Product Description
Single Nylon Sheave Pulley/ Nylon Pulley Hook Cable Roller
1. Maximum suitable conductor LGJ720.
2. Dimension of block ( outside diameter*root diameter * sheave width) Φ916*Φ800*110(mm).
Cable roller introduction
Specifications of nylon cable pulleys
1)nylon pulleys could be used for releasing insulated wires and cables in transmission line.
2)very smoothly
3)kind: single wheel nylon pulleys, double wheels nylon pulleys, three wheels nylon pulleys
4)material:nylon wheels
Product Data
| Order number | Model | Number of sheave | Rated load (Kn) | Weight | Feature |
| 10151 | SHDN916 | 1 | 50 | 51 | MC nylon sheave |
| 10152 | SHSQN916 | 3 | 75 | 120 | |
| 10153 | SHWQN916 | 5 | 150 | 200 |
ONEREEL is specialized in the design and manufacture Steel Spools, Plastic Spools, Cable roller, Yarn Bobbin, aluminum spool , Cable Reel Stand, Sheave Pulley, Cable Conveyor, Hydraulic Puller Tensioner, Gin Poles, Cable Pulling Winch, Safety Tools, Wire Grip, Plastic Parts, and Pump in the industry since 1991. All of our customer spool and wire carrier are engineered and manufactured in our 120,000 square foot state-of-the-art manufacturing plant located in HangZhou, ZHangZhoug.
ONEREEL is specialized in the manufacture of reels for cables and electric wires, iron axles, disc spool for steel cables and various delivery reels. With strong technological capabilities and full series of production equipment. All of our products go through the dynamic and static balance tests. We have passed the quality system certification ISO9001:2000 to ensure the product quality. Following the standards of GB4004-83, JB/T8997, DIN46395 and DIN46397 in productions.
Hot Product
Our Customer
Packaging & Transportation
Authoritative Certificate
FAQ
Q1: Can I get samples?
A: According to spool model and material, we will advise.
Q2: How long is the sample LEAD TIME?
A: For existing samples, it takes 2-3 days. If no stock, we will advise lead time.
Q3: Can you develop new products?
A: Yes, we have new products developing ability and we are good at developing new mold.
Q4: How much is the freight charge?
A: It depends on spool package volume, if small quantity, volume and urgent goods,
we may advise FEDEX or other couriers’ charge for your check.
If volume bigger and by seaway suitable, we provide FOB or CIF price to you.
Q5: What format of the file do you need if I want my own design?
A: We have our own mound workshop and can provide spool or other plastic product developing and injection service.
Q6: How about your service?
A: We have pre-sale service, in-sale service and after-sale service. As “Customer First” is the most important principle of company operation.
You can freely help you out either Tech issue or Products requirements. Pls contact with us. Thanks. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Stringing Block |
|---|---|
| Certification: | CE, RoHS, CCC, ISO |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Samples: |
US$ 5.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Red
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
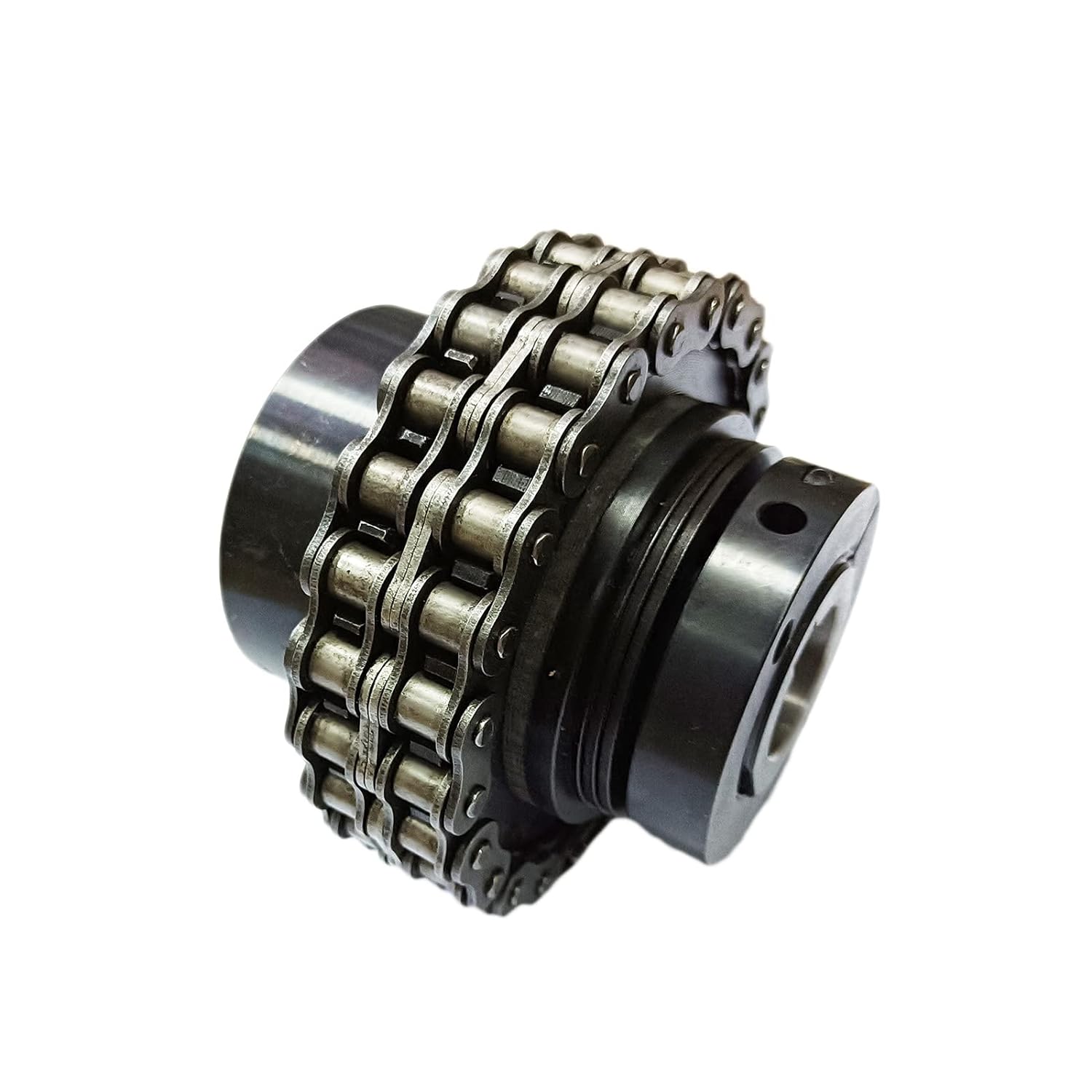

Are there aftermarket upgrades available for tensioner rollers to improve their functionality?
Yes, there are aftermarket upgrades available for tensioner rollers that can improve their functionality and performance. Aftermarket upgrades offer alternatives to the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) tensioner rollers, providing enhanced features, materials, and design. Here’s a detailed explanation of aftermarket upgrades for tensioner rollers:
1. High-Performance Materials:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers often utilize high-performance materials that offer improved durability, heat resistance, and wear characteristics compared to standard OEM rollers. These materials may include advanced polymers, reinforced composites, or specialty alloys. Upgrading to tensioner rollers with high-performance materials can enhance their functionality by increasing their lifespan and performance under demanding operating conditions.
2. Upgraded Bearing Systems:
Bearing systems in tensioner rollers can be upgraded with higher-quality bearings or specialized bearing designs. Improved bearing systems can offer smoother operation, reduced friction, and increased load-bearing capacity. Upgraded bearing systems contribute to improved functionality by reducing noise, vibration, and wear, and enhancing overall performance and reliability.
3. Damping Mechanisms:
Some aftermarket tensioner rollers feature enhanced damping mechanisms to reduce belt noise and vibration. These damping mechanisms can include rubberized coatings, silicone inserts, or advanced damping materials. Upgrading to tensioner rollers with improved damping capabilities can enhance functionality by providing a quieter and smoother operation, improving the overall driving experience.
4. Tension Adjustment Features:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers may offer additional features for tension adjustment. These features can include adjustable tension springs, mechanical or hydraulic tensioners, or built-in tension adjustment mechanisms. Upgraded tension adjustment features allow for fine-tuning of belt tension to meet specific performance requirements, optimizing functionality and performance under varying load and operating conditions.
5. Performance-Enhancing Designs:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers may incorporate performance-enhancing design elements. These designs can include optimized pulley profiles, improved belt contact surfaces, or modified geometries for better belt tracking. Performance-enhancing designs contribute to improved functionality by reducing belt slippage, improving power transfer efficiency, and minimizing wear on the belt and other components.
