Product Description
Applied in Textile Machinery Ceramic Wire Xihu (West Lake) Dis.s Caged Ceramic Pulley
1.Applicable for wire jump preventing during winding.
2. The precision ceramics circle inside has an ultra-fine polishing degree Ra0.2.
3. Hign-speed bearing in its’ porcelain circle controls the sliding distance between enameled wire and the circle under 0.2mm.
4.The structure protect the film and assure the beating of the enameled wire in a very small scope to stabilize the tension.
5. Being popular in the market for easy installation, low maintenance cost, robust construction and longer service life.
| Installation Specification Ø2 Series | ||||||||
| Nubmer | Model | specificationmm | ||||||
| L | L1 | D | D1 | d1 | d2 | H | ||
| 1 | RC0326-2-1006 | 26 | 6 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 2 | RC0326-2-0806 | 26 | 6 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 3 | RC0330-2-0807 | 30 | 7 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | N/A |
| 4 | RC571-2-571 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | N/A |
| 5 | RC571-2-1008 | 35 | 8 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | N/A |
| 6 | RC571-2.5-1411 | 35 | 11 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.8 | N/A |
| 7 | RC0336-2.5-1011 | 36 | 11 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 8 | RR 0571 -2-1610 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | N/A |
| 9 | RS571-2.5-1210 | 35 | 10 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | N/A |
| 10 | RC571-2-1208 | 30 | 8 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 11 | RS 0571 -2 | 30 | N/A | 2 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | N/A |
HARTAI TECHNOLOGY INDUSTRY Co., Ltd is professional manufacturer for coil winding pulley, We offer ceramic coated rollers, caged caramic pulleys, wire jump preventer and ceramic wire guides for coil winding machine at competitive price.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE |
|---|---|
| Material: | Ceramic |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Application: | Wire Guide |
| Item: | Ceramic Wire Guides Caged Ceramic Pulley |
| Weight: | 14G |
| Samples: |
US$ 1.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
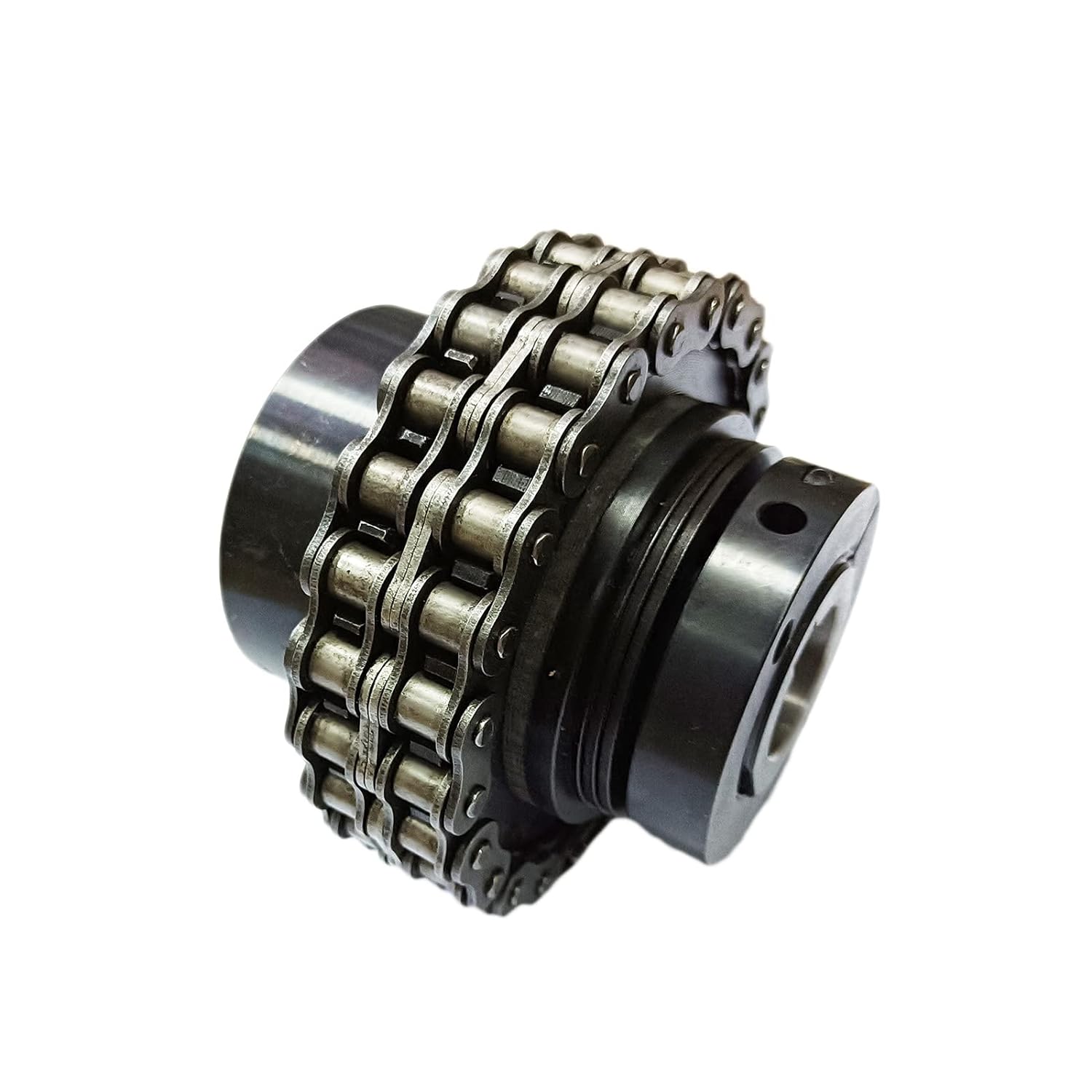

Are there aftermarket upgrades available for tensioner rollers to improve their functionality?
Yes, there are aftermarket upgrades available for tensioner rollers that can improve their functionality and performance. Aftermarket upgrades offer alternatives to the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) tensioner rollers, providing enhanced features, materials, and design. Here’s a detailed explanation of aftermarket upgrades for tensioner rollers:
