Product Description
Product Description
Finish: Zinc Plated Place of Origin:ZheJiang , China
Brand Name:WDL Model Number: Steel chain
Structure:Welded Chain Function: for lifting
Standard or Nonstandard:Standard Size: 3/32″-1″
Surface treatment: White Zinc Plated Usage:Dragging, safety, general use
Color: White Packing:Gunny Bag, Bucket, Reel, Iron Drums
Grade:G30 MOQ:1 Ton
Product Parameters
LONG LINK CHAIN
| LINK SPECIFICATION | TEST LOAD | BREAKING LOAD | NET WT PER 200F(KG) | ||||
| D | L | W | |||||
| IN | MM | MM | MM | KG | KG | B.F | H.D.G |
| 1/8 | 3.20 | 23 | 12 | 200 | 400 | 10.40 | 10.70 |
| 5/32 | 4.00 | 27 | 15 | 300 | 600 | 16.60 | 17.50 |
| 3/16 | 4.70 | 31 | 17 | 400 | 800 | 22.40 | 23.30 |
| 7/32 | 5.50 | 32 | 19 | 550 | 1100 | 32.00 | 33.00 |
| 1/4 | 6.35 | 33 | 21 | 750 | 1500 | 43.50 | 44.80 |
| 5/16 | 7.94 | 48 | 31 | 1200 | 2400 | 68.00 | 70.00 |
| 3/8 | 9.50 | 60 | 37 | 1700 | 3400 | 96.00 | 99.00 |
| 7/16 | 11.11 | 71 | 41 | 2300 | 4600 | 126.00 | 129.00 |
| 1/2 | 12.70 | 85 | 48.5 | 3000 | 6000 | 167.00 | 172.00 |
| 5/8 | 15.80 | 114 | 61.5 | 4700 | 9400 | 256.00 | 264.00 |
| 3/4 | 19.00 | 125 | 75 | 6800 | 13600 | 381.00 | 392.00 |
| 7/8 | 22.20 | 140 | 88 | 9250 | 18500 | 527.00 | 543.00 |
| 1 | 25.40 | 155 | 100 | 12150 | 24300 | 696.00 | 716.00 |
SHORT LINK CHAIN
| LINK SPECIFICATION | TEST LOAD | BREAKING LOAD | NET WT PER 200F(KG) | ||||
| D | L | W | |||||
| IN | MM | MM | MM | KG | KG | B.F | H.D.G |
| 1/8 | 3.20 | 16 | 12 | 200 | 400 | 11.40 | 11.74 |
| 5/32 | 4.00 | 18.5 | 14.5 | 300 | 600 | 18.60 | 19.00 |
| 3/16 | 4.70 | 19 | 17 | 400 | 800 | 26.20 | 27.00 |
| 7/32 | 5.50 | 20 | 19 | 550 | 1100 | 36.80 | 38.00 |
| 1/4 | 6.35 | 22 | 21 | 750 | 1500 | 50.00 | 51.50 |
| 5/16 | 7.94 | 26.5 | 27.2 | 1200 | 2400 | 80.00 | 82.40 |
| 3/8 | 9.50 | 30 | 32 | 1700 | 3400 | 122.00 | 125.70 |
| 7/16 | 11.11 | 34 | 36 | 2300 | 4600 | 164.00 | 169.00 |
| 1/2 | 12.70 | 39 | 43 | 3000 | 6000 | 210.00 | 216.00 |
| 5/8 | 15.80 | 45 | 53 | 4700 | 9400 | 334.00 | 344.00 |
| 3/4 | 19.00 | 55 | 63 | 6800 | 13600 | 485.00 | 799.00 |
| 7/8 | 22.20 | 64 | 74 | 9250 | 18500 | 656.00 | 675.00 |
| 1 | 25.40 | 73 | 84 | 12150 | 24300 | 870.00 | 896.00 |
MEDIUM LINK CHAIN
| LINK SPECIFICATION | TEST LOAD | BREAKING LOAD | NET WT PER 200F(KG) | ||||
| D | L | W | |||||
| IN | MM | MM | MM | KG | KG | B.F | H.D.G |
| 1/8 | 3.20 | 20 | 12 | 200 | 400 | 10.80 | 11.00 |
| 5/32 | 4.00 | 23 | 15 | 300 | 600 | 17.40 | 18.00 |
| 3/16 | 4.70 | 25 | 18 | 400 | 800 | 24.40 | 25.00 |
| 7/32 | 5.50 | 26 | 19 | 550 | 1100 | 34.00 | 35.00 |
| 1/4 | 6.35 | 26 | 23 | 750 | 1500 | 48.80 | 50.00 |
| 5/16 | 7.94 | 32 | 29 | 1200 | 2400 | 76.00 | 78.00 |
| 3/8 | 9.50 | 35 | 35 | 1700 | 3400 | 111.00 | 114.00 |
| 7/16 | 11.11 | 38 | 38 | 2300 | 4600 | 154.00 | 158.00 |
| 1/2 | 12.70 | 50 | 45.5 | 3000 | 6000 | 194.00 | 200.00 |
| 5/8 | 15.80 | 60 | 56.7 | 4700 | 9400 | 303.00 | 312.00 |
| 3/4 | 19.00 | 76 | 69 | 6800 | 13600 | 432.00 | 445.00 |
| 7/8 | 22.20 | 90 | 80 | 9250 | 18500 | 586.00 | 603.00 |
| 1 | 25.40 | 105 | 95 | 12150 | 24300 | 770.00 | 792.00 |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
Hello everyone, we are a company specializing in the production of various types of ordinary chains, high-strength chains, stainless steel chains, animal chains, and more than 300 specifications and varieties of chains. We can provide you with the best quality and price products. We hope to achieve cooperation
Always provide online customer service.
CHINAMFG link chain always lead the new development of technologies, new products
And value-added services. Over the years, link chains have been created, applied,
And enable real growth forcustomers into newmarketplaces.
Link chains are widely used in various industries.
Factory Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Usage: | Transmission Chain, Drag Chain, Conveyor Chain, Dedicated Special Chain, Link Chain |
|---|---|
| Material: | Iron |
| Surface Treatment: | Electroplating |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can you provide insights into the importance of proper tensioner roller alignment?
Proper tensioner roller alignment is of utmost importance in a belt drive system as it directly affects the system’s functionality, performance, and longevity. Here are detailed insights into the importance of proper tensioner roller alignment:
1. Optimal Belt Tension:
Proper tensioner roller alignment ensures optimal belt tension, which is crucial for the efficient operation of the belt drive system. When the tensioner roller is correctly aligned, it applies the appropriate tension to the belt, keeping it properly tensioned and preventing excessive slack or tightness. Optimal belt tension ensures efficient power transfer, minimizes belt slippage, reduces wear on the belt and other components, and maximizes the overall performance of the system.
2. Prevents Belt Misalignment:
Tensioner roller alignment plays a vital role in preventing belt misalignment. Misalignment occurs when the belt deviates from its intended path, causing it to run off-center or make contact with adjacent components. Improper tensioner roller alignment can introduce lateral forces on the belt, leading to misalignment. Belt misalignment can result in reduced power transmission efficiency, increased wear on the belt and pulleys, and the generation of noise and vibrations. Proper tensioner roller alignment helps maintain the belt’s alignment, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing the risk of misalignment-related issues.
3. Reduces Belt Wear and Failure:
Proper tensioner roller alignment helps minimize belt wear and failure. Misalignment can cause the belt to rub against the pulleys or other components, resulting in accelerated wear and damage to the belt. Excessive wear can lead to belt stretching, cracking, or even premature failure. By ensuring proper tensioner roller alignment, the belt remains in its intended position, reducing friction, wear, and the risk of belt failure. This extends the lifespan of the belt and minimizes the need for frequent replacements, resulting in cost savings and improved system reliability.
4. Minimizes Noise and Vibration:
Correct tensioner roller alignment contributes to reduced noise and vibration levels in the belt drive system. Misalignment can cause the belt to oscillate, vibrate, or produce noise as it rubs against the pulleys or other components. These vibrations and noise can be transmitted throughout the system, leading to discomfort, increased wear on components, and a decrease in overall system efficiency. Proper tensioner roller alignment ensures smooth belt operation, minimizing vibrations and noise, and providing a quieter and more comfortable working environment.