6. Enhanced Durability:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers may offer enhanced durability features to withstand demanding conditions. These features can include reinforced construction, corrosion-resistant coatings, or additional protection against contaminants. Upgrading to tensioner rollers with enhanced durability can enhance their functionality by reducing the risk of premature failure, extending their lifespan, and improving overall system reliability.
7. Compatibility and Fitment:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers are designed to be compatible with specific vehicle makes and models. They are engineered to match the original specifications and fitment requirements, ensuring proper installation and functionality. Upgrading to aftermarket tensioner rollers that are compatible with the vehicle’s belt system promotes optimal functionality and performance.
8. Manufacturer Reputation and Quality:
When considering aftermarket upgrades for tensioner rollers, it is important to choose reputable manufacturers known for their quality products. Selecting aftermarket tensioner rollers from trusted manufacturers ensures that the upgrades will provide the desired functionality and performance improvements, backed by reliable engineering and manufacturing processes.
In summary, aftermarket upgrades for tensioner rollers offer various enhancements to improve their functionality and performance. These upgrades can include high-performance materials, upgraded bearing systems, damping mechanisms, tension adjustment features, performance-enhancing designs, enhanced durability, and compatibility with specific vehicles. Choosing aftermarket upgrades from reputable manufacturers can provide reliable improvements to the functionality of tensioner rollers, contributing to enhanced belt system performance and overall vehicle drivability.
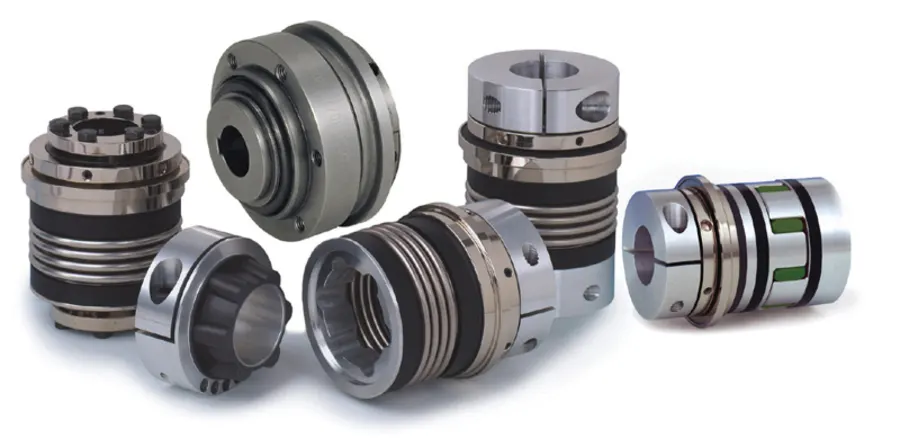

Can tensioner rollers be customized for specific industries or machinery configurations?
Yes, tensioner rollers can be customized to suit specific industries or machinery configurations. The ability to customize tensioner rollers allows for optimal performance and compatibility with unique requirements. Here are some aspects to consider:
1. Size and Dimensions:
Tensioner rollers can be customized to meet specific size and dimensional requirements. This includes variations in diameter, width, and overall dimensions to ensure proper fit and alignment within the machinery or system. Custom sizing ensures that the tensioner roller integrates seamlessly with other components and accommodates the available space constraints.
2. Load Capacity:
Industries and machinery configurations can have varying load capacities based on the application’s demands. Customized tensioner rollers can be designed to handle specific load requirements, ensuring they can support the intended loads without compromising performance or longevity. This customization helps prevent premature wear or failure due to excessive loads.
3. Material Selection:
Tensioner rollers can be customized by selecting materials that are best suited for the specific industry or machinery configuration. Different materials offer varying properties such as strength, durability, resistance to heat, chemicals, or abrasion. Customization allows for the selection of materials that can withstand the unique environmental conditions and operational demands of the application.
4. Coatings and Surface Treatments:
Customization of tensioner rollers also includes the application of coatings or surface treatments to enhance their performance and durability. Coatings such as ceramic, rubber, or Teflon can provide increased wear resistance, reduce friction, and improve the lifespan of the tensioner roller. Customized surface treatments can enhance corrosion resistance or provide specific surface properties required for the application.
5. Mounting and Adjustment Mechanisms:
Tensioner rollers can be customized to incorporate specific mounting and adjustment mechanisms based on the machinery or system configuration. This includes options for adjustable mounting positions, tension adjustment features, or quick-release mechanisms for easy installation, maintenance, and tension adjustments. Customized mounting and adjustment mechanisms ensure optimal functionality and ease of use.
6. Special Features and Accessories:
Depending on the industry or machinery requirements, tensioner rollers can be customized with special features and accessories. These may include additional bearings, seals, or guards to enhance protection, improve performance, or meet specific safety standards. Customized tensioner rollers can also incorporate sensors or monitoring systems to enable condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.
7. Compliance with Industry Standards:
Customized tensioner rollers can be designed to comply with specific industry standards, regulations, or certifications. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, or food processing may have stringent requirements that need to be met. Customization ensures that tensioner rollers meet the necessary standards and provide reliable performance within the specified guidelines.
In summary, tensioner rollers can be customized to suit specific industries or machinery configurations. Customization allows for tailoring the size, load capacity, material selection, coatings, mounting mechanisms, special features, and compliance with industry standards. By customizing tensioner rollers, industries can ensure optimal performance, longevity, and compatibility with their unique requirements.

What is a tensioner roller, and what role does it play in mechanical systems?
A tensioner roller, also known as a belt tensioner or idler pulley, is a component commonly used in mechanical systems to maintain proper tension in belts or chains. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of various systems that rely on the power transmission provided by belts or chains. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a tensioner roller is and the role it plays in mechanical systems:
1. Definition and Construction:
A tensioner roller is a pulley-like component that is typically mounted on a spring-loaded arm or bracket. It consists of a smooth or grooved surface that comes into contact with the belt or chain. The tensioner roller is designed to rotate freely on bearings or bushings, allowing it to accommodate the movement of the belt or chain and maintain the desired tension.
2. Tension Maintenance:
The primary role of a tensioner roller is to maintain the appropriate tension in belts or chains. Tension is crucial for the proper functioning of power transmission systems. If the tension is too loose, the belt or chain may slip, resulting in a loss of power transfer and potential damage to the system. On the other hand, excessive tension can cause increased wear on the belt or chain, as well as strain on other components. The tensioner roller applies the necessary force to keep the belt or chain properly tensioned, ensuring optimal power transmission efficiency and preventing premature wear or failure.
3. Compensation for Belt or Chain Stretch:
Over time, belts and chains can experience stretching due to normal wear and tear or changes in operating conditions. This stretching can lead to a decrease in tension and affect the performance of the mechanical system. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt or chain stretch by automatically adjusting their position to maintain the desired tension. The spring-loaded arm or bracket allows the tensioner roller to move and adapt to the changing length of the belt or chain, ensuring consistent tension throughout the system’s operation.
4. Noise and Vibration Dampening:
Tensioner rollers also contribute to reducing noise and vibration in mechanical systems. The smooth rotation of the tensioner roller on its bearings or bushings helps absorb and dampen the vibrations generated during the operation of the belt or chain. This reduces the overall noise level and improves the smoothness of the system’s operation, enhancing user comfort and minimizing potential damage caused by excessive vibrations.
5. Maintenance and Replacement:
Proper maintenance of tensioner rollers is essential to ensure their continued functionality. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If a tensioner roller is found to be worn, damaged, or no longer providing adequate tension, it should be promptly replaced to prevent further complications and maintain the optimal operation of the mechanical system.
6. Applications:
Tensioner rollers are used in a wide range of mechanical systems that rely on belts or chains for power transmission. They can be found in automotive engines, industrial machinery, HVAC systems, printing equipment, and many other applications. The specific design and size of tensioner rollers may vary depending on the requirements of the system in which they are used.
In summary, a tensioner roller is a crucial component in mechanical systems that rely on belts or chains for power transmission. It ensures the proper tension of the belt or chain, compensates for stretch, reduces noise and vibration, and contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of tensioner rollers are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues in mechanical systems.


editor by Dream 2024-04-22
China Professional Head Sheave/ Sheave Pulley/Lifting Equipment CZPT Wheel Device with Free Design Custom
Product Description
Head Sheave/ Sheave Pulley/Lifting Equipment Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Wheel Device
Introduction:
Mine hoist can be divided into 2 kinds; 1 kind is JKE series single rope mining hoist and the other is Multi-rope friction hoist.
This series mine hoist including 2m-5m single tubular and double tubular types, and can be used for mining hoist, personnel lifting and material and equipment descending from vertical shafts or inclined shafts of coal, metal and nonmetal ores.