1. High-Performance Materials:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers often utilize high-performance materials that offer improved durability, heat resistance, and wear characteristics compared to standard OEM rollers. These materials may include advanced polymers, reinforced composites, or specialty alloys. Upgrading to tensioner rollers with high-performance materials can enhance their functionality by increasing their lifespan and performance under demanding operating conditions.
2. Upgraded Bearing Systems:
Bearing systems in tensioner rollers can be upgraded with higher-quality bearings or specialized bearing designs. Improved bearing systems can offer smoother operation, reduced friction, and increased load-bearing capacity. Upgraded bearing systems contribute to improved functionality by reducing noise, vibration, and wear, and enhancing overall performance and reliability.
3. Damping Mechanisms:
Some aftermarket tensioner rollers feature enhanced damping mechanisms to reduce belt noise and vibration. These damping mechanisms can include rubberized coatings, silicone inserts, or advanced damping materials. Upgrading to tensioner rollers with improved damping capabilities can enhance functionality by providing a quieter and smoother operation, improving the overall driving experience.
4. Tension Adjustment Features:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers may offer additional features for tension adjustment. These features can include adjustable tension springs, mechanical or hydraulic tensioners, or built-in tension adjustment mechanisms. Upgraded tension adjustment features allow for fine-tuning of belt tension to meet specific performance requirements, optimizing functionality and performance under varying load and operating conditions.
5. Performance-Enhancing Designs:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers may incorporate performance-enhancing design elements. These designs can include optimized pulley profiles, improved belt contact surfaces, or modified geometries for better belt tracking. Performance-enhancing designs contribute to improved functionality by reducing belt slippage, improving power transfer efficiency, and minimizing wear on the belt and other components.
6. Enhanced Durability:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers may offer enhanced durability features to withstand demanding conditions. These features can include reinforced construction, corrosion-resistant coatings, or additional protection against contaminants. Upgrading to tensioner rollers with enhanced durability can enhance their functionality by reducing the risk of premature failure, extending their lifespan, and improving overall system reliability.