5. Improves System Efficiency:
Proper tensioner roller alignment improves the overall efficiency of the belt drive system. Misalignment can result in energy losses due to increased friction, belt slippage, or inefficient power transfer. When the tensioner roller is correctly aligned, it helps maintain optimal belt contact with the pulleys, reducing energy losses and ensuring efficient power transmission. Improved system efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption, increased productivity, and cost savings over the long term.
6. Ensures Reliable Performance:
Tensioner roller alignment is critical for ensuring reliable performance of the belt drive system. Misalignment can lead to unexpected system failures, breakdowns, or unplanned downtime. Proper tensioner roller alignment helps maintain the overall stability and reliability of the system, reducing the risk of sudden failures or disruptions. By ensuring reliable performance, proper tensioner roller alignment contributes to increased productivity, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced system longevity.
7. Facilitates Maintenance and Service:
Proper tensioner roller alignment simplifies maintenance and service tasks. When the tensioner roller is correctly aligned, it is easier to access and adjust, allowing for straightforward tension adjustments or replacement when necessary. Maintenance personnel can quickly identify and address any alignment issues, ensuring that the system remains in optimal working condition. Proper tensioner roller alignment facilitates efficient maintenance practices, reduces downtime during servicing, and enhances the overall serviceability of the belt drive system.
In summary, proper tensioner roller alignment is crucial for the optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of a belt drive system. It ensures optimal belt tension, prevents misalignment, reduces wear on the belt, minimizes noise and vibration, improves system efficiency, and facilitates maintenance and service. By giving due attention to tensioner roller alignment, system operators can maximize the benefits of their belt drive systems and avoid potential issues that can arise from misalignment.

What factors should be considered when selecting tensioner rollers for different industrial applications?
When selecting tensioner rollers for different industrial applications, several factors need to be taken into consideration. These factors include:
1. Load and Tension Requirements:
The load and tension requirements of the specific industrial application are crucial factors to consider. It is important to determine the maximum load the tensioner roller will experience and the required tension for proper belt operation. This information helps in selecting a tensioner roller that can handle the anticipated loads and provide the necessary tension to prevent belt slippage or excessive wear.
2. Belt Type and Size:
The type and size of the belt being used in the industrial application are important considerations. Different belts have varying characteristics, such as width, thickness, and tooth profile. It is essential to choose a tensioner roller that is compatible with the specific belt type and size to ensure proper fit, alignment, and tension distribution.
3. Operating Speed:
The operating speed of the industrial application is a critical factor when selecting tensioner rollers. High-speed applications generate centrifugal forces that can impact belt tension and introduce vibrations. Tensioner rollers designed for high-speed applications are typically equipped with features to absorb vibrations and maintain consistent tension, ensuring reliable power transmission at elevated speeds.
4. Environmental Conditions:
The environmental conditions in which the tensioner roller will operate should be considered. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, dirt, chemicals, and exposure to moisture or corrosive substances can affect the performance and durability of the tensioner roller. Selecting a tensioner roller with appropriate materials and protective coatings ensures its reliability and longevity in the specific environmental conditions.
5. Alignment and Adjustment Mechanism:
The alignment and adjustment mechanism of the tensioner roller play a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension. Consider the ease of installation, adjustment, and alignment when selecting a tensioner roller. Look for features such as adjustable mounting positions, tension adjustment mechanisms, and reliable locking mechanisms that facilitate easy and precise tension adjustment and alignment of the belt.
6. Maintenance and Serviceability:
The maintenance and serviceability aspects of the tensioner roller should be taken into account. Evaluate the accessibility of the tensioner roller for inspection, lubrication, and maintenance tasks. Choose a tensioner roller that allows for easy replacement of worn or damaged components, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs in the industrial application.