JK mine hoist is mainly used in inclined roadways and wells of coal mines, metal mines and non-metal mines to hoist or lower personnel and materials.
Technical parameters:
| Model | Drum | Tension PF |
Tension Differe |
Rope Diameter |
Lift height (m) | Max Speed |
Reduce speed ratio |
Motor Speed |
||||||
| Number | Dia | Width | 1-layer | 2-layer | 3-layer |
|||||||||
| m | KN | mm | m | m/s | r/min | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.5/20 | 1 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 62 | 24 | 305 | 650 | 1571 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 1000 | |||
| JK-2×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/20 | 1.80 | 375 | 797 | 1246 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2/20 | 2.5 | 2.00 | 83 | 28 | 448 | 945 | 1475 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 750 | ||||
| JK-2.5×2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/20 | 2.30 | 525 | 1100 | 1712 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-3×2.2/20 | 3.0 | 2.20 | 135 | 36 | 458 | 966 | 1513 | 6.0 | 20.0 | |||||
| 2JK-2×1/11.2 | 2 | 2.0 | 1.00 | 62 | 40 | 24 | 182 | 406 | 652 | 7.0 | 11.2 | |||
| 2JK-2×1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/11.2 | 1.25 | 242 | 528 | 838 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.20 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 843 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.50 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 319 | 685 | 1080 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/11.2 | 3.0 | 135 | 90 | 36 | 289 | 624 | 994 | 10.5 | 11.2 | |||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/11.2 | 1.80 | 362 | 770 | 1217 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/11.2 | 3.5 | 1.70 | 170 | 115 | 40 | 349 | 746 | – | 12.6 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 2.10 | 450 | 950 | – | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/10 | 4.0 | 245 | 160 | 48 | 421 | 891 | – | 12.6 | 10.0 | 600 | ||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/11.2 | 11.2 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-5×2.3/10 | 5.0 | 2.30 | 280 | 180 | 52 | 533 | – | – | 12 | 10.0 | 500 | |||
| 2JK-5×2.3/11.2 | ||||||||||||||
Possible defects:
| Defect | Causes |
| Unfilled sections | Insufficient material Low pouring temperature |
| Porosity | Melt temperature is too high Non-uniform cooling rate Sand has low permeability |
| Hot tearing | Non-uniform cooling rate |
| Surface projections | Erosion of sand mold interior A crack in the sand mold Mold halves shift |
FAQ
Q: How about the quality of your products?
A: Our machines are manufactured strictly according to national and international standards, and we take a test on each equipment before delivery.
Q: How about the price?
A: We are manufactory, and we can give you lower price than those trade companies. Besides, customers from Made in China can get a discount.
Q: Do you provide after-sale service?
A: Yes. The warranty period of our machines is 1 year, and we have a professional after-sale team to promptly and thoroughly solve your problems.
Q: Do you provide equipment operation training?
A: Yes. We can send professional engineers to the working site for equipment installation, adjustment, and operation training. All of our engineers have passports.
What Is a V-Belt?
What is a v-belt? It is a rubber belt that is trapezium-shaped and has an elastomer core that holds the parts together. Its elastomer core is generally made of polyurethane and has good shock resistance and flexural strength. V-belts sometimes have 2 sections, 1 of which is a compression rubber and the other cushion rubber. They can be narrow or wide, depending on their use.
Classical V-belts replace leather belts
Classical V-belts are a popular choice among truck drivers because they are more durable. They are typically made of polymer or rubber, with fibers from other materials added for reinforcement. These belts are a good replacement for leather belts and offer many benefits. They are durable, offer excellent temperature and oil resistance, and are easy to use. If you’re considering replacing your current belt, consider buying a replacement belt made of the same material.
Most classical V-belts are used individually and come in A and B sizes. They are rarely used in single-belt drives. Buying several A or B belts instead of 1 C belt can save money. The narrow V-belts also provide higher power ratings. This is due to their narrow profile, which places more of the reinforcing cord under the sheave. Narrow V-belts are ideal for heavy duty applications.
When you’re replacing an existing V-belt, you’ll need to measure its top width and circumference. Once you’ve determined these parameters, you’ll be able to select the right replacement belt. Make sure to take measurements of the belt’s dimensions and top width before ordering. Using these measurements will help you determine the best size for your new belt. You’ll be able to tell whether you need a larger or smaller belt after measuring the top width and circumference.
If you’re looking to replace your leather belt with a belt made of synthetic material, a Classical V-belt may be the right choice. Classical V-belts are available in many materials and are more durable than leather. And because they are so versatile, they are the perfect replacement for your current belts. You’ll be glad you did. So, don’t be afraid to experiment with this type of belt. They’ll work well in any setting, including heavy equipment.
When buying a Classical V-belt, be sure to check the dimensions and type of belt you choose. These are available in notched or cogged designs. Notches are a great way to reduce bending stress. Notches also help dissipate heat from the belt, a major factor in premature belt failure. Notched V-belts are designed to balance a combination of flexibility and tensile cord support. They are spaced properly to minimize cracking and undercord damage.
Unlike leather belts, Classical V-belts are made of synthetic materials. They are easy to install, have a wide range of sizes, and come in light to heavy-duty varieties. The V-belt’s trapezoidal shape helps it track in the grooves of pulleys and prevents it from slipping while in use. It also helps in reducing power loss, since it’s easier to grip the pulleys than leather.
Narrow v-belts are more efficient
There are 5 basic types of V-belts. Their differences in cross-sectional size and power transmission make them superior to multiple single v-belts. The diagram below shows these types and how each differs from 1 another. The included angle of each belt is 40 degrees. The lower number indicates the more efficient version. Narrow V-belts are generally less expensive. Narrow v-belts are generally more efficient than wider belts.
There are several factors that influence a V-belt’s efficiency. Although the efficiency is high when a new belt is installed, the efficiency can drop to the low nineties. However, these belts are relatively resilient, and even with lower efficiency can function properly. Even if the efficiency of a V-belt is lower than it could be, it will still function. In fact, the higher the efficiency, the more energy it will save.
The first is the type of pulley. A narrow V-belt is more flexible than its wider counterpart. The belt pitch diameter is 32deg or 38deg. In addition, the belt can be cogged for added flexibility. In this way, the belt will not touch the bottom of the groove, but will only contact the inclined flanks. Without this wedge effect, the belt’s total friction force is higher. This means that it can transfer higher forces.
While a V-belt looks like a glorified rubber band, it has undergone tremendous technological development since it was first used in 1917. Synthetic rubber compounds and other cover materials have replaced rubber in the belt. New construction methods, tensile cord improvements, and cross-section profiles have resulted in a confusing variety of V-belts. Their differences, however, are based on the type of application for which they’re used.
Another type of V-belt is the raw edge variety. This type of belt is commonly used in manufacturing facilities. This type of belt requires less energy to operate. The raw edge also resists hardening. This is important since unmatched flexibility results in a smooth belt. Also, notched V-belts reduce vibration by 80%. Further, angular misalignment increases the risk of premature failure of a V-belt.
These belts differ in their overall design. While conventional V-belts are more common, narrow V-belts are more efficient and versatile. They are made of different types of rubber and reinforcements, which combine to create a trapezium-shaped cross-section. They can handle fractional loads and even 500 horsepower. Furthermore, their durability is largely dependent on their ability to withstand poor operating conditions.
Double-sided v-belts have unique features. These belts are used in applications with multiple pulleys. They can be operated clockwise or counter-clockwise. They can also be used to drive around multiple reverse bends. Further, they are more efficient and quieter than their counterparts. Finally, double-sided v-belts have 2 compression cores. The tension cord runs through both sections.
Double cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip
A double cogged v-belt is a hybrid of a traditional double versus a cogged vee-belt. These belts are useful for applications that require a large amount of flexibility without compromising durability. The double cogged design also allows the belt to follow a serpentine path. The varying dimensions of a double cogged v-belt depend on manufacturer standards.
A v-belt is measured by defining the centerline, the inside length of the v-belt, and the pitch line, which is the distance between the top and bottom sides of the trapezium. The width and height of a v-belt are defined by its cross-section. Each cross-section is given a different designation, including the width and height.
A standard V-belt is a v-belt with a fabric cover. It provides firmness in a smaller space and is less prone to belt whip when used in heavy-duty applications. Its slim profile and light gauge tensile cord make it suitable for many industrial applications. The standard length of a double cogged v-belt varies from 530 to 3,000 mm.
Single cogged v-belts are commonly used in manufacturing machines that operate in close proximity to 1 another. Single cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity and reduce belt whip. They are also ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as in mining or quarrying. Double cogged v-belts also increase lateral rigidity to minimize belt whip.