7. Compatibility and Fitment:
Aftermarket tensioner rollers are designed to be compatible with specific vehicle makes and models. They are engineered to match the original specifications and fitment requirements, ensuring proper installation and functionality. Upgrading to aftermarket tensioner rollers that are compatible with the vehicle’s belt system promotes optimal functionality and performance.
8. Manufacturer Reputation and Quality:
When considering aftermarket upgrades for tensioner rollers, it is important to choose reputable manufacturers known for their quality products. Selecting aftermarket tensioner rollers from trusted manufacturers ensures that the upgrades will provide the desired functionality and performance improvements, backed by reliable engineering and manufacturing processes.
In summary, aftermarket upgrades for tensioner rollers offer various enhancements to improve their functionality and performance. These upgrades can include high-performance materials, upgraded bearing systems, damping mechanisms, tension adjustment features, performance-enhancing designs, enhanced durability, and compatibility with specific vehicles. Choosing aftermarket upgrades from reputable manufacturers can provide reliable improvements to the functionality of tensioner rollers, contributing to enhanced belt system performance and overall vehicle drivability.
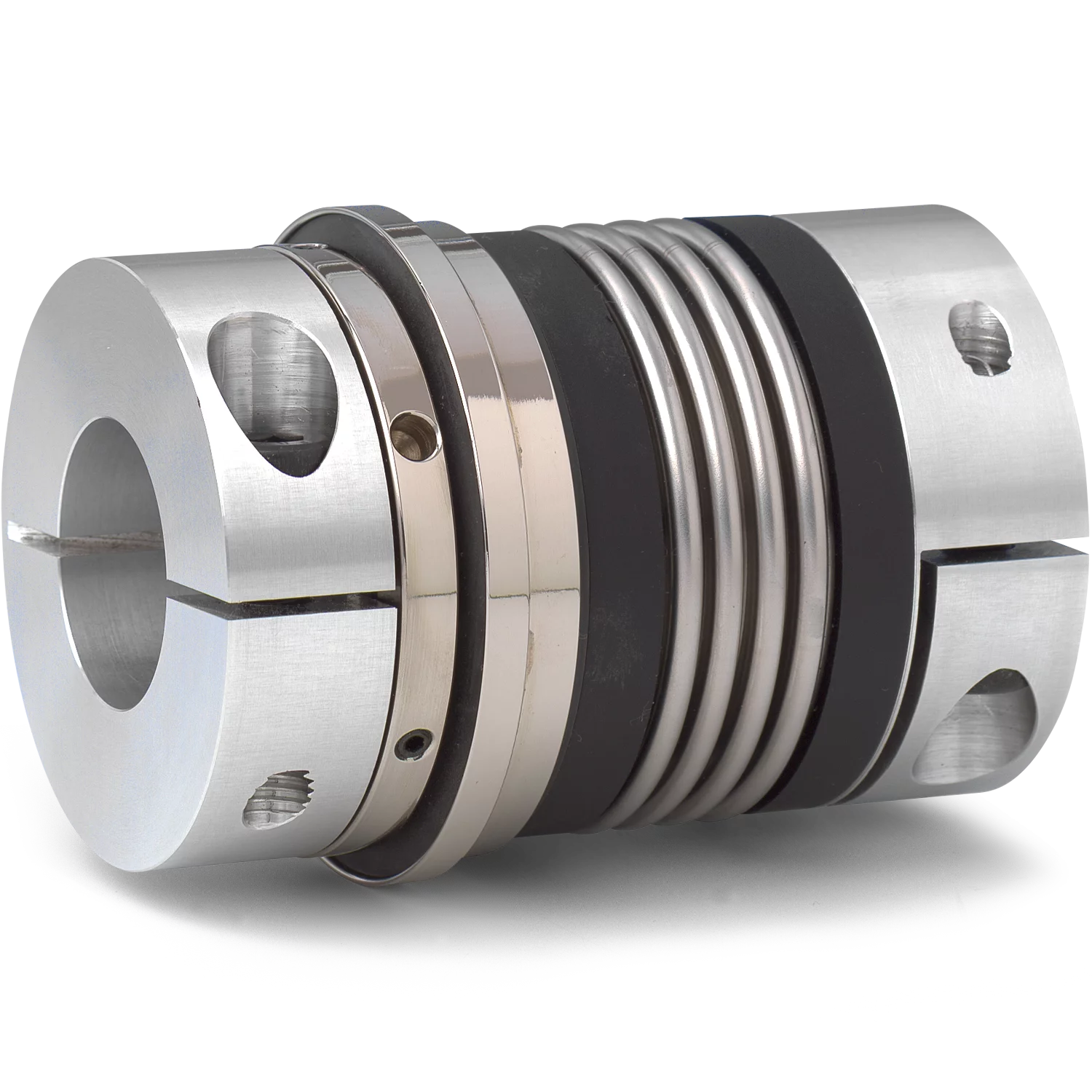

How do tensioner rollers contribute to reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of belts?