7. Compatibility with the System:
Ensure that the tensioner roller is compatible with the overall belt drive system and other components in the industrial application. Consider factors such as the mounting arrangement, space constraints, and integration with other system elements. Compatibility ensures proper fit, functionality, and overall system performance.
8. Industry Standards and Regulations:
Complying with industry standards and regulations is essential when selecting tensioner rollers for industrial applications. Consider any specific requirements or guidelines set by relevant regulatory bodies or industry associations. Adhering to these standards helps ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with applicable regulations.
In summary, when selecting tensioner rollers for different industrial applications, it is important to consider factors such as load and tension requirements, belt type and size, operating speed, environmental conditions, alignment and adjustment mechanism, maintenance and serviceability, compatibility with the system, and adherence to industry standards and regulations. Considering these factors ensures the appropriate selection of tensioner rollers that will effectively support the belt drive system and optimize the performance and reliability of the industrial application.

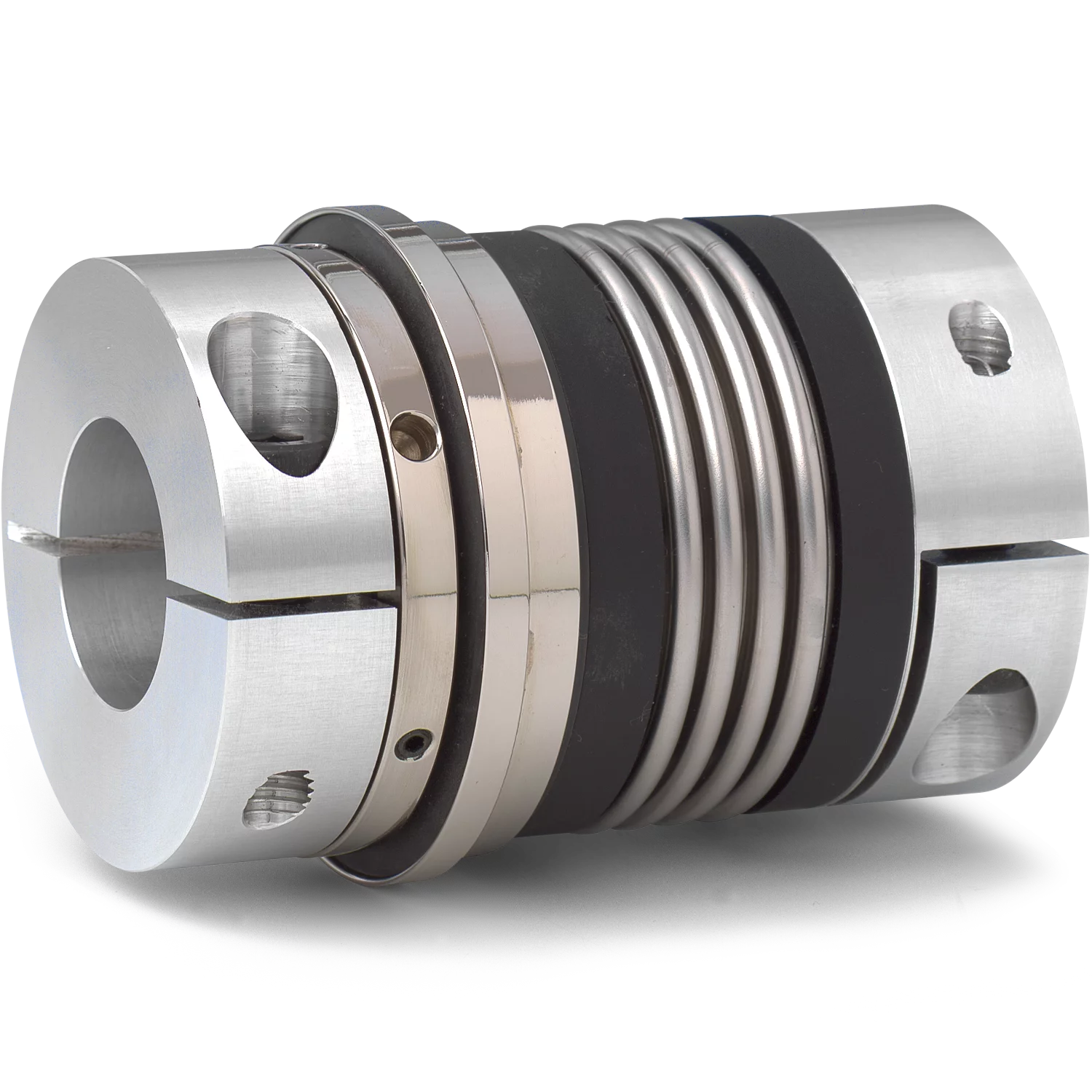
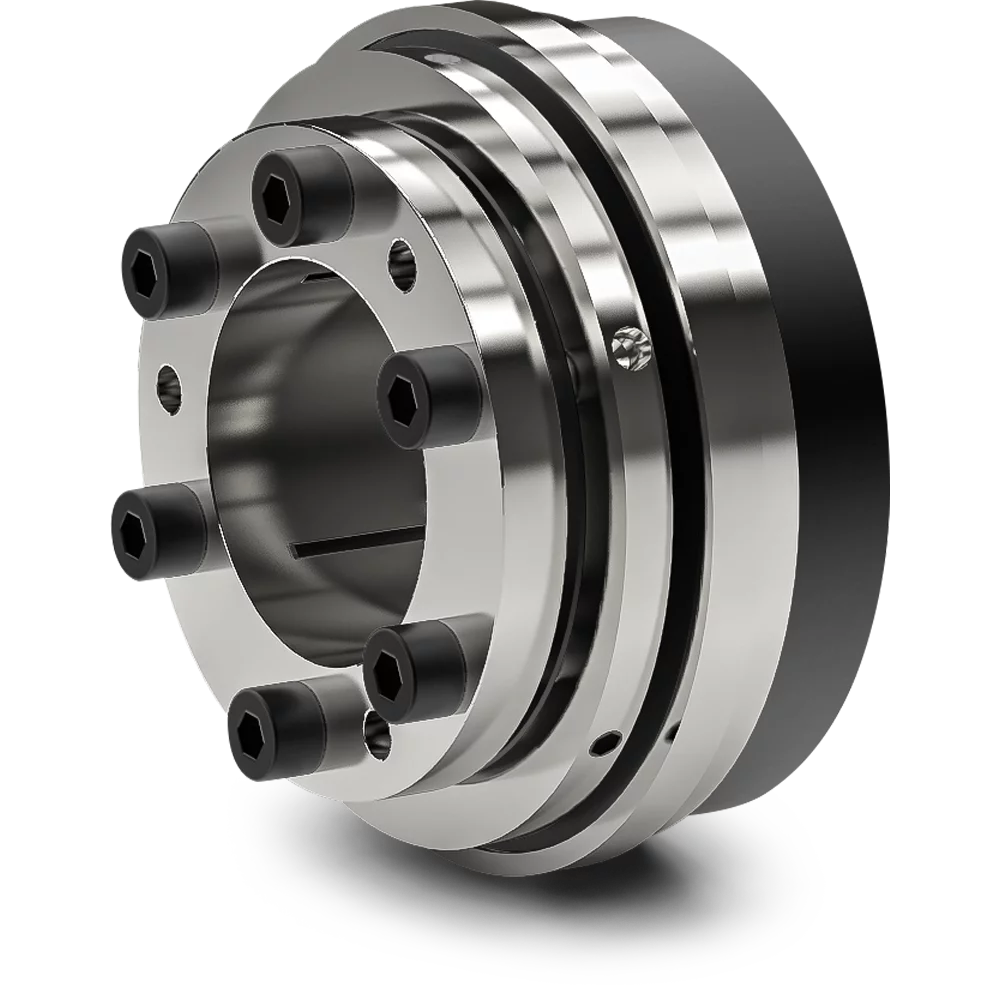
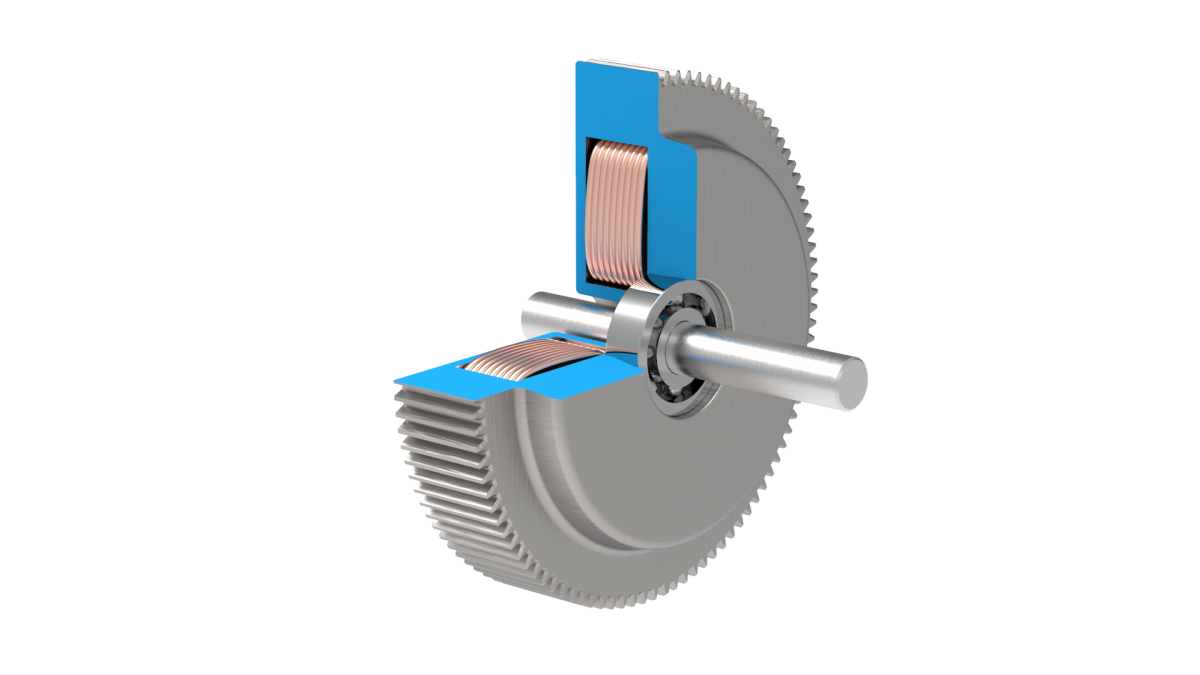
What is a tensioner roller, and what role does it play in mechanical systems?
A tensioner roller, also known as a belt tensioner or idler pulley, is a component commonly used in mechanical systems to maintain proper tension in belts or chains. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of various systems that rely on the power transmission provided by belts or chains. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a tensioner roller is and the role it plays in mechanical systems:
1. Definition and Construction:
A tensioner roller is a pulley-like component that is typically mounted on a spring-loaded arm or bracket. It consists of a smooth or grooved surface that comes into contact with the belt or chain. The tensioner roller is designed to rotate freely on bearings or bushings, allowing it to accommodate the movement of the belt or chain and maintain the desired tension.
2. Tension Maintenance:
The primary role of a tensioner roller is to maintain the appropriate tension in belts or chains. Tension is crucial for the proper functioning of power transmission systems. If the tension is too loose, the belt or chain may slip, resulting in a loss of power transfer and potential damage to the system. On the other hand, excessive tension can cause increased wear on the belt or chain, as well as strain on other components. The tensioner roller applies the necessary force to keep the belt or chain properly tensioned, ensuring optimal power transmission efficiency and preventing premature wear or failure.
3. Compensation for Belt or Chain Stretch:
Over time, belts and chains can experience stretching due to normal wear and tear or changes in operating conditions. This stretching can lead to a decrease in tension and affect the performance of the mechanical system. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt or chain stretch by automatically adjusting their position to maintain the desired tension. The spring-loaded arm or bracket allows the tensioner roller to move and adapt to the changing length of the belt or chain, ensuring consistent tension throughout the system’s operation.
4. Noise and Vibration Dampening:
Tensioner rollers also contribute to reducing noise and vibration in mechanical systems. The smooth rotation of the tensioner roller on its bearings or bushings helps absorb and dampen the vibrations generated during the operation of the belt or chain. This reduces the overall noise level and improves the smoothness of the system’s operation, enhancing user comfort and minimizing potential damage caused by excessive vibrations.
5. Maintenance and Replacement:
Proper maintenance of tensioner rollers is essential to ensure their continued functionality. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If a tensioner roller is found to be worn, damaged, or no longer providing adequate tension, it should be promptly replaced to prevent further complications and maintain the optimal operation of the mechanical system.
6. Applications:
Tensioner rollers are used in a wide range of mechanical systems that rely on belts or chains for power transmission. They can be found in automotive engines, industrial machinery, HVAC systems, printing equipment, and many other applications. The specific design and size of tensioner rollers may vary depending on the requirements of the system in which they are used.