The elastomer core of a v-belt is surrounded by tension cords. These tension cords are embedded into the rubber compound, creating a composite structure that provides a high degree of shock resistance and flexural strength. The tension cords are often made of steel, polyester, or aramid fibers. This material makes it much stronger and more durable.
A double cogged v-belt is a highly rigid option for applications where lateral rigidity is an important concern. The double cogged design also increases lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip and enhances power transmission efficiency. Double cogged v-belts also offer positive slip-proof engagement. These belts are also easier to maintain, require less maintenance, and require no lubrication.


China Standard Jk Series Mining Hoist Winch Parts Head Sheave for Coal Mine with Best Sales
Product Description
Jk Series Mining Hoist Winch Parts for Coal Mine
Introduction:
Mine hoist can be divided into 2 kinds; 1 kind is JKE series single rope mining hoist and the other is Multi-rope friction hoist.
This series mine hoist including 2m-5m single tubular and double tubular types, and can be used for mining hoist, personnel lifting and material and equipment descending from vertical shafts or inclined shafts of coal, metal and nonmetal ores.
JK mine hoist is mainly used in inclined roadways and wells of coal mines, metal mines and non-metal mines to hoist or lower personnel and materials.
Technical parameters:
| Model | Drum | Tension PF |
Tension Differe |
Rope Diameter |
Lift height (m) | Max Speed |
Reduce speed ratio |
Motor Speed |
||||||
| Number | Dia | Width | 1-layer | 2-layer | 3-layer |
|||||||||
| m | KN | mm | m | m/s | r/min | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.5/20 | 1 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 62 | 24 | 305 | 650 | 1571 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 1000 | |||
| JK-2×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/20 | 1.80 | 375 | 797 | 1246 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2/20 | 2.5 | 2.00 | 83 | 28 | 448 | 945 | 1475 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 750 | ||||
| JK-2.5×2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/20 | 2.30 | 525 | 1100 | 1712 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-3×2.2/20 | 3.0 | 2.20 | 135 | 36 | 458 | 966 | 1513 | 6.0 | 20.0 | |||||
| 2JK-2×1/11.2 | 2 | 2.0 | 1.00 | 62 | 40 | 24 | 182 | 406 | 652 | 7.0 | 11.2 | |||
| 2JK-2×1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/11.2 | 1.25 | 242 | 528 | 838 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.20 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 843 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.50 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 319 | 685 | 1080 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/11.2 | 3.0 | 135 | 90 | 36 | 289 | 624 | 994 | 10.5 | 11.2 | |||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/11.2 | 1.80 | 362 | 770 | 1217 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/11.2 | 3.5 | 1.70 | 170 | 115 | 40 | 349 | 746 | – | 12.6 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 2.10 | 450 | 950 | – | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/10 | 4.0 | 245 | 160 | 48 | 421 | 891 | – | 12.6 | 10.0 | 600 | ||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/11.2 | 11.2 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-5×2.3/10 | 5.0 | 2.30 | 280 | 180 | 52 | 533 | – | – | 12 | 10.0 | 500 | |||
| 2JK-5×2.3/11.2 | ||||||||||||||
Possible defects:
| Defect | Causes |
| Unfilled sections | Insufficient material Low pouring temperature |
| Porosity | Melt temperature is too high Non-uniform cooling rate Sand has low permeability |
| Hot tearing | Non-uniform cooling rate |
| Surface projections | Erosion of sand mold interior A crack in the sand mold Mold halves shift |
FAQ
Q: How about the quality of your products?
A: Our machines are manufactured strictly according to national and international standards, and we take a test on each equipment before delivery.
Q: How about the price?
A: We are manufactory, and we can give you lower price than those trade companies. Besides, customers from Made in China can get a discount.
Q: Do you provide after-sale service?
A: Yes. The warranty period of our machines is 1 year, and we have a professional after-sale team to promptly and thoroughly solve your problems.
Q: Do you provide equipment operation training?
A: Yes. We can send professional engineers to the working site for equipment installation, adjustment, and operation training. All of our engineers have passports.
How to Prevent Timing Belt Problems
Unlike their predecessors, timing chains and timing belts are made of rubber and synchronize the opening and closing of valves in the engine. While their benefits are numerous, they are prone to wear and tear over time. Here are some tips for ensuring your timing belt lasts for many years. Listed below are some of the most common problems that you may encounter when changing your timing belt. Read on to find out how to prevent them and keep your car running at peak performance.
Timing belts are rubber
There are many advantages to using timing belts in your car. They are lightweight and reduce the strain on your vehicle’s internal components. They are also quiet when running, so you won’t have to listen to your car to know that maintenance is needed. If you’re concerned about noise, a quiet engine can help you determine whether your timing belts are broken or if you need to replace them altogether. A quiet engine can also help you notice signs of wear and tear before you do.
Regardless of material, rubber timing belts can be susceptible to stretching and breaking. They also are susceptible to high temperatures and the lubrication of motor oil, reducing their lifespan. Manufacturers have responded to this problem by creating timing belts made of engine-temperature-resistant rubber materials. The improved rubber compounds also provide greater strength and resistance to distortion. Reinforcing fibers also protect the teeth from shearing, reducing the risk of a worn-out timing belt.
While the open-ended, or spliced, types of timing belts have many advantages, they are generally unsuitable for high-speed applications. In most cases, rubber timing belts are used in high-speed machine tools and automatic doors. They are also quiet and require minimal maintenance. These characteristics make rubber timing belts a great choice for high-speed applications. You can even order custom-made timing belts for unusual applications.
Timing belts are important for the functioning of an engine. They link the camshaft and crankshaft to the crankshaft. They control the movement of valves and pistons. If a timing belt fails, it can cause major damage to the engine. If you are unsure of the benefits of rubber timing belts, consider a video on the topic. This will provide you with more information on timing belts.
They synchronize the opening and closing of the engine’s valves
During the combustion process of the engine, the valves in the cylinder head open and close. Fresh air enters the cylinder, which burns with the fuel to generate power. Exhaust escapes the engine through the exhaust valve. Each cylinder contains between 2 and 4 valves. The timing belt drives a camshaft, which rotates in a precise manner to synchronize the valve opening and closing.
A timing belt is a toothed rubber belt that connects the engine’s crankshaft to the crankshaft. Like most rubber parts, timing belts degrade over time, so it’s important to replace them at the proper intervals. Replacement intervals vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle, but they should be replaced every 60 to 90 thousand miles.
A broken timing belt will not start the engine. A timing belt driven vehicle will need to be towed to a repair shop for repairs. In the automotive industry, timing belts drive both “free running” and “interference” engines. The timing belt transfers the crankshaft’s rotation to the camshafts, which in turn actuate the valves in the intake and exhaust system. When they malfunction, the pistons can contact open valves, bending or punching them.
Timing belts also work with pistons and connecting rods to create power. Perfect timing is essential for the engine to run smoothly. The timing belt regulates both the pistons and the valves. If they are out of sync, they may not ignite properly, leading to catastrophic engine failure. When you’re looking for a replacement, look for these signs of wear.
They are lighter, quieter and more efficient than timing chains
While the initial choice was for quieter performance, variable timing has led to greater efficiency and power. While noise is a factor, the average consumer cannot tell the difference. And while timing belts are generally lighter and quieter, a chain can be more noisy than a belt, which can cause more engine damage. If you’re unsure whether you should opt for a chain or a belt, consult your owner’s manual.
A timing chain functions similar to a timing belt but is made from metal and is housed inside the engine compartment. It receives its lubrication from engine oil. Timing chains can last a long time as long as you keep them properly maintained. A timing chain is not as efficient as a timing belt, but it is more accurate, quieter and easier to maintain.
A timing belt uses teeth to time the movement of various components in an engine. When the timing belt is broken, the valves in the engine will not be in sync, leading to a loss of pressure in the combustion chamber. This can cause a plethora of engine problems and cost-increasing repairs. A timing belt is also quieter and requires less lubrication, so it is safer and quieter than a timing chain.
After the advent of variable valve timing, cars began to use a timing chain. This design improved engine performance and reduced maintenance, but it also caused a backlash as consumers were no longer interested in this kind of routine maintenance. Today, however, timing chains are making a comeback in the automotive industry. While modern chains can still be noisy, they are easier to maintain, are lighter, and last longer than their chain counterparts.
They wear out over time
Even the best drive belts will eventually wear out. The main causes of belt wear include mileage and heat. The belt bends as it passes the pulley, producing heat that hardens the rubber. When the belt slips, it increases friction, accelerating the process. A worn-out belt can be very difficult to start, causing an engine to lose fuel efficiency. To help prevent this problem, check the belt for wear and tear.