Tensioner rollers play a vital role in reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of belts in various applications. They offer several key contributions in achieving these objectives:
1. Maintaining Proper Belt Tension:
Tensioner rollers help maintain the optimal tension in belts throughout their operation. Proper tension is crucial for efficient power transmission and preventing belt slippage. When belts operate under inadequate tension, slippage can occur, leading to increased wear on the belt and associated components. Tensioner rollers ensure that the belts remain appropriately tensioned, reducing wear and extending their lifespan.
2. Absorbing Belt Vibrations:
Vibrations can occur in belt drive systems due to imbalances, misalignments, or variations in load. These vibrations can accelerate belt wear by causing friction and excessive flexing. Tensioner rollers are designed to absorb and dampen vibrations, minimizing their impact on the belt. By reducing vibrations, tensioner rollers help to decrease wear and prolong the life of the belt.
3. Distributing Tension Evenly:
Tensioner rollers distribute tension more evenly along the length of the belt. They help prevent localized areas of excessive tension, which can lead to premature wear and belt failure. By ensuring a more uniform distribution of tension, tensioner rollers contribute to reducing wear and extending the lifespan of belts.
4. Compensating for Belt Stretch:
Over time, belts can stretch due to the mechanical stresses they experience during operation. Belt stretch can result in reduced tension and compromised power transmission. Tensioner rollers are designed to compensate for belt stretch by applying additional tension to maintain the desired level of belt tension. This compensation helps to prevent belt slippage, wear, and premature failure, thereby increasing the lifespan of the belt.
5. Reducing Belt Misalignment:
Proper belt alignment is essential for minimizing wear and optimizing belt life. Tensioner rollers assist in maintaining belt alignment by exerting consistent pressure on the belt and guiding it along the desired path. By reducing belt misalignment, tensioner rollers help prevent edge wear, side-loading, and premature belt failure.
6. Providing Belt Support:
Tensioner rollers provide support to the belt, especially in longer spans or applications with heavy loads. They help prevent belt sagging and excessive flexing, which can lead to accelerated wear and reduced belt life. By offering support, tensioner rollers contribute to minimizing wear and increasing the durability of the belt.
7. Facilitating Belt Tracking:
Proper belt tracking is crucial for belt longevity and performance. Tensioner rollers aid in maintaining belt tracking by applying controlled pressure and guiding the belt along the intended path. By promoting accurate belt tracking, tensioner rollers help prevent edge wear, rubbing, and premature belt failure.
8. Minimizing Belt Slippage:
Belt slippage can occur when there is insufficient tension or excessive loads in the system. Tensioner rollers help maintain the necessary tension in the belt, ensuring a secure grip between the belt and the pulleys. By minimizing belt slippage, tensioner rollers reduce wear, heat generation, and premature belt failure.
In summary, tensioner rollers contribute significantly to reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of belts by maintaining proper tension, absorbing vibrations, distributing tension evenly, compensating for belt stretch, reducing belt misalignment, providing belt support, facilitating belt tracking, and minimizing belt slippage. These contributions help optimize the performance, efficiency, and longevity of belt drive systems in various applications.