In summary, a tensioner roller is a crucial component in mechanical systems that rely on belts or chains for power transmission. It ensures the proper tension of the belt or chain, compensates for stretch, reduces noise and vibration, and contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of tensioner rollers are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues in mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China wholesaler 12mm Welded Galvanized DIN5685A Short Link Chain Made in China
Product Description
CHINAMFG link chain always lead the new development of technologies, new products
And value-added services. Over the years, link chains have been created, applied,
And enable real growth forcustomers into newmarketplaces.
Link chains are widely used in various industries.
Service: Your inquiry will be replied within 12 hours.
Place of origin: ZheJiang , China.
Brand: CHINAMFG
Material: Carton steel ( Iron, Alloy Steel 20Mn2, 25MNV).
Surface: Electro Galvanized (Hot Dip Galivanized,
Polished, Self-color).
Standard: Ordinary Mild Steel Link Chain
Grade: G30,G43,g70,G80,G10
1. Decoration; Protection; Lifting; Traction etc.
2. Fishing &boat chain; Mine chain; Cement lifting round chain.
We have good relationship with clients around the world, we welcome your visiting.
We welcome your inquiry!
real factory , own our galvanizing factory , the price and quality could be 100% guaranted .
Take us, take the world!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Usage: | Transmission Chain, Drag Chain, Conveyor Chain, Dedicated Special Chain |
|---|---|
| Material: | Iron, Carton Steel ( Iron, Alloy Steel 20mn2, 25mnv) |
| Surface Treatment: | Electroplating |
| Feature: | Heat Resistant |
| Chain Size: | 1/2"*3/32" |
| Structure: | Welded Chain |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | |
|---|
What are the signs that indicate a need for tensioner roller replacement, and how can they be diagnosed?
Identifying the signs that indicate a need for tensioner roller replacement is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and reliability of a belt drive system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the signs and diagnostic methods for determining when tensioner roller replacement is necessary:
1. Excessive Belt Slack:
If the tensioner roller has worn out or lost its tensioning capability, it may result in excessive belt slack. Excessive belt slack can be observed visually by noticing sagging or drooping of the belt between pulleys. To diagnose this, visually inspect the belt and check for any significant slack or looseness. Excessive belt slack indicates that the tensioner roller is no longer providing adequate tension and should be replaced.
2. Belt Misalignment:
A failing tensioner roller can lead to belt misalignment, causing the belt to deviate from its intended path. Belt misalignment can be diagnosed by observing the belt’s position in relation to the pulleys. Signs of misalignment include the belt running off-center, making contact with adjacent components, or riding too close to the edge of the pulleys. If belt misalignment is detected, it is essential to inspect the tensioner roller for any wear, damage, or misalignment and replace it if necessary.
3. Unusual Noise or Vibration:
A failing tensioner roller can generate unusual noise or vibrations in the belt drive system. This can be caused by worn bearings, misalignment, or other internal damages within the tensioner roller. To diagnose this, carefully listen for any abnormal noises such as grinding, squeaking, or rattling coming from the tensioner roller area while the system is in operation. Additionally, pay attention to any excessive vibrations or shaking of the belt drive system. If unusual noise or vibration is present, it indicates a potential issue with the tensioner roller that may require replacement.
4. Visible Wear or Damage:
Inspecting the tensioner roller for visible wear or damage is an essential diagnostic method. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks, grooves, or uneven surface texture on the roller. Additionally, check for any signs of physical damage, such as dents or deformation. If the tensioner roller shows visible signs of wear or damage, it is an indication that it has reached the end of its service life and should be replaced.
5. Inadequate Tension:
If the tensioner roller fails to provide sufficient tension to the belt, it can lead to belt slippage, reduced power transfer, and decreased overall system performance. Insufficient tension can be diagnosed by observing belt slippage or excessive wear on the belt’s contact surfaces with the pulleys. Check the tension of the belt by applying moderate pressure to it with your finger. If the belt deflects significantly, it indicates inadequate tension provided by the tensioner roller. In such cases, the tensioner roller should be inspected and replaced if necessary.
6. Maintenance Schedule:
Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is an important aspect of diagnosing the need for tensioner roller replacement. Manufacturers often provide guidelines on the expected service life or recommended replacement intervals for tensioner rollers. It is essential to consult the maintenance schedule specific to the belt drive system and adhere to the recommended replacement intervals. This proactive approach helps prevent potential failures or performance issues associated with worn or damaged tensioner rollers.
7. Professional Inspection:
In complex or critical applications, it may be necessary to seek the expertise of a professional technician or engineer to diagnose the need for tensioner roller replacement. Professionals can perform comprehensive inspections using specialized tools and techniques, such as laser alignment or vibration analysis, to assess the condition of the tensioner roller accurately. They can identify any underlying issues or potential risks and provide recommendations for replacement based on the specific requirements of the belt drive system.
In summary, the signs that indicate a need for tensioner roller replacement include excessive belt slack, belt misalignment, unusual noise or vibration, visible wear or damage, inadequate tension, adherence to maintenance schedules, and professional inspections. By regularly inspecting the tensioner roller and promptly addressing any signs of wear or malfunction, operators can ensure the reliable and efficient operation of their belt drive systems.

Can tensioner rollers be customized for specific industries or machinery configurations?
Yes, tensioner rollers can be customized to suit specific industries or machinery configurations. The ability to customize tensioner rollers allows for optimal performance and compatibility with unique requirements. Here are some aspects to consider:
1. Size and Dimensions:
Tensioner rollers can be customized to meet specific size and dimensional requirements. This includes variations in diameter, width, and overall dimensions to ensure proper fit and alignment within the machinery or system. Custom sizing ensures that the tensioner roller integrates seamlessly with other components and accommodates the available space constraints.
2. Load Capacity:
Industries and machinery configurations can have varying load capacities based on the application’s demands. Customized tensioner rollers can be designed to handle specific load requirements, ensuring they can support the intended loads without compromising performance or longevity. This customization helps prevent premature wear or failure due to excessive loads.
3. Material Selection:
Tensioner rollers can be customized by selecting materials that are best suited for the specific industry or machinery configuration. Different materials offer varying properties such as strength, durability, resistance to heat, chemicals, or abrasion. Customization allows for the selection of materials that can withstand the unique environmental conditions and operational demands of the application.
4. Coatings and Surface Treatments:
Customization of tensioner rollers also includes the application of coatings or surface treatments to enhance their performance and durability. Coatings such as ceramic, rubber, or Teflon can provide increased wear resistance, reduce friction, and improve the lifespan of the tensioner roller. Customized surface treatments can enhance corrosion resistance or provide specific surface properties required for the application.
5. Mounting and Adjustment Mechanisms:
Tensioner rollers can be customized to incorporate specific mounting and adjustment mechanisms based on the machinery or system configuration. This includes options for adjustable mounting positions, tension adjustment features, or quick-release mechanisms for easy installation, maintenance, and tension adjustments. Customized mounting and adjustment mechanisms ensure optimal functionality and ease of use.
6. Special Features and Accessories:
Depending on the industry or machinery requirements, tensioner rollers can be customized with special features and accessories. These may include additional bearings, seals, or guards to enhance protection, improve performance, or meet specific safety standards. Customized tensioner rollers can also incorporate sensors or monitoring systems to enable condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.
7. Compliance with Industry Standards:
Customized tensioner rollers can be designed to comply with specific industry standards, regulations, or certifications. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, or food processing may have stringent requirements that need to be met. Customization ensures that tensioner rollers meet the necessary standards and provide reliable performance within the specified guidelines.
In summary, tensioner rollers can be customized to suit specific industries or machinery configurations. Customization allows for tailoring the size, load capacity, material selection, coatings, mounting mechanisms, special features, and compliance with industry standards. By customizing tensioner rollers, industries can ensure optimal performance, longevity, and compatibility with their unique requirements.