A timing belt is an engine component that connects the camshaft to the crankshaft and controls the timing of combustion. These belts are made of industrial-strength rubber, and often contain nylon-reinforced cords. Although they are meant to last, they will eventually wear out. If the timing belt fails, your engine won’t run smoothly or you could spend thousands of dollars fixing it.
A faulty timing belt can cause the valves to open too early or too late, causing poor combustion and a drop in engine performance. If the timing belt breaks, the valves may hit the pistons and cause damage. This can lead to engine breakage, which requires a new engine. To prevent this, you should replace the timing belt every couple of thousand miles. If you can’t find a reliable mechanic, it is best to seek professional help from a reputable mechanic.
Another warning sign that your timing belt needs replacing is a ticking sound coming from within your engine. This is an indication of a lower oil pressure than normal. Low oil pressure can affect the timing belt as it can cause the tensioner that holds the belt taut will lose pressure. Eventually, the belt may even break, allowing the camshafts to slip and break. Once this happens, it is time to replace the timing belt.
They can be repaired
Timing belts can be repaired. If your timing belt breaks, you can take your car to a repair shop to have it repaired or replaced. The price of a repair depends on the labor hours and how many hours it takes to do the job. A bad timing belt can ruin your engine and cause it to break down completely. If you’re unable to drive your vehicle, it may require towing and a new engine.
For most drivers, a timing belt replacement will cost about $1,000 at a dealership. Luckily, you can often get the same service for less at an independent auto repair shop. Often, a timing belt repair requires replacing the water pump, too. It makes sense to replace both at the same time. But remember that timing belts are more complicated than that. If you’re worried about the cost, you can replace the water pump along with the timing belt.
If you’re in the mood to do this repair, there are many companies that offer this service. The cost is relatively low and you’ll probably save hundreds of dollars over the course of the job. However, timing belt repair is not a simple job and must be done correctly or you could end up damaging your car engine. Therefore, it’s important to know how to repair a timing belt yourself to avoid the high price of hiring a mechanic.
When timing belts start to fail, there are a few warning signs you can listen for. A difficult start-up can be a sign that your belt needs to be replaced. Also, thick smoke coming from the tailpipe can be a sign that the timing belt needs to be changed. In addition to these symptoms, your timing belt may have a crack or broken gear teeth, which means it needs to be replaced.


China Professional High Quality Pulley/Head Sheave for Mine Hoist/Winder with high quality
Product Description
2jk Series Mining Hoist Winch Parts for Coal Mine
Introduction:
Mine hoist can be divided into 2 kinds; 1 kind is JKE series single rope mining hoist and the other is Multi-rope friction hoist.
This series mine hoist including 2m-5m single tubular and double tubular types, and can be used for mining hoist, personnel lifting and material and equipment descending from vertical shafts or inclined shafts of coal, metal and nonmetal ores.
JK mine hoist is mainly used in inclined roadways and wells of coal mines, metal mines and non-metal mines to hoist or lower personnel and materials.
Technical parameters:
| Model | Drum | Tension PF |
Tension Differe |
Rope Diameter |
Lift height (m) | Max Speed |
Reduce speed ratio |
Motor Speed |
||||||
| Number | Dia | Width | 1-layer | 2-layer | 3-layer |
|||||||||
| m | KN | mm | m | m/s | r/min | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.5/20 | 1 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 62 | 24 | 305 | 650 | 1571 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 1000 | |||
| JK-2×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/20 | 1.80 | 375 | 797 | 1246 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2/20 | 2.5 | 2.00 | 83 | 28 | 448 | 945 | 1475 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 750 | ||||
| JK-2.5×2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/20 | 2.30 | 525 | 1100 | 1712 | 20.0 | |||||||||
| JK-2.5×2.3/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| JK-3×2.2/20 | 3.0 | 2.20 | 135 | 36 | 458 | 966 | 1513 | 6.0 | 20.0 | |||||
| 2JK-2×1/11.2 | 2 | 2.0 | 1.00 | 62 | 40 | 24 | 182 | 406 | 652 | 7.0 | 11.2 | |||
| 2JK-2×1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/11.2 | 1.25 | 242 | 528 | 838 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2×1.25/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.20 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 843 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.2/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/11.2 | 2.5 | 1.50 | 83 | 65 | 28 | 319 | 685 | 1080 | 8.8 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-2.5×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/11.2 | 3.0 | 135 | 90 | 36 | 289 | 624 | 994 | 10.5 | 11.2 | |||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.5/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/11.2 | 1.80 | 362 | 770 | 1217 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3×1.8/31.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/11.2 | 3.5 | 1.70 | 170 | 115 | 40 | 349 | 746 | – | 12.6 | 11.2 | ||||
| 2JK-3.5×1.7/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 2.10 | 450 | 950 | – | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 2JK-3.5×2.1/11.2 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/10 | 4.0 | 245 | 160 | 48 | 421 | 891 | – | 12.6 | 10.0 | 600 | ||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/11.2 | 11.2 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-4×2.1/20 | 20.0 | |||||||||||||
| 2JK-5×2.3/10 | 5.0 | 2.30 | 280 | 180 | 52 | 533 | – | – | 12 | 10.0 | 500 | |||
| 2JK-5×2.3/11.2 | ||||||||||||||
Possible defects:
| Defect | Causes |
| Unfilled sections | Insufficient material Low pouring temperature |
| Porosity | Melt temperature is too high Non-uniform cooling rate Sand has low permeability |
| Hot tearing | Non-uniform cooling rate |
| Surface projections | Erosion of sand mold interior A crack in the sand mold Mold halves shift |
FAQ
Q: How about the quality of your products?
A: Our machines are manufactured strictly according to national and international standards, and we take a test on each equipment before delivery.
Q: How about the price?
A: We are manufactory, and we can give you lower price than those trade companies. Besides, customers from Made in China can get a discount.
Q: Do you provide after-sale service?
A: Yes. The warranty period of our machines is 1 year, and we have a professional after-sale team to promptly and thoroughly solve your problems.
Q: Do you provide equipment operation training?
A: Yes. We can send professional engineers to the working site for equipment installation, adjustment, and operation training. All of our engineers have passports.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Neoprene Timing Belts
The timing belt is an important component of an automobile engine. Made of special materials, this belt coordinates the rotational motion of the crankshaft with the camshaft. The coordinated precision is essential for sustainable combustion, and ensures that the valves in the combustion chamber open at the right times. Timing belts determine the engine’s pace, so it is essential that they perform at high synchronicity and strong enough to operate in extreme conditions.
Fabric timing belt
A timing belt is made of a yarn that has been crimped and woven into a mating surface, called the engagement surface. This yarn, known as the warp, must be able to stretch from a substantially flat state along irregularities in the mold. It must be flexible enough to stretch by several tens of percent under low load conditions. The warp yarn of a timing belt is made of synthetic fiber and is crimped into the right shape to be stretched easily.
This fabric can be used without thickening the base cloth. It can contain a large number of warp threads, and its wear resistance can be enhanced over time. The timing belt of the present invention does not crack or wear out after a long time of use. The base cloth does not wear out, which allows the timing belt to last for a long time. This makes it an extremely durable material. To learn more, read on.
The teeth of a timing belt are made of tough rubber and a nylon fabric facing. The fabric is coated with a plastic compound that gives it its shape and covers the cord. The materials used to make these belts vary, but all are strong and durable. They are also suitable for high-load applications. In addition to nylon timing belts, strongbelt premiums are also available. In addition to nylon and neoprene timing belts, they are also compatible with RPP and HTD pulleys.
The teeth of timing belts are made of high-strength polychloroprene elastomer. The teeth are made of a special manufacturing process that ensures good adhesion. The facing fabric is made of low-elongation glass cord and is covered by a polyamide fabric that has a low coefficient of friction. If you need an exact fit, you can buy a high-quality belt from TransDev.
Neoprene timing belt
When it comes to dependable drive belts, neoprene is hard to beat. It’s widely used in insulated clothing and weather stripping, and has been a key component in the development of timing belts since the late 1970s. And because it’s so hardy, neoprene timing belts are incredibly reliable. Here are a few reasons why. Neoprene is the most durable synthetic material for timing belts, and these 3 reasons should not discourage you from purchasing a new neoprene timing belt.
Neoprene timing belts are made of a high-quality chloroprene compound with a hardness of 74 Shore A. The high-strength glass fiber strands in the belt’s body transmit high power while enhancing its flexural strength. In addition, it’s covered with a high-strength polyamide fabric to reduce friction and protect contact surfaces from wear and tear.
Unlike neoprene, polyurethane synchronous belts are resistant to temperature and abrasion. Polyurethane timing belts are resistant to acids and chlorides, and exhibit excellent abrasion resistance. A neoprene belt can be used in high-speed applications, and can withstand extreme temperatures. However, the resistance of polyurethane to abrasion is not as good as that of neoprene.