In what types of vehicles or machinery are tensioner rollers commonly used?
Tensioner rollers are commonly used in a variety of vehicles and machinery where belt drive systems are employed. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of vehicles and machinery in which tensioner rollers are commonly found:
1. Automobiles:
Tensioner rollers are extensively used in automobiles, including passenger cars, SUVs, and light trucks. They are an integral part of the engine’s accessory drive system, where they help maintain proper tension in the belts that drive components such as the alternator, water pump, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Tensioner rollers contribute to the reliable operation of these accessories and play a crucial role in the overall performance of the vehicle’s engine.
2. Commercial Vehicles:
Tensioner rollers are also commonly utilized in commercial vehicles, such as heavy-duty trucks, buses, and delivery vans. These vehicles often have larger and more complex engine systems that require multiple belts to drive various accessories. Tensioner rollers help ensure proper tension in these belts, allowing for efficient power transmission and reliable operation of the engine accessories.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
In the agricultural sector, tensioner rollers find widespread use in various types of machinery, including tractors, combine harvesters, and other farm equipment. These machines often rely on belt drive systems to power critical components like the water pump, alternator, hydraulic systems, or conveyor belts. Tensioner rollers play a vital role in maintaining optimal belt tension, enabling proper functionality and efficient operation of agricultural machinery.
4. Construction and Heavy Machinery:
Tensioner rollers are employed in construction and heavy machinery, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes. These machines utilize belt drive systems to power auxiliary components like hydraulic pumps, generators, or air compressors. Tensioner rollers help ensure that the belts remain properly tensioned, allowing for reliable power transmission and smooth operation of the machinery in demanding construction or industrial environments.
5. Industrial Equipment:
In various industrial applications, tensioner rollers are used in machinery and equipment such as manufacturing systems, conveyor systems, packaging machines, printing presses, and textile machinery. These systems often rely on belt drive mechanisms to transfer power between different components. Tensioner rollers assist in maintaining the desired tension in the belts, ensuring efficient power transmission and reliable operation of industrial equipment.
6. Recreational Vehicles and Boats:
Tensioner rollers are also found in recreational vehicles (RVs) and boats. RVs may have belt drive systems for powering components like air conditioning units, generators, or water pumps. Tensioner rollers help maintain belt tension in these systems, ensuring reliable operation during camping or travel. In boats, tensioner rollers can be used in propulsion systems or to drive accessories like water pumps or alternators, contributing to the smooth and efficient operation of marine engines.
7. Other Applications:
Additionally, tensioner rollers may be utilized in various other applications where belt drive systems are employed. This can include power tools, industrial pumps, compressors, agricultural machinery attachments, and more. Tensioner rollers are versatile components that find application in diverse machinery and equipment that rely on belt drives.
In summary, tensioner rollers are commonly used in vehicles and machinery such as automobiles, commercial vehicles, agricultural equipment, construction and heavy machinery, industrial equipment, recreational vehicles, boats, and other applications where belt drive systems are utilized. Their presence ensures proper tension in belts, contributing to efficient power transmission, reliable operation, and optimal performance in a wide range of equipment and machinery.


editor by CX 2024-03-29
China Good quality 99% 95% Alumina Al2O3 Textile Ceramics for Spinning Machinery near me supplier
Product Description
Textile ceramics are mainly produced from alumina ceramic materials, which have excellent comprehensive technical properties such as high mechanical strength, high hardness, low high-frequency dielectric loss, high temperature insulation resistance, chemical resistance and good thermal conductivity.
Material option:
Steatite
Alumina up to 99.7 % or 95% alumina
Titania
Zirconia
Range of products:
Flange Eyelet, Double flange eyelet, Slotted eyelet, groove eyelets, step eyelet, Cut Eyelet, Step Eyelets, Tubes, Rods, Sleeve,
Ring, Bush, Disc, Dish, Washer, Plates Trap Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Traverse Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Pig tail Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Dog tail Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Rollers, Oilers, Oiling Nozzles Cutters
Application :
Yarn manufacturing machines
Twister machines
Airjet looms
Circular looms
weaving machines
winder machines
Rope,Tap plants
Customized guides as per detailed drawings and specifications.