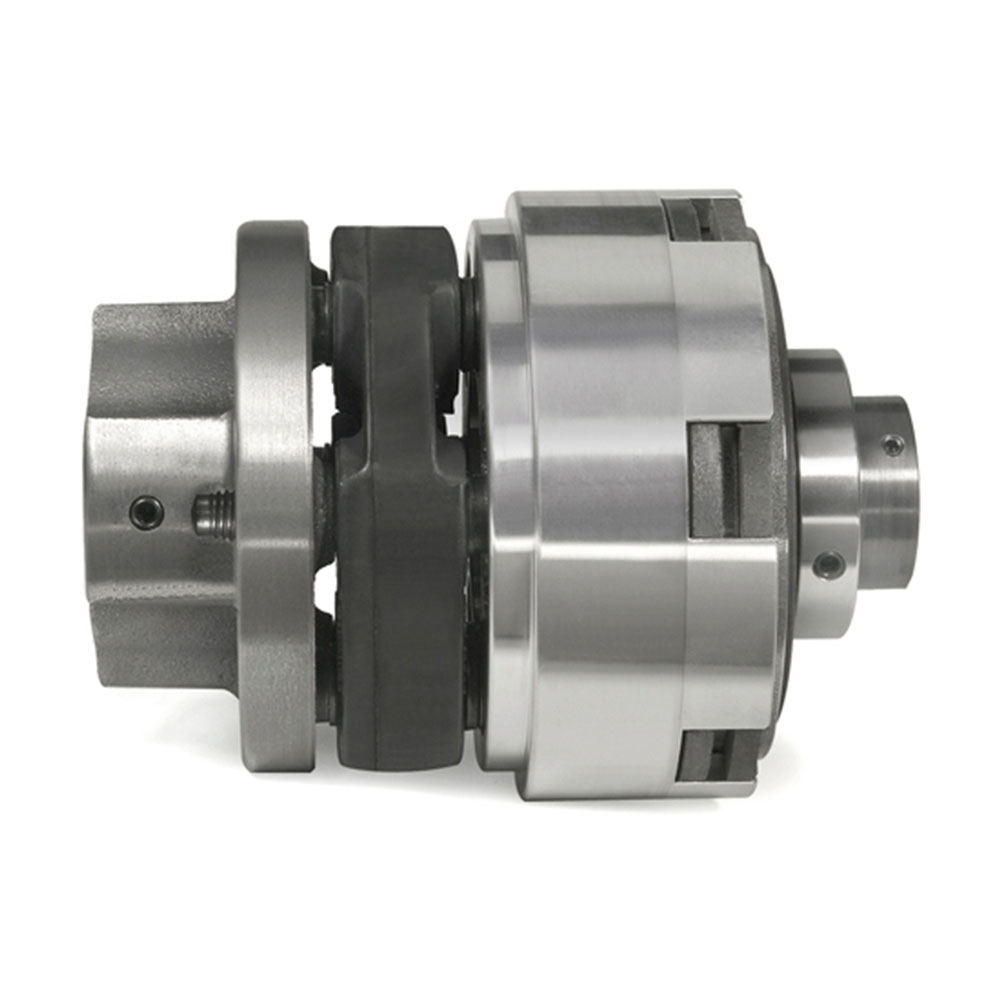

Are there specific applications where tensioner rollers are essential for proper belt operation?
Yes, there are specific applications where tensioner rollers are essential for proper belt operation. Tensioner rollers play a critical role in maintaining optimal belt performance and are particularly important in the following applications:
1. High-Torque Systems:
In applications where high torque is involved, such as heavy machinery or industrial equipment, tensioner rollers are essential for proper belt operation. High torque can exert significant forces on belts, leading to increased tension and potential belt slippage. Tensioner rollers help maintain the correct tension, ensuring secure power transmission and preventing belt failures or damage in these demanding applications.
2. Variable-Speed Drives:
In applications where variable speed is required, such as in automotive engines or industrial machinery, tensioner rollers are crucial for proper belt operation. Variable-speed drives often rely on belt drive systems to adjust the speed of driven components. Tensioner rollers help maintain consistent belt tension, allowing for smooth speed adjustments and reliable operation across different speed ranges.
3. Long Belt Lengths:
In applications that involve long belt lengths, such as conveyor systems or large-scale manufacturing equipment, tensioner rollers are essential. Long belts are prone to stretching and sagging, which can cause misalignment and decreased power transmission efficiency. Tensioner rollers help counteract belt stretch, maintaining the proper tension and alignment over extended distances, ensuring optimal belt operation in these applications.
4. High-Speed Applications:
For high-speed applications, such as in racing vehicles, aircraft engines, or industrial machinery with rapid rotational speeds, tensioner rollers are vital for proper belt operation. High speeds can generate significant centrifugal forces that impact belt tension and introduce vibrations. Tensioner rollers help maintain the necessary tension, absorb vibrations, and prevent belt slippage, ensuring reliable and efficient power transmission at high speeds.
5. Challenging Environments:
In applications exposed to challenging environments, such as off-road vehicles, construction machinery, or marine equipment, tensioner rollers are essential for proper belt operation. Harsh conditions, including dust, dirt, moisture, and temperature variations, can accelerate belt wear and affect performance. Tensioner rollers help maintain optimal belt tension, reducing the risk of belt damage and ensuring reliable operation in these demanding environments.
6. Multi-Belt Systems:
Applications that utilize multi-belt systems, such as heavy-duty trucks, agricultural machinery, or printing presses, require tensioner rollers for proper belt operation. Multi-belt systems often have several belts driving different components or accessories. Tensioner rollers help maintain individual belt tension and overall system balance, preventing belt slippage, ensuring consistent power transmission, and optimizing the performance of the entire system.
7. High-Precision Applications:
In applications that demand high precision, such as CNC machines, robotics, or medical equipment, tensioner rollers are essential for proper belt operation. These applications require accurate and reliable power transmission to ensure precise movements or operations. Tensioner rollers help maintain the correct belt tension, minimizing variations and ensuring consistent performance in high-precision operations.
In summary, tensioner rollers are essential for proper belt operation in various specific applications, including high-torque systems, variable-speed drives, long belt lengths, high-speed applications, challenging environments, multi-belt systems, and high-precision applications. Incorporating tensioner rollers in these applications is crucial for maintaining optimal belt performance, preventing belt failures, and ensuring reliable and efficient operation of the belt drive systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-09
China Best Sales Gears and Chain Drive Stainless Steel Industrial Driven Conveyor Roller Chain Tensioner Idler Round Link Metric Fabricated Steel Motorcycle Sprockets with Free Design Custom
Product Description
gears and chain drive stainless steel industrial driven conveyor roller chain tensioner idler round link metric Fabricated Steel motorcycle sprockets
Manufacturer of Sprocket, Chain sprockets, wheel and sprocket, drive sprocket, sprocket wheel, taper lock sprocket, gear sprocket, idle sprocket, motorcycle sprocket and stainless steel sprocket, can interchange and replace with martin size sprocket, jt size sprockets, did size chain sprocket and so on.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Neoprene Timing Belts
The timing belt is an important component of an automobile engine. Made of special materials, this belt coordinates the rotational motion of the crankshaft with the camshaft. The coordinated precision is essential for sustainable combustion, and ensures that the valves in the combustion chamber open at the right times. Timing belts determine the engine’s pace, so it is essential that they perform at high synchronicity and strong enough to operate in extreme conditions.
Fabric timing belt
A timing belt is made of a yarn that has been crimped and woven into a mating surface, called the engagement surface. This yarn, known as the warp, must be able to stretch from a substantially flat state along irregularities in the mold. It must be flexible enough to stretch by several tens of percent under low load conditions. The warp yarn of a timing belt is made of synthetic fiber and is crimped into the right shape to be stretched easily.
This fabric can be used without thickening the base cloth. It can contain a large number of warp threads, and its wear resistance can be enhanced over time. The timing belt of the present invention does not crack or wear out after a long time of use. The base cloth does not wear out, which allows the timing belt to last for a long time. This makes it an extremely durable material. To learn more, read on.
The teeth of a timing belt are made of tough rubber and a nylon fabric facing. The fabric is coated with a plastic compound that gives it its shape and covers the cord. The materials used to make these belts vary, but all are strong and durable. They are also suitable for high-load applications. In addition to nylon timing belts, strongbelt premiums are also available. In addition to nylon and neoprene timing belts, they are also compatible with RPP and HTD pulleys.
The teeth of timing belts are made of high-strength polychloroprene elastomer. The teeth are made of a special manufacturing process that ensures good adhesion. The facing fabric is made of low-elongation glass cord and is covered by a polyamide fabric that has a low coefficient of friction. If you need an exact fit, you can buy a high-quality belt from TransDev.
Neoprene timing belt
When it comes to dependable drive belts, neoprene is hard to beat. It’s widely used in insulated clothing and weather stripping, and has been a key component in the development of timing belts since the late 1970s. And because it’s so hardy, neoprene timing belts are incredibly reliable. Here are a few reasons why. Neoprene is the most durable synthetic material for timing belts, and these 3 reasons should not discourage you from purchasing a new neoprene timing belt.