The 2 most common types of timing belts are rubber and urethane. Rubber is the least expensive and quietest, and is the least flexible of the two. Neoprene is also highly elastic and does not retain its shape when it’s stretched, making it a popular choice for applications in manufacturing, agriculture, and robotics. They are also great for applications where precision and motion control are important. These properties make timing belts extremely effective in leading the industry toward its goals.
Chain timing belt
Traditionally, a vehicle’s timing system consists of a timing belt or chain. These components keep the engine’s intake and exhaust valves in the proper order. When these components go bad, it can ruin the engine in seconds. But there are advantages and disadvantages to each of them. Read on to learn about the pros and cons of each type of timing system. Here are some examples. Chain: A timing belt is generally made of reinforced rubber.
Chain: A timing chain is generally found in heavy-duty vehicles with higher torque. This type of timing belt is also found on many cars and SUVs with 4 cylinder engines that do not require a lot of torque. Unlike timing belts, timing chains are more durable and will last longer than their rubber counterparts. But there are certain things to keep in mind when replacing a timing belt. Make sure to change the oil regularly to avoid premature wear.
Chain: A chain is easier to maintain than a timing belt. It does not change length in response to temperature. And it requires a smaller tensioner. However, this also means that the timing belt is more prone to breaking. It can jump out of place if oil is flowing along it, causing an engine malfunction. If this happens, you’ll have to replace the entire timing belt and the engine will not work correctly. That’s why replacing a chain is so important.
A timing belt is a critical part of an engine. A failed timing belt can cause catastrophic engine damage. It can slip and break, colliding with the piston and valves. Fortunately, there are a variety of ways to check your timing belt. But a good rule of thumb is to replace it as soon as possible. You’ll also need to remove the front engine cover and any other components that may be in the way. In some cases, the engine might even have to be moved.
Trapezoid shaped teeth
In terms of tooth profile, there are 2 main types of timing belts: the curvilinear and trapezoidal types. Curvilinear timing belts are more rounded and less likely to result in excessive tension loss. These types of timing belts are also more prone to backlash and reduce accuracy. Here’s how they differ from each other. These 2 types of belts share similarities but differ in important ways.
Older timing belts generally have trapezoidal-shaped teeth, but newer types use curved teeth. Curved teeth are less prone to wear out quickly and last longer than straight ones. The trapezoidal teeth also tend to wear out more quickly at higher speeds. As a result, they’re only suitable for cars that get very little use. If you’re planning on using your timing belt frequently, you may want to choose a new 1 with curved teeth.
Curvilinear teeth are designed to alleviate the stress concentrations caused by trapezoidal tooth profiles. They also have a greater depth and reduce ratcheting. In addition to their efficiency, curvilinear timing belts are quieter than their trapezoidal counterparts. And they’re a little bit more expensive than their trapezoidal counterparts. So, what’s the difference between these 2 types of teeth?
Timing belts have a tendency to favor the tracking of an “S”-shaped twist. As a result, a trapezoid-shaped timing belt is more likely to keep the engine in sync. A good quality timing belt will help you achieve this. If you don’t, consider replacing your timing belt with a metric-styled one. That way, you’ll get the best performance out of your belt.
Other types of timing belts
Timing belts are essential for operating your vehicle’s engine. These belts connect the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft. The belts synchronize the timing of the engine’s valves and pistons to prevent damage. Previously, the belt was referred to as the “gilmer drive belt.”
There are 3 basic designs for timing belts. Some are shaped like a trapezoid, while others have a curvy tooth shape. Timing belts with this tooth design are generally more efficient for force transmission, although they suffer from backlash. These teeth also wear quickly at high speeds, which can make them prone to noise. In order to solve these issues, manufacturers now offer belts with curved teeth.
Another popular type is polyurethane. These are resistant to oil and high temperatures, and are energy-efficient solutions. Polyurethane timing belts offer increased elasticity and load capacity, which are important for optimal torque production. These belts are favored by a variety of industries because of their ease of cleaning and maintenance. They can be used for power transmission systems, as well as in roller conveyor systems. However, fabric timing belts are best used when acceleration forces are high.
Other types of timing belts are not always as durable. V-Belts have teeth-like structures on their surfaces and work under constant speed. They are typically a lighter option, but have similar disadvantages. They are more expensive than chains and lack the flexibility of customizing. Unlike chains, timing belts are sold in predetermined length loops. Their pitch is easily identified. It is a key indicator of whether or not they are suitable for a specific application.


China Good quality High Precision Nylon POM Plastic Wire Cable CZPT Pulley / Roller Wheel / Sheave near me factory
Product Description
Description
- OEM size suit for customers’ requirment
- Multiple color can be choosed
- Engraved or embossed logo accepted
- Large order quantity are CZPT to be fulfilled
- Strict quality control system
- In time delivery and thoughtful custom-service
- Certification: SGS, GB/T 19001-2016, ISO9001:2005
| material | Nylon ,mcnylon,POM,ABS,PU,PP,PE,PTFE,UHMWPE,HDPE,LDPE, PVC,etc. |
| color | Black, white, red, green, transparent or any color according to Pantone code |
| size | As per customer’s requirements |
| Technology | Injection molding, CNC machining, Extrusion. |
| Surface Treatment | Powder coating, Zinc coating, Galvanization, Electro-deposition coating, Chrome/zinc/nickel plating, Polishing, Silkscreen, Black oxide |
| Application | Automotive, ATV, Mechanical equipment, Construction, Home appliance, Aviation, Office facilities, Agriculture, etc. |
| Shippment | We have longterm cooperation with internation shipping agent and express company, so that shipping safty and arriving time are secured |
More Product
Our Factory
Our Machine
Our Certification
Zhongde is a SGS verified manufacture. We have passed ISO9001:2005 quality control certifacation as well as environment management certification.
For fast quotation, please inform below detials;
1. Product type
2. Size (provide samples or 2d/3d drawings for reference)
3. Material specification (or let us using environment)
4. Quantity request
5. Prefer color
Our Advantage:
OEM service—We are a company specialsing in making OEM mechanical parts in rubber & plastic & pu material, and we produce according to your samples or drawings ,if they are not available, we design according to your requirements and the application. Various existing molds—We have our own CZPT factory,and after more than 30 years of continued accumulation, there is a very large amount of moulds ,so that we may save the CZPT cost for you.
Our Packing
Our usual packaging ways are as followings,or it can be as customer’s request.
Shipping:
We will choose the shipping methods according to your request.
Contact Us
How to Tell If Your Timing Belt is Worn Out
The timing belt is a component of your engine that consists of special materials that coordinate the rotational movement of your camshaft and crankshaft. This synchronization is vital for sustainable combustion. In addition to being vital for the proper operation of your engine, the belt is also responsible for setting the pace at which it will turn. Timing belts must be extremely strong and resilient, able to maintain a high degree of synchronicity, and operate effectively even in the most severe conditions.
Problems caused by a worn-out timing belt
A worn-out timing belt can cause misfiring. Because the belt controls the movement of the pistons in the engine, it’s critical that it’s functioning properly. Misfires can cause serious engine damage and should be fixed as soon as possible. But how do you know if your timing belt is worn out? Here are 3 of the most common symptoms of a worn-out belt.
A car engine will misfire if the timing belt is broken, which could lead to severe damage. A broken belt may also cause excessive smoke to be produced by the exhaust system. If these symptoms are present, it’s time to take the car in for a timing belt replacement. A worn-out belt will affect the performance of your car. It will also affect the engine’s starting speed. When it’s time to replace it, you should do it now to avoid future problems.
Misfiring and premature cylinder closing are 2 of the most common symptoms of a worn-out timing belt. A worn-out belt can cause permanent engine damage. Because the timing belt contains teeth that grip the gears, it can slip. If the timing belt slips, the teeth can fall into the gears, causing the engine to misfire. Worn-out timing belts can also cause the engine to stall.
Engine ticking is another common sign of a worn-out timing belt. It can also be caused by low oil pressure. When oil pressure drops, the timing belt will become loose and cause a ticking sound. You should replace the timing belt as soon as it’s damaged. But it’s not enough if you don’t notice any of these signs right away. If the ticking sound continues, you’ll probably have an engine-related problem.
Types of timing belts
Timing belts are made of special materials that help the engine synchronize the crankshaft’s rotation with the camshaft’s. This precision is vital for the combustion process, as it ensures the proper opening and closing of the valves within the combustion chamber. The belts control the engine’s pace, which is why they must be strong enough to maintain synchronicity and operate at high speeds. However, timing belts do not come cheap, so there are several factors that you should be aware of before buying one.