What Is a V-Belt?
A v-belt is a type of belt that provides a continuous motion to the vehicle’s wheels. This type of belt is made of several different components. They usually have a trapezium-shaped cross-section because of its elastomer core. Elastomers are often made of polyurethane or a synthetic rubber with good shock resistance. Sometimes, a v-belt will have 2 sections – cushion rubber and compression rubber.
Link-type V-belt
A laminated link-type V-belt is 1 embodiment of the present invention. The belt comprises individual lamina sections connected longitudinally by studs and tubes, each of which has at least 1 connecting means. The slots in the links allow for a full share of the load to be transferred through the belt, and they also reduce substantially all internal mechanical stresses. The belt is preferably designed to extend substantially the entire width of the machine being driven.
Conventional link-type V-belts are installed between 2 pulleys on the tight side of the V-drive. A wide end of a link moves in the direction of rotation, while the stud of a second, smaller link pulls the nose end of the third link forward. The shank of the stud pivots on a solid fabric located in hole 2 of the third link below. The bottom link, however, curls over the stud and the belt is assembled.
The present invention offers an improved method of forming a link-type V-belt. The belt is manufactured using links and does not have to be fitted as tightly as conventional link-type V-belts. This belt is flexible and strong enough to handle normal tension loads in a well-designed drive. In addition, the belts made using the present invention will have a longer life, thereby extending the drive’s load-carrying capacity.
Classical V-belt
A classical trapezoidal belt profile makes the VB Classical V-belt ideal for various industrial applications. Available in small sizes from 5mm to 3mm, these belts are available with cogged or raw edges. Their highly engineered construction makes them ideal for a variety of uses. These belts are commonly used in motors, compressors, milling machines, mixers, and other mechanical devices. To determine the right belt for your application, consider the following factors.
The classic v-belt is the most common and economically-priced type of v-belt. They are manufactured using special formulated rubber reinforced with polyester cords. These belts can span from 16 inches to 400 inches in length. The classic V-belt is also very easy to replace. The belt’s outer diameter and pitch can be measured. The length is typically standardized by the Association for Rubber Product Manufacturers.
Typically, classical V-belts are used in single-belt drives. Because they don’t require lubrication or maintenance, these belts are often available in sizes A and B. However, larger belt sizes are rarely used for single-belt drives. In such cases, multiple A or B belts are an economical alternative to single-belt C. In addition, narrower-profile V-belts provide higher power ratings than conventional V-belts because of their higher depth-to-width ratio. These belts are ideal for heavy-duty applications.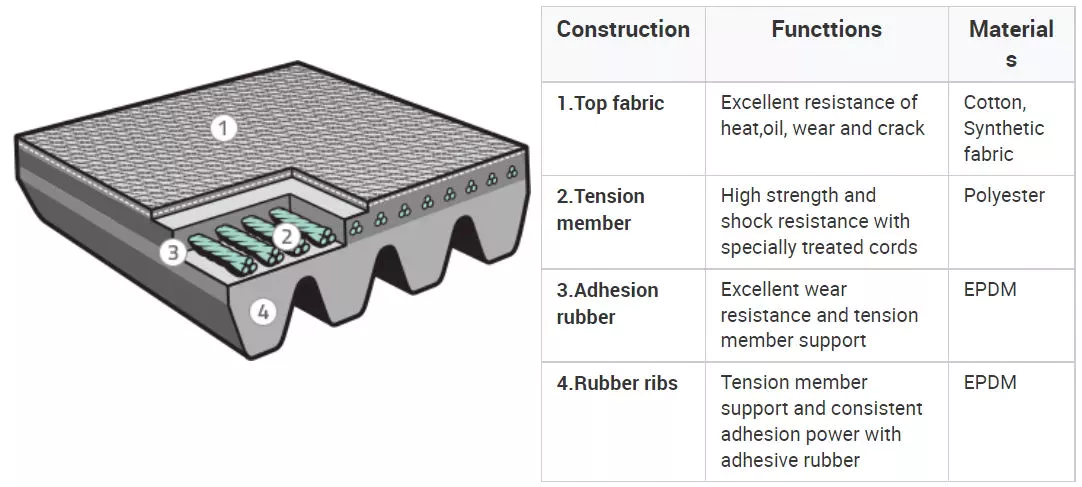
Narrow V-belt
The narrow v-belt is the same as a conventional v-belt, but it has a smaller top and bottom width. This makes it suitable for higher horsepower applications, and it is used in high-end sports cars. Narrow v-belts are generally characterized by a letter “v” on the top side and a length of outside dimensions of 1.6:1.