Neoprene timing belts are made of a high-quality chloroprene compound with a hardness of 74 Shore A. The high-strength glass fiber strands in the belt’s body transmit high power while enhancing its flexural strength. In addition, it’s covered with a high-strength polyamide fabric to reduce friction and protect contact surfaces from wear and tear.
Unlike neoprene, polyurethane synchronous belts are resistant to temperature and abrasion. Polyurethane timing belts are resistant to acids and chlorides, and exhibit excellent abrasion resistance. A neoprene belt can be used in high-speed applications, and can withstand extreme temperatures. However, the resistance of polyurethane to abrasion is not as good as that of neoprene.
The 2 most common types of timing belts are rubber and urethane. Rubber is the least expensive and quietest, and is the least flexible of the two. Neoprene is also highly elastic and does not retain its shape when it’s stretched, making it a popular choice for applications in manufacturing, agriculture, and robotics. They are also great for applications where precision and motion control are important. These properties make timing belts extremely effective in leading the industry toward its goals.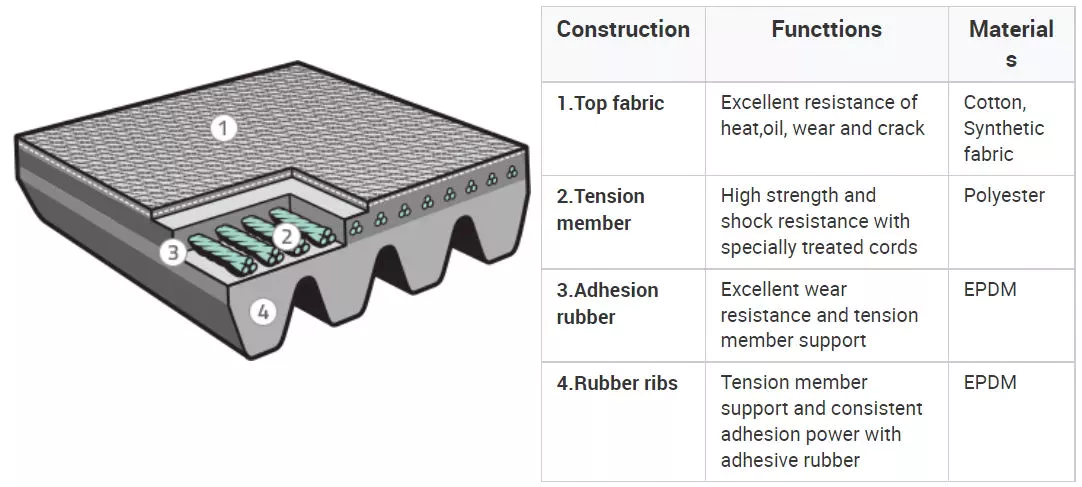
Chain timing belt
Traditionally, a vehicle’s timing system consists of a timing belt or chain. These components keep the engine’s intake and exhaust valves in the proper order. When these components go bad, it can ruin the engine in seconds. But there are advantages and disadvantages to each of them. Read on to learn about the pros and cons of each type of timing system. Here are some examples. Chain: A timing belt is generally made of reinforced rubber.
Chain: A timing chain is generally found in heavy-duty vehicles with higher torque. This type of timing belt is also found on many cars and SUVs with 4 cylinder engines that do not require a lot of torque. Unlike timing belts, timing chains are more durable and will last longer than their rubber counterparts. But there are certain things to keep in mind when replacing a timing belt. Make sure to change the oil regularly to avoid premature wear.
Chain: A chain is easier to maintain than a timing belt. It does not change length in response to temperature. And it requires a smaller tensioner. However, this also means that the timing belt is more prone to breaking. It can jump out of place if oil is flowing along it, causing an engine malfunction. If this happens, you’ll have to replace the entire timing belt and the engine will not work correctly. That’s why replacing a chain is so important.
A timing belt is a critical part of an engine. A failed timing belt can cause catastrophic engine damage. It can slip and break, colliding with the piston and valves. Fortunately, there are a variety of ways to check your timing belt. But a good rule of thumb is to replace it as soon as possible. You’ll also need to remove the front engine cover and any other components that may be in the way. In some cases, the engine might even have to be moved.
Trapezoid shaped teeth
In terms of tooth profile, there are 2 main types of timing belts: the curvilinear and trapezoidal types. Curvilinear timing belts are more rounded and less likely to result in excessive tension loss. These types of timing belts are also more prone to backlash and reduce accuracy. Here’s how they differ from each other. These 2 types of belts share similarities but differ in important ways.
Older timing belts generally have trapezoidal-shaped teeth, but newer types use curved teeth. Curved teeth are less prone to wear out quickly and last longer than straight ones. The trapezoidal teeth also tend to wear out more quickly at higher speeds. As a result, they’re only suitable for cars that get very little use. If you’re planning on using your timing belt frequently, you may want to choose a new 1 with curved teeth.
Curvilinear teeth are designed to alleviate the stress concentrations caused by trapezoidal tooth profiles. They also have a greater depth and reduce ratcheting. In addition to their efficiency, curvilinear timing belts are quieter than their trapezoidal counterparts. And they’re a little bit more expensive than their trapezoidal counterparts. So, what’s the difference between these 2 types of teeth?
Timing belts have a tendency to favor the tracking of an “S”-shaped twist. As a result, a trapezoid-shaped timing belt is more likely to keep the engine in sync. A good quality timing belt will help you achieve this. If you don’t, consider replacing your timing belt with a metric-styled one. That way, you’ll get the best performance out of your belt.
Other types of timing belts
Timing belts are essential for operating your vehicle’s engine. These belts connect the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft. The belts synchronize the timing of the engine’s valves and pistons to prevent damage. Previously, the belt was referred to as the “gilmer drive belt.”
There are 3 basic designs for timing belts. Some are shaped like a trapezoid, while others have a curvy tooth shape. Timing belts with this tooth design are generally more efficient for force transmission, although they suffer from backlash. These teeth also wear quickly at high speeds, which can make them prone to noise. In order to solve these issues, manufacturers now offer belts with curved teeth.
Another popular type is polyurethane. These are resistant to oil and high temperatures, and are energy-efficient solutions. Polyurethane timing belts offer increased elasticity and load capacity, which are important for optimal torque production. These belts are favored by a variety of industries because of their ease of cleaning and maintenance. They can be used for power transmission systems, as well as in roller conveyor systems. However, fabric timing belts are best used when acceleration forces are high.
Other types of timing belts are not always as durable. V-Belts have teeth-like structures on their surfaces and work under constant speed. They are typically a lighter option, but have similar disadvantages. They are more expensive than chains and lack the flexibility of customizing. Unlike chains, timing belts are sold in predetermined length loops. Their pitch is easily identified. It is a key indicator of whether or not they are suitable for a specific application.


China high quality Aftermarket Excavator Undercarriage Parts PC1250-6 Idler Track Roller Track Link Chain Assembly with 50L with high quality
Product Description
Professional Excavator&Bulldozer Aftermarket Undercarriage Parts Factory
Factory Supplying Directly, Super Quality with Competitive Price!
