is responsible for ensuring proper timing. Proper alignment of timing marks is essential to the proper operation of the engine, and improper alignment may lead to damage to the engine. To repair a timing belt tensioner, there are several repair options available. First, you need to remove the engine cover. You can then remove the timing belt tensioner by loosening the pulley using a ratchet or breaker bar.
When the timing belt isn’t properly tensioned, the engine will misfire. The engine misfires when the valve opens and the pistons rise at the wrong time. When this happens, the timing belt cannot properly grip the gears and the engine will not function. If this part fails, you’ll have to replace the whole timing chain. However, if you are handy with tools, you can easily replace the entire timing belt tensioner yourself.
If your timing belt tensioner is out of alignment, you should replace it. If you’re not sure whether it needs to be replaced, check it with a professional and learn the details of the repair. The timing belt tensioner is the most critical part of the engine, so it’s important to know about it. Otherwise, your car won’t run as well as it could. Repair options for a timing belt tensioner will vary depending on the severity of the problem and how much damage it has done.
While there are several repair options for a timing belt tensioner, the average cost of replacement is $364 to $457, and this doesn’t take into account any tax or fee you may be charged. DIY repair methods will usually cost you $50 to $150, and you’ll likely save a lot of money in the process. However, you need to remember that you may be unable to do the job yourself because you don’t know how to use the proper tools and equipment.
While it is not difficult to replace a timing belt tensioner on your own, you should know that you’ll need to remove other parts of the engine as well as special tools to make the repair properly. This is an advanced repair job and requires a great deal of skill. If you’re new to home car repair, you may not want to attempt it yourself. There are many other options, such as hiring a mechanic.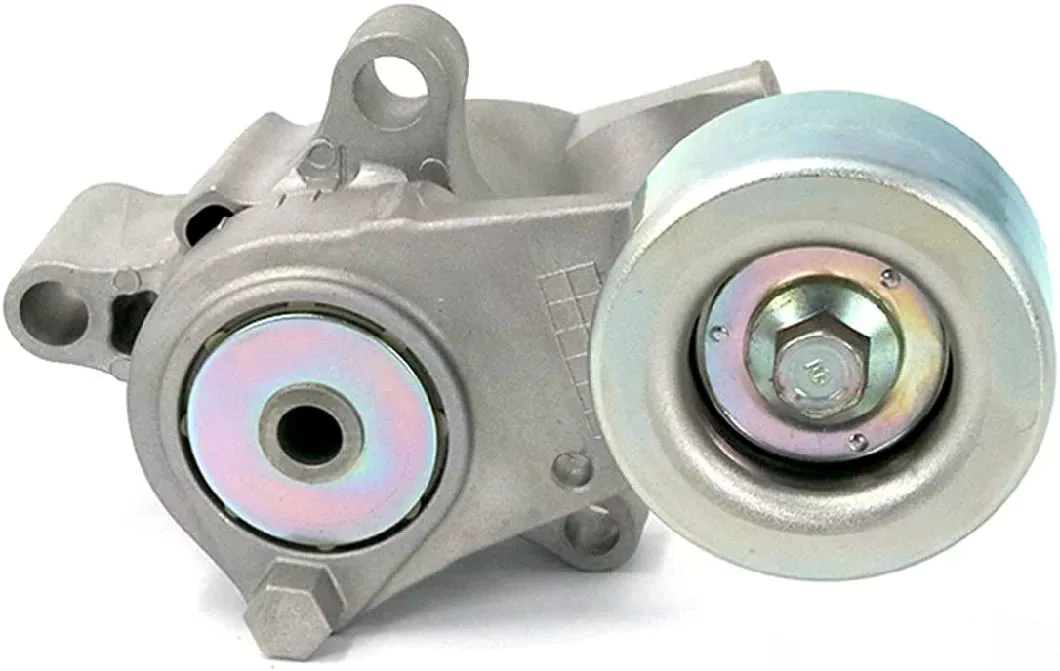
Installation instructions
While there are no universal installation instructions for belt tensioners, the manufacturer of your car may provide detailed instructions. Before attempting to replace your tensioner, read the manufacturer’s recommended procedures carefully. To install a new tensioner properly, unload the old 1 and take a picture or sketch of how the belt should be routed. Once the old tensioner is out, follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications. Make sure to unload and remove the belt from the tensioner, and follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications to install the new one.
If your car comes with a manual belt tensioner, you can follow the instructions. The manual will have a corresponding guide for installation. When installing a belt tensioner, make sure the manual clearly states the static tension for your particular model. Check that it is in line with the engine relief to ensure proper belt tension. You can then use a 6mm allen key to turn the tensioner clockwise and counterclockwise. Once it is in position, release the tensioner to operate. The belt tensioner should now apply the proper tension to your belt.
Before installing a new belt tensioner, make sure you read the manual completely. You should follow these steps carefully to avoid any problems with the tensioner. If the tensioner has failed, you must replace it immediately. A new belt tensioner will help you ensure proper performance of your accessory belt drive system. If you are installing a new multi-ribbed belt, you should replace the tensioner as well. However, it is important to note that replacing the belt tensioner is a complicated process and requires a mechanic to be able to safely remove the belt from the engine.
To install a second stage drive belt, walk the belt onto the input drive and generator. Ensure that the belt is seated properly in the grooves of the pulleys. Next, replace the input drive belt and right and left Drive Disk covers. Test the machine to ensure that it is working properly. If it doesn’t, replace the original drive belt. After installing the new belt, you may want to read the manual again to make sure it is in perfect condition.