First, timing belts come in different pitch sizes. A typical metric pitch is 5 millimeters, but some manufacturers use a higher or lower pitch. The pitch determines how much tension the belt will be able to carry and whether or not it will wear out prematurely. Other pitch sizes are more common. Timing belts come in 3 different widths, and they all have different tooth profiles. To find the right 1 for your engine, you need to know the pitch.
Modified curvilinear belts are made of 2 different types of materials. They combine the strengths of trapezoidal and curvilinear belts. The outer surface of these belts has a steeper angle than the belt’s teeth, which means that the power transmitted by the motor is much higher. Consequently, they are the primary choice for high-performance industrial applications. A synchronous timing belt is ideal for applications where precise synchronization of the driven and driver shafts is important.
Spliced and welded timing belts are used in many general applications. These belts typically have no joints or weak points and are more durable. These types of timing belts are also made with a smooth back and sealed edges. If you need a custom length or shape, these can also be manufactured. Then, you can order them for your exact measurements. When you need a new timing belt, you can simply ask for a quote and order 1 online.
Common problems
Timing belts are a crucial part of your car’s drive system, and improper installation can cause a whole host of issues. It is also susceptible to crimping and premature wear. In either case, it is vital to take action early to prevent excessive engine wear and extend the life of the timing belt. Here are some common problems with timing belts. You may be surprised to learn that these problems are often caused by common car maintenance practices.
Regardless of the cause of the problem, a worn or faulty timing belt will affect the engine’s timing. This may result in misfires or excessive exhaust release. Engine misfiring is a serious sign that something is amiss. Depending on the extent of the problem, it could even lead to engine damage. If you experience erratic performance or excessive smoke, it’s likely the timing belt is faulty. Here are some common problems with timing belts and their causes.
Engine misfire is a common warning sign that your timing belt is wearing. This occurs when the timing belt slips off the gears or camshaft, causing the cylinder to open too early. If you notice this problem, take immediate action by visiting your mechanic immediately. Moreover, timing belt failures can cause a large amount of damage to your car’s engine, so it is essential to have your timing belt replaced in time.
Improperly adjusting the tension of your timing belt can also lead to serious problems. This can cause excessive wear on your engine’s pistons and valves, and damage the engine. Ultimately, a damaged timing belt may result in an expensive engine rebuild. While this might seem like a good option, it is not always the most practical solution. Ultimately, your car’s timing belt will wear down if you don’t fix these problems immediately.
Symptoms of a worn-out timing belt
If your car’s engine makes a high-pitched squeal when you start or run it, you may be experiencing a worn-out timing belt. You can check the belt by opening the hood and listening closely to the noise. You may also notice uneven RPM counts. The squealing sound can be caused by a number of factors, such as low oil pressure, engine lubrication problems, or even the timing belt.
If your car is exhibiting these symptoms, then it’s time for a replacement. A timing belt breaks down while your engine is running, and this can cause major engine damage. The timing belt is connected to the crankshaft and camshaft by a belt that keeps the 2 parts in sync rotation. When the timing belt wears out, it may cause a jump in the belt’s tooth, causing cylinders to open and close randomly, resulting in blow-by.
A timing belt is crucial to the functioning of your car’s engine. It synchronizes the engine rotation system and opens and closes the valves at the right time. Because it is subject to great forces inside the engine, the belt must be replaced at some point. Every vehicle needs a new timing belt at least once in its lifecycle. But what are the symptoms of a worn-out timing belt?
The timing belt is crucial to your car’s performance, so if you notice any of these signs in your vehicle, you should make an appointment with a qualified mechanic. The best way to tell if your timing belt needs to be replaced is to visually inspect the belt. You can visually inspect the belt while the engine is off, and if you notice it’s sagging, you should replace it.
When to replace a timing belt
A timing belt is an essential part of your vehicle’s engine and is responsible for synchronizing the rotation system, allowing the valves to open and close at the correct time. Due to its constant use and great forces inside the engine, timing belts must be replaced at some point. The recommended interval for timing belt replacement is anywhere from 60,000 to 150,000 miles. In most cases, timing belt replacement is recommended for vehicles between 6 and 10 years old.
Costs for a timing belt replacement can vary widely depending on the make and model of your vehicle. The labour and parts used for timing belt replacement are relatively inexpensive, but you’ll have to remove several parts of your engine to access them. Timing belt replacement also involves replacing the water pump, which is driven by the timing belt. These other parts will be replaced with new ones, but the overall cost of the repair depends on the type of car you drive.
A timing belt is a thin, rubber piece that runs along the front of the engine. It’s responsible for synchronizing the valves and camshafts and is an important component of an engine. The belt’s custom teeth make it easy to see when it’s time to replace your car’s timing belt. Oftentimes, car manufacturers recommend timing belt replacement every 2 to 4 years or 50,000 miles, and they’re not the only ones who recommend it.
A professional mechanic can replace the timing belt and water pump in 1 service, saving you both time and money. Timing belt replacement is an intricate task and can last anywhere between 4 and 8 hours, depending on the make and model of your car. However, it is worth it if you can get your vehicle into a garage or repair shop sooner rather than later. You can save a lot of money on labor costs by replacing your timing belt and water pump yourself.


China Standard OEM Timing Motor Belt Pulley Tensioner Pulley/Belt Sheave Pulley near me shop
Product Description
OEM Timing Motor Belt Pulley Tensioner Pulley/Belt Sheave Pulley
|
General Products Application/Service Area |
Metal Parts Solution for Vehicle, Agriculture machine, Construction Machine, transportation equipment, Valve and Pump system. E.g. Engine bracket, truck chassis bracket, gear box , gear housing , gear cover, shaft, spline shaft , pulley, flange, connection pipe, pipe, hydraulic valve , valve housing ,Fitting , flange, wheel, flywheel, oil pump housing, starter housing, coolant pump housing, transmission shaft , transmission gear, sprocket, chains etc. |
|
Main blank Process for Casting Iron |
Sand Casting , Resin Sand Casting, Green Sand Casting, Shell Molding, Automatic Molding, Lost Wax Casting, Lost Foam Molding Casting etc. |
|
Blanks Casting Tolerance |
CT9-10 for Machine Molding Process, |
|
Applicable Material |
Ductile Iron, Grey Iron Casting, or as customer request. |
|
Casting Blank Size /Dimensions |
2 mm-2000mm / 0.08inch-79inch for casting iron, as per customer requirement |
|
Casting Blank Weight |
Range from 0.01kg-1000kg for gray cast iron prices per kg |
|
Applicable Machining Process |
CNC Machining/ Lathing/ Milling/ Turning/ Boring/ Drilling/ Tapping/ Broaching/ Reaming /Grinding/Honing and etc. |
|
Machining Tolerance |
From 0.005mm-0.01mm-0.1mm |
|
Machined Surface Quality |
Ra 0.8-Ra3.2, according to customer requirement |
|
Applicable Heat Treatment |
Normalization , annealing, quenching and tempering, Case Hardening, Nitriding, Carbon Nitriding, Induction Quenching. |
|
Applicable Finish Surface Treatment |
Shot/sand blast, polishing, Surface passivation, Primer Painting , Powder coating, ED- Coating, Chromate Plating, zinc-plate, Dacromat coating, Finish Painting etc. |
|
MOQ per batch |
For cast iron: 1pc available for sample test |
|
Lead Time |
about 50 days of gray cast iron prices per kg |
Production capacity:
1. Casting classification: Sand casting; Precision casting; Vacuum process casting etc.
2. Gray iron, ductile iron, stainless steel, carbon steel, alloy steel, etc.
3. Adoption standard: BS, DIN, ASTM GB etc.
4. Weight range: 0.5~5000kg.
5. Producing capacity: 2, 000 tons per month.
6. Main application: Metallurgy; Machinery; Plastics; Rubber; Pharmaceutical;
Textiles; Mining; Paper-making; Packaging.
7. Main equipments: Furnaces; Heat treatment furnaces; Direct-reading spectrometer; Shot -blasting
equipments, etc.
8. Surface treatment: Polishing, plating, shot blasting, heat treatment, etc
9. Inspection and test: Foundry in home, third part inspection, Material report, UT, MT, RT, and PT, etc…
10. Packing and shipping: Stand export packing; 20day make modul & sample; Delivery time against
your quantity.
11. Casting service: Your logo, character, trade name, number etc can be casted on the surface clearly.
1. Q: Why choose CZPT product?
A: We CZPT have our own plant — HangZhou CZPT machinery Co., Ltd, therefore, we can
surely promise the quality of every product and provide you comparable price.
2. Q: Do you provide OEM Service?
A: Yes, we provide OEM Service.