Product Features:
| Product Name: | Komatsu PC600 PC650 PC700 PC850 PC1000 PC1100 PC1250 PC2000 Excavator Undercarriage Parts Track Link Assy Track Chain with Shoe Assembly Track Group |
| Technical: | Forging/Casting |
| Surface Hardness: | HRC52-58, Deepth:8mm-12mm |
| Colors: | Yellow |
| Finishing: | Smooth |
| Applicable Industries: | Machinery Repair Shops, Construction works |
| Material: | 35MnB |
| Related Products: | Track Link, Track Pad, Track Roller, Idler. Sprockets, Carrier Roller, Tensioner for Excavators And Dozers |
Choose XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.N Undercarriage Parts Factory
Better Quality, Longer Using Life, Good Price
Confirming Dimensions With Us Before Ordering
Make Sure the Parts Matching with Your Machine
XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.N Excavator&Bulldozer Undercarriage Parts&Components Including:
- Track Chain With Track Shoe Assembly
- Segments for Heavy Duty Excavator and Bulldozer
- Drive Sprockets
- Track Roller
- Carriaer Roller
- Idler
- Tensioner Spring
- Bolts&Nuts for All Part
Related Models:
| THE MODELS FOR EXCAVATOR/BULLDOZER | ||||||||
| FOR HITACHI | ||||||||
| EX40-1 | EX40-2 | EX55 | EX60 | EX60-2 | EX60-3 | EX60-5 | EX70 | EX75 |
| EX100 | EX110 | EX120 | EX120-1 | EX120-2 | EX120-3 | EX120-5 | EX130-1 | EX200-1 |
| EX200-2 | EX200-3 | EX200-5 | EX220-3 | EX220-5 | EX270 | EX300 | EX300-1 | EX300-2 |
| EX300-3 | EX300-5 | EX300A | EX330 | EX370 | EX400-1 | EX400-2 | EX400-3 | EX400-5 |
| EX450 | ZAX30 | ZAX55 | ZAX200 | ZAX200-2 | ZAX330 | ZAX450-1 | ZAX450-3 | ZAX450-5 |
| ZX110 | ZX120 | ZX200 | ZX200-1 | ZX200-3 | ZX200-5G | ZX200LC-3 | ZX210 | ZX210-3 |
| ZX210-5 | ZX225 | ZX240 | ZX250 | ZX270 | ZX300 | ZX330 | ZX330C | ZX350 |
| ZX450 | ZX450LC | ZX500 | ZX500LC | ZX520 | ZX670 | ZX690 | ZX870 | ZX130 |
| ZX170 | ZX170LC | ZX195 | ZX260 | ZX360 | ZX360LC | ZX400 | ZX470 | ZX490 |
| FOR KOMATSU(EXCAVATOR) | ||||||||
| PC20-7 | PC30 | PC30-3 | PC30-5 | PC30-6 | PC40-7 | PC45 | PC45-2 | PC55 |
| PC120-6 | PC130 | PC130-7 | PC200 | PC200-1 | PC200-3 | PC200-5 | PC200-6 | PC200-7 |
| PC200-8 | PC210-6 | PC220-1 | PC220-3 | PC220-6 | PC220-7 | PC220-8 | PC270-7 | PC202B |
| PC220LC-6 | PC220LC-8 | PC240 | PC300 | PC300-3 | PC300-5 | PC300-6 | PC300-7 | PC300-7K |
| PC300LC-7 | PC350-6/7 | PC400 | PC400-3 | PC400-5 | PC400-6 | PC400LC-7 | PC450-6 | PC450-7 |
| PC600 | PC650 | PC750 | PC800 | PC1100 | PC1250 | PC2000 | PC360 | PC460 |
| FOR KOMATSU(BULLDOZER) | ||||||||
| D20 | D31 | D50 | D60 | D61 | D61PX | D65A | D65P | D64P-12 |
| D80 | D85 | D155 | D275 | D355 | D85PX | D85EX | D65EX | D65PX |
| D65E | D68 | D68ESS | D75 | D75S | D85ESS | D155 | D155A | D155AX |
| D275 | D275AX | D355 | D475 | |||||
| FOR CATERPILLAR(EXCAVATOR) | ||||||||
| E200B | E200-5 | E320D | E215 | E320DL | E324D | E324DL | E329DL | E300L |
| E320S | E320 | E320DL | E240 | E120-1 | E311 | E312B | E320BL | E345 |
| E324 | E140 | E300B | E330C | E120 | E70 | E322C | E322B | E325 |
| E325L | E330 | E450 | CAT225 | CAT312B | CAT315 | CAT320 | CAT320C | CAT320BL |
| CAT330 | CAT322 | CAT245 | CAT325 | CAT320L | CAT973 | CAT939C | CAT963C | CAT313 |
| CAT323 | CAT318 | CAT326 | CAT328 | CAT329 | CAT336 | CAT340 | CAT345 | CAT349 |
| FOR CATERPILLAR(BULLDOZER) | ||||||||
| D3 | D3B | D3C | D3D | D4 | D4C | D4D | D4E | D4H |
| D5 | D5B | D5C | D5D | D5H | D5M | D6 | D6C | D6D |
| D6H | D6M | D6R | D6G | D6N | D7 | D7C | D7D | D7E |
| D7F | D7G | D7H | D7R | D8 | D8R | D8N | D8H | D8T |
| D8L | D8K | D8G | D8M | D9 | D9L | D9N | D9R | D9T |
| D10 | D10R | D10N | D10T | D11 | D11R | D11N | ||
| FOR KOBELCO | ||||||||
| SK120-6 | SK120-5 | SK210-8 | SK210LC-8 | SK220 | SK220-1 | SK220-3 | SK220-5/6 | SK200 |
| SK200 | SK200 | SK200-3 | SK200-6 | SK200-8 | SK200-5/6 | SK60 | SK290 | SK100 |
| SK230 | SK250 | SK250-8 | SK260LC-8 | SK300 | SK300-2 | SK300-4 | SK310 | SK320 |
| SK330-8 | SK330 | SK350LC-8 | SK235SR | SK450 | SK480 | SK30-6 | ||
| FOR SUMITOMO | ||||||||
| SH120 | SH120-3 | SH200 | SH210-5 | SH200 | SH220-3 | SH220-5/7 | SH290-3 | SH350-5/7 |
| SH220 | SH280 | SH290-7 | SH260 | SH300 | SH300-3 | SH300-5 | SH350 | SH60 |
| FOR VOLVO | ||||||||
| EC160C | EC160D | EC180B | EC180C | EC180D | EC210 | EC210 | EC210B | EC240B |
| EC290 | EC290B | EC240 | EC55 | EC360 | EC360B | EC380D | EC460 | EC460B |
| EC460C | EC700 | EC140 | EC140B | EC160B | EC350 | EC350DL | EC480 | EC340 |
| FOR LIEBHERR | ||||||||
| R914 | R924 | R934 | R944 | R916 | R926 | R936 | R954 | R966 |
| R974 | R984 | |||||||
| FOR KUBOTA | ||||||||
| JH60-7 | JH115 | JH135 | JH161 | JH185 | ||||
| FOR DAEWOO | ||||||||
| DH200 | DH220-3 | DH220 | DH220S | DH280-2 | DH280-3 | DH55 | DH258 | DH130 |
| DH370 | DH80 | DH500 | DH450 | DH225 | DH150 | DH330 | DH400 | DH580 |
| FOR HYUNDAI | ||||||||
| R60-5 | R60-7 | R80-7 | R200 | R200-3 | R210 | R210-1 | R210-9 | R210LC |
| R210LC-7 | R225 | R225-3 | R225-7 | R250 | R250-7 | R290 | R290LC | R290LC-7 |
| R320 | R360 | R954 | R205 | R210-5 | R215 | R230 | R235 | R275 |
| R300 | R385 | R485 | ||||||
| FOR KATO | ||||||||
| HD512 | HD1430 | HD512III | HD820III | HD820R | HD1430III | HD700VI | HD1250VII | HD250SE |
| HD400SE | HD500SE | HD1880 | ||||||
| FOR DOOSAN | ||||||||
| DX225 | DX225LC | DX258 | DX300 | DX300LCA | DX420 | DX430 | DX140 | DX150 |
| DX220 | DX250 | DX255 | DX260 | DX370 | DX480 | DX520 | ||
| FOR SHXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.I | ||||||||
| SD13-2 | DH16J2XL | DH16J2LGP | SD16 | SD22 | SD32 | |||
| FOR CASE | ||||||||
| CX210 | CX210B | CX210C | CX210D | CX210LC | CX225 | CX235 | CX235C | CX240 |
| CX240C | CX245 | CX250 | CX250C | CX300 | CX300C | CX330 | CX330C | CX350 |
| CX350C | CX460 | CX460LC | CX470 | CX470C | CX490 | CX490D | CX700 | CX700B |
| CX750 | CX750D | |||||||
| FOR JCB | ||||||||
| JS200 | JS200SC | JS210 | JS210SC | JS220 | JS220LC | JS230 | JS230LC | JS240 |
| JS240LC | JS290 | JS290LC | JS300 | JS300LC | JS330 | JS330LC | ||
| FOR XCMG | ||||||||
| XE55DA | XE60DA | XE65DA | XE75DA | XE80C | XE80D | XE85C | XE85D | XE135D |
| XE155DK | XE150D | XE155D | XE200DA | XE200D | XE200C | XE205DA | XE215DA | XE215C |
| XE215D | XE215HB | XE225DK | XE230C | XE245DK | XE240D | XE260C | XE265C | XE270DK |
| XE305D | XE335DK | XE335C | XE370D | XE370DK | XE370CA | XE370C | XE380DK | XE470D |
| XE490DK | XE490CK | XE500HB | XE520DK | XE550DK | XE750D | XE750G | XE950D | XE950G |
| XE950DA | XE55 | XE60 | XE65 | XE75 | XE80 | XE85 | XE135 | XE150 |
| XE155 | XE200 | XE205 | XE215 | XE225 | XD230 | XE240 | XE245 | XE260 |
| XE265 | XE270 | XE305 | XE335 | XE370 | XE380 | XE470 | XE490 | XE500 |
| XE520 | XE550 | XE750 | XE950 | |||||
| FOR MITSUBISHI | ||||||||
| MS30 | MS110 | MS110-3 | MS110-5 | MS110-8 | MS180 | |||
| FOR SAMSUNG | ||||||||
| SE210 | SE280 | SE320 | ||||||
| FOR IHI | ||||||||
| IHI35 | IHI50 | IHI55 | IHI60 | IHI75 | ||||
| FOR YMMA | ||||||||
| YM15 | YM30 | YM35 | YM55 | YM65 | YM85 | |||
| FOR LIUGONG | ||||||||
| LG906C | LG907 | LG200 | LG220 | LG925 | LG934 | |||
Packing&Shipping
FAQ
1. You are a trader or a manufacture?
We are an industry and trade integration business.