The steel wires that comprise the core of the v-belt are endless and are free of joints. This provides the strength required for torque transmission. A base rubber compound is placed around the steel wire and acts as a medium of compression and shock absorption during power transmission. A plastic layer acts as a protective cover, and provides the rubber with a degree of temperature tolerance. While choosing a narrow v-belt, it is important to keep in mind that there are some disadvantages to a narrow V-belt.
For example, a narrow V-belt is suitable for high-power applications, and may be used in a small assembly space. Its narrow profile also allows it to be space-saving in layout and allows high-speed drives without additional belts. Furthermore, it reduces operating and maintenance costs. It is ideal for applications where space is limited, and a high torque is required. The benefits of a narrow V-belt are plentiful.
Banded belt
Identifying a banded v-belt can be tricky, but there are a few signs that can indicate a possible problem. Cracked belts can be difficult to spot, but they can be an early indicator of a more serious problem. Look for cracked underside edges, worn covers, and misplaced slack. If 1 or more of these factors applies to your belt, you may want to seek a replacement.
Banded v-belts are made with an elastomer core. The main component of this belt is the elastomer, which is used for the band’s flexural strength and shock resistance. It’s sometimes separated into 2 sections, with each section connected to the other by a tension cord. This gives the belt its trapezium cross-section, which increases tensile strength.
The 2 main types of banded v-belts are wrapped or raw edge. Wrapped v-belts have a fiber-covered body while raw edge belts are uncovered. Banded v-belts are often classified by their cross-section, and include: standard v-belt, wedge v-belt, narrow versus double v-belt, cogged v-belt, and double t-belt.
Banded v-belts are popular with commercial applications. Whether you’re looking for a 2V-belt or a large 8V-belt, V-Belt Guys has what you need. We also stock a wide variety of different banded v-belts and can help you find 1 that fits your needs and budget. Take a look at our selection today!
Traditional V-belt
Although a traditional V-belt may be a glorified rubber band, modern variations reflect advances in engineering. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for trouble-free service. When you are replacing a traditional V-belt, be sure to follow these simple steps to ensure its longevity. Read on to learn more. Listed below are the features of each type of V-belt. Identify the type of belt you need by measuring its top width, circumference, and dimensions.
TEC Traditional V-belts have an exceptionally low slip rate and are resistant to high operating temperatures. These types of belts do not experience early belt aging. They are also highly resistant to poor operating conditions. However, the maintenance is more extensive than other types of belts. A typical V-belt part number is B50, which is the cross-section size of a 50-inch belt. The belt’s lifespan is greatly increased because of this feature.
A ribbed V-belt is another option. It has a deeper V than a traditional V-belt. The ribs in this type are narrower and more flexible. These ribs are smaller than the classic V-belt, but they can transmit 3 times as much horsepower. Because they are thinner, these belts are more flexible than traditional V-belts. The thickness of the ribs is less critical.
Metric V-belt
Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.
Metric V-belts are generally more durable than their equivalents made of standard American-sized belts. Metric V-belts are available in many different sizes to fit different machineries. In addition to offering superior load-carrying capacity, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are known for their exceptional flex and stretch characteristics. For optimum performance in textile mills, food processing, and machine tool applications, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are manufactured using a proprietary construction that combines a higher load-carrying capacity with superior flex and stretch.