3. Q: Do you provide customized flywheel?
A: Yes. Customers give us drawings and specifications, and we will manufact accordingly.
4. Q: What is your payment term?
A: We provide kinds of payment terms such as L/C, T/T, Paypal, Escrow, etc.
1. Investment casting sand casting/ lost wax casting/precision casting/gravity casting/stainless
steel casting/carbon steel casting/ die casting/cookware handle casting/pan handle casting/home
hardware casting;
2. Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel and duplex steel, wcc, wcb, lcc, color metal
etc;
3. Surface treatment: Heat treatment, machining, polishing, anodizing, hard anodizing, galvanized,
enp, chrome plating, powder coating and painting;
4. Software for specification drawings: Pdf, auto CAD, solid work, proe;
5. Main production equipments: Wax injection, CNC-machine, heat treatment furnace;
6. Quality assurance in accordance with ISO9001: 2008, strict material inspection and exact
dimension control, 100% quality control.
7. OEM order is welcome;
8. The parts can be made completely based on your specifications such as drawing, design,
sample etc.
9. Export Markets: Australia Investment Casting / Precision Casting, America, United States.
U. S. A. Investment Casting / Precision Casting, Canada Investment Casting / Precision Casting;
U. K. England, Britain Investment Casting / Precision Casting, Germany.
Quality First, Price Best, Service Foremost!
Why Timing Belts Are So Important
What is a timing belt? A timing belt is a toothed synchronous belt that transfers rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley. Newer cars often have a synchronous timing belt to increase efficiency. Compared to traditional belts, these are quieter and more efficient. However, they do have their drawbacks. In this article, you’ll learn why timing belts are so important. And if you’re wondering how to replace them, keep reading to find out how you can do this quickly and affordably.
Timing belts are toothed, synchronous belts
Toothed, synchronous, and cogged belts are the 3 most common types of mechanical drive belts. Both toothed and synchronous belts are designed to run over pulleys with corresponding teeth. This positive engagement prevents slippage and speed loss. Timing belts can be toothed or toothless, and the toothed profile meshes with the grooves of the sprocket. They improve energy efficiency and reduce downtime. They are also smaller, quieter, and require no lubrication. These properties allow synchronous belts to operate at higher speeds than chains and gears.
These toothed belts are commonly used in motorcycles and automobiles. They are highly durable and can provide more power than friction-drive belts. Toothed belts are often designed for high-power transmissions and the primary drive of some motorcycles. While timing belts and synchronous belts may seem similar, they are quite different. Synchronous belts, or “toothed belts,” have 2 distinct failure modes. The former is gradual and preventive, whereas the latter is catastrophic.
Despite their similarities, timing belts are often not compatible with all machines. Excessive installation tension will result in belt tooth shear and stress breakage. The teeth of timing belts show signs of excessive tension, as illustrated in Figure 6. Broken teeth are caused by root cracks, which propagate along the tensile member. The individual teeth of the belt will separate from the body of the timing belt.
Synchronous belts have various advantages. Synchronous belts are generally more durable, as they have low installation tension and less stress on the drive system. However, when choosing a timing belt, it is important to consider the conditions that apply to your application. Ideally, you will choose a toothed belt with the lowest possible installation tension. Then, you’ll be on your way to a more efficient drive.
They transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley
Timing belts are a common type of transmission, which transfers rotary motion from the central motor to the driving pulley through a series of pulleys. Their basic design is the same as an open belt drive, but they have an idler pulley in the middle to increase the tension and power transfer. Another type of drive is a stepped pulley, which allows different speeds and torques to be obtained.
The center distance between the pulley and the drive pulley determines their distance from each other. The distance between the pulley and the drive pulley determines how much power is transmitted through each pulley. When the pulleys are cross-connected, they cannot transmit as much power as they could if they were parallel, which limits the transmission of torque and prevents parts from breaking.
The main advantages of a timing belt are its comparatively low weight and low maintenance requirements. It has a tensile strength of about 90 percent and is also resistant to harsh conditions. The best timing belt pulleys are made of steel because they are resistant to wear and corrosion and can handle long-term chemical exposure. Plastic timing belt pulleys are also available. These are the lightest and cheapest options for the operator.
Another type of timing belt is a spring belt. Like elastic belts, spring belts are composed of a helical steel spring. They are typically used in model and toy engines for transmission from the crankshaft to other parts of the vehicle. Compared to elastic belts, spring belts last longer and do not have to be adjusted, although the spring belts are more likely to slip under heavy loads.
They are quieter
When choosing a replacement timing belt for your car, consider whether you prefer a rubber belt or a metal one. Rubber timing belts are more prone to wear out over time, while metal timing chains are durable and last longer than their rubber counterparts. Timing belts and chains both need maintenance to keep them operating smoothly and quiet. Listed below are some of the most common benefits of timing belts. Read on for more details.
While both timing belts and chains perform the same function, timing belts are quieter and more affordable. Although timing belts are cheaper to produce, they last less. In addition, timing chains are stronger and less likely to fail. If you’re considering changing your timing belt, you can find a good video about the pros and cons of each. Both belts and chains work to optimize fuel economy, reduce emissions, and improve engine efficiency.
Timing belts are much quieter than rubber belts. However, they are not as effective at regulating engine timing. If you’re concerned about noise when changing timing belts, make sure they’re properly fitted. If your timing belts are too loose, they can cause engine damage. A loose timing belt can force other parts out of sync, and can even cause a serious engine malfunction. Timing belts are quieter than rubber belts, but they’re no match for the sound-proofing properties of rubber.
While the noise of a timing belt can be bothersome, it’s a simple process that will help you drive your car more quietly. Their function is simple and straightforward: the timing belt keeps the engine running at the right speed, and they’re also cheaper than other mechanisms. They’re also easier to maintain and use at high speeds without any problems. Timing belts are available in many different tooth profiles, pitch lengths, widths, and materials. Some manufacturers even offer customized belts for specific purposes.
They are more efficient
Timing belts are more efficient than chains because they have a smaller cross-section and smaller bend radius. These characteristics also enable them to have a smaller overall cost. However, because they require more energy to operate, V-belts are typically chosen because of their relatively low face-value cost. This is because they are less expensive overall, but can cost more over time when you factor in their operational costs. Even so, the initial product cost can be paid off in the first month or 2 with energy savings.
Using a timing belt can greatly improve energy efficiency in many applications. Not only does it increase the torque and power transmitted, but it also minimizes friction and elongation losses. This can lead to a 15 percent energy savings, which is equivalent to EUR 2,390 per year in energy costs! The benefits of timing belts are also numerous. By eliminating the need for tooth-drive sprockets, timing belts can improve the efficiency of a drive system.
In many automobiles from the 1980s to the early 2000s, timing belts were a popular choice. This is because they were less expensive and durable, yet still capable of maintaining the correct timing of an engine. However, timing chains are more reliable these days, and many drivers opt for them over timing belts. They are quieter and last longer, which makes them more desirable for drivers. In general, timing chains are cheaper but less efficient than belts.
Timing chains were a more expensive option, but the oil crisis pushed manufacturers to make cars with fuel efficiency their top priority. With timing belts, manufacturers realised that they were cheaper, easier to install, and more reliable. However, timing chains had a few drawbacks. One of the main disadvantages was that they were harder to replace, and required more engine oil. But with the price of fuel and gas, timing chains were preferred by many drivers.
They require lubrication
Timing belts are an integral part of engine performance. They keep the engine’s valves open and closed at the correct times and are designed to fit around the gears inside the engine. Timing belts do not require lubrication but are still important to keep the engine working smoothly. Self-servicing car parts can be used to maintain the health of your timing belt. Here are some helpful tips for self-servicing your timing belt.
When timing belts are wearing out, they can cause a noise. This noise is usually due to impact, where the belt tooth engages with the pulley. While the noise isn’t particularly annoying, it can be damaging over time. The second noise that you may hear is called air volume displacement. It occurs when air fills the space between the belt and the pulley and increases with the speed of the engine.
In addition to timing belts, timing gears and chains are often inaccessible, with their hidden mechanisms. The year and type of engine will determine which type you have, but each type is susceptible to wear and tear. Timing gears and timing belts are usually coated in engine oil for protection. Lubricating them regularly will ensure that they work as they are supposed to. These belts can also be driven by other components in the engine, which will require lubrication.
Oil leaks can lead to timing belt failure. If you notice a leak in the oil, try to identify it as soon as possible. Getting your timing belt replaced will prevent downtime caused by engine failure. You may also notice clunks, grinding noises, and knocking sounds under the vehicle. These are common signs that your timing belt needs lubrication. You can reduce the chances of these problems by regularly changing the engine oil and making sure it is of high quality.