2. How can I be sure the part will fit my excavator/bulldozer?
Give us correct model number/machine serial number/ any numbers on the parts itself. Or measure the parts give us dimension or drawing.
3. How about the payment terms?
We usually accept T/T(Wire Transfer). other terms also could be negotiated.
4. What is your minimum order?
It depends on what you are buying. Normally, 1 pcs also can be suppllied.
5. What is your delivery time?
FOB HangZhou or any Chinese port : 20 days . If there are any parts in stock , our delivery time is only 1-5 days.
6. What about Quality Control?
We have a perfect QC system for the perfect products. A team who will detect the product quality and specification piece carefully, monitoring every production process until packing is complete, to ensure product safety into container.
Contact Us:
| Melon Lin —————- Sales Manager ZheJiang XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.N MACHINERY CO., LTD. |
Tips For Replacing a Belt Tensioner
When replacing a serpentine belt or automatic tensioner, you will need a special tool. This tool has a long, flat extension handle that allows you to place a socket onto the bolt and flats on the tensioner arm. The following are some tips to follow when replacing the belt or tensioner on your vehicle. To replace your belt or tensioner, you should start by checking the tensioner’s lubrication.
Serpentine belt
If you notice that the power steering or air conditioning are not working, you should check the serpentine belt tensioner. A malfunctioning serpentine belt tensioner can lead to a host of other issues. The belt may stretch, which can be caused by several factors. Over time, serpentine belt tensioners can also get worn down. Additionally, they can have a variety of other problems, including rust or dirt in the housing.
You can replace your serpentine belt by following the instructions found on your vehicle’s manual. Some tensioners attach to the engine via a single bolt. To remove and replace the belt, remove the old unit and the retaining bolt. Locate the locking pin in the engine and place the new tensioner over it. Use a torque wrench or hand tool to tighten the bolts. When installing the new tensioner, be sure to line up the mounting bolt holes with the mounting bolts. Once the tensioner is installed, test the tension by ensuring that the gauge is above the ribs. If it slides down, it is time to replace the tensioner.
Before you begin the process of replacing your serpentine belt, be sure to park your vehicle in a level area. Turn off the engine and chock both rear wheels before starting the process. Using a diagram from your vehicle’s repair manual can make the process easier, especially if you are a beginner. You can draw it in your hand, or refer to a repair manual to find out the exact location of the tensioner pulley.
If you notice that the belt is slipping or squealing while driving, it may be time to replace the serpentine belt tensioner. A worn-out belt can cause the belt to slip and can cause power steering, air conditioning, and alternator malfunctions. You should also check the belt tensioner regularly. The motor may stall or make a loud noise. These are all signs of worn-out serpentine belt.
A serpentine belt uses less space in the engine than a V-belt. It also provides more tension for the serpentine belt, which prevents it from running hot and squealing. Serpentine belts are manufactured to last for several hundred thousand miles. They are a must-have item for your car! So be sure to keep it maintained and properly adjusted! Then, you can be sure to have your car running smoothly and safely.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should replace your serpentine belt tensioner. A serpentine belt tensioner is a simple self-10sioning device that is mounted on the front of the engine. These devices are usually easy to replace and are not complicated to install. You can find 1 at any parts store or online. When the time comes to replace your serpentine belt, don’t hesitate to get the parts you need from a local auto part store.
Idler pulley
The idler pulley and the belt tensioner are essential components of your car’s drivetrain. If any 1 of them fails, all of them must be replaced. This is because they were manufactured at the same time and most likely have the same number of miles on them. As a result, they can all fail within a few thousand miles of each other. Here are some of the symptoms that you should look for when inspecting your idler pulley or belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys are a common part of most cars. They play a vital role in the operation of the belt system by directing the belt’s path and providing additional contact with the pulley. The idler pulley is also responsible for turning the cooling fan in an air-cooled Corvair engine. Because of these functions, idler pulleys are often replaced with idlers that differ in size.
Idler pulleys are small, 2 to 4 inches in diameter and mounted on the front of the engine block. Their purpose is to create a constant amount of tension on the drive belt. When the idler pulley is worn out, the accessory drive belt may experience excessive vibration and squealing noises. You may wish to replace it as soon as possible. You can do so at AutoZone.
A worn or damaged idler pulley will require a replacement. The belt itself will not fall off the car unless the idler pulley is damaged. A squealing sound can be a sign of a broken spring. Alternatively, a mechanic can recommend a replacement based on the condition of the idler pulley. In most cases, idler pulleys are more durable than the belts and are therefore recommended for replacement.
You can also notice that the idler pulley is slipping or causing excessive noise. Its constant rotation wears the idler pulley and reduces the tension of the belt. This causes the belt to slip and may even tear off the engine. Ultimately, this could result in stalling. And if you notice the engine belt squealing or making excessive noises, you should consider replacing it.
An idler pulley for a belt tensioner are often confused. Though both of them are used in the same application, they differ in many ways. The tensioner is the 1 that receives pressure from the belts and moves them. The idler pulley is not attached to an adjustable bolt, and it can cause unusual noises. It might even make squealing or odd noises.
Spring tensioner
A spring belt tensioner is a solution to a loose belt. It features a strong torsion spring that reduces slack. These devices are designed to fit up to 6mm wide belts. They are highly reliable and durable. They are also suitable for applications where the engine speed is often fluctuating. Here’s how you can choose the best 1 for your vehicle. The spring in the tensioner should be in the proper position to keep the belt taut and free of slippage.
The RunRight tensioner is a durable, high-quality product that uses aluminum alloy. Its elastomeric inserts rely on highly elastic natural rubber for good shape memory and durability. Spring tensioners are easy to install and maintain. They are designed for both axial and helical drives. They feature detailed technical drawings and 3-D models to help you determine the best 1 for your application. To choose a spring tensioner, visit our website.
A worn bushing in the tensioner pulley or a loose pivot arm can result in excessive noise, vibration, and premature belt failure. In addition, worn springs cannot maintain proper tension. Over time, they lose tension. The pulley arm itself can also become damaged, preventing it from rotating properly. If these problems occur, you’ll need to replace the spring tensioner. If you don’t see any signs of wear, check your mounting bracket and tensioner.
A worn pivot bushing can cause the tensioner arm to misalign, leading to excessive back and forth sway. It may also cause the tensioner to jam, which means the belt is too long or too short. If you notice excessive wobble, you should replace the spring tensioner. A faulty tensioner may also be causing excessive oscillation in the pulley. To determine if the spring tensioner is too weak or jammed, check the belt’s length by using a breaker bar or socket with a long handle ratchet.
When it’s time to replace your serpentine belt, don’t forget to replace the belt tensioner. The tensioner protects other components from premature failure. It is a relatively inexpensive repair. It should be replaced as part of a larger multi-ribbed belt. It also provides protection for other components of the drive system. In addition to its protection and performance, the tensioner is inexpensive and relatively easy to replace.
It’s vital to check the tensioner and idler pulleys to make sure the system is aligned properly. If they don’t align, the belt will slip and cause premature wear. Alternatively, the tensioner may have too much tension, overloading the shaft bearings and causing premature failure in other parts. You should also check the idler pulleys for noise as well, since these are engine-driven accessories.