Metric belts can generate 50% to 100% more horsepower than conventional and classic sectioned belts. This is achieved through improved construction and placement of the cord line. These belts also have unique wedge designs that help them support the cord in motion. However, you must ensure the proper tension when buying a Metric V-belt, because improper tension may damage the belt. They are compatible with both U.S. and international standards.


China Best Sales Low Friction Ceramic Type Tensioner for Textile Machinery with Hot selling
Product Description
Low Friction Ceramic Type Tensioner for Textile Machinery
The main features of ceramic tensioner for textile machinery
1. Exceptional wear resistance and hardness better than metal ones
2. Low yarn tensions without any yarn damage
3. Long service life on both special yarns and raw materials with aggressive additives
4. Highest yarn cleanliness without any fault silk occasion
5. Excellent mechanical strength, fracture toughness, and bending strength
6. Exceptional wear resistance and hardness better than metal ones
7. Good insulation, free of static electricity, resistant magnetic
8. Superb thermal conductivity coefficient and thermal shock property
9. Corrosion resistance in harsh working conditions
10. Excellent thermal shock resistance and good thermal stability
11. Nox-toxic, healthy material, eco-friendly material
12. Meet with RoHS, REACH regulation completely
The specification of textile tensioner
| Material option | Alumina(Al2O3), Zirconia (ZrO2), Titania (TiO2) |
| Forming methods | Dry pressed, Ceramic injection molding, Hot pressed |
| Specification | OD can be from 1 to 50mm |
| Precision processing | Precision Grinding, Polishing, Lapping, |
| Key parameters | Fine grade roughness to be 0.4mm, diamond-like polish to be Ra0.1 |
| Surface quality | Free of cracks, foreign contamination, mirror surface |
The description of textile ceramic grooved rollers
Advanced ceramic melt spinning parts, including traverse guides, pigtail guides, air-jet nozzle, spin finish applicators have been extensively using the polymer fiber production. With our veteran knowledge for materials and growing experience for the design of the physical application in the production, we can design the contact surface with yarn, thread to be the ideal state with the CZPT polishing finish.
We offer a number of ceramic yarn guides for thread guides, yarn forming, and yarn modification via different shaping methods in different technical raw materials as per customers’ needs.
All these ceramic yarn guides are designed for use in processes at low yarn tensions with no damage. It helps decrease and maintain times and improve production efficiency greatly.
The gallery of ceramic wire guides
Remark:
We have been producing a variety of ceramic wire guide, including ceramic pigtail, ceramic traverse guide,
ceramic roller, ceramic bobbin, and so on.
Datasheet of Technical ceramics
| Property | Units | Material |
||||
| 99.5% alumina |
99% alumina |
95% alumina |
ZrO2 (Y-TZP) |
ZrO2 |
||
| Density | g/cm3 | ≥3.85 | ≥3.80 | ≥3.60 | ≥5.95 | ≥5.72 |
| Water absorption | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hardness | HV | 1700 | 1700 | 1500 | 1300 | 900 |
| Flexural strength | Mpa | ≥379 | ≥338 | ≥320 | ≥1200 | ≥1200 |
| Compressive strength | Mpa | ≥2240 | ≥2240 | ≥2000 | ≥1990 | 1750 |
| Fracture toughness | Mpa m1/2 | 4-5 | 4-5 | 3-4 | 6.5-8 | 11 |
| Max. service temperature |
ºC | 1675 | 1600 | 1450 | 1000 | |
| CTE | 1×10 -6 /ºC | 6.5~8.0 | 6.2~8.0 | 5.0~8.0 | 8.0~9.5 | 10.2 |
| Thermal shock | T(ºC) | ≥250 | ≥200 | ≥220 | ≥300 | 350 |
| Thermal conductivity(25ºC) | W/m.k | 30 | 29 | 24 | 3 | 3 |
| Volume resistivity | ohm.cm | |||||
| 25ºC | >1 x 10 14 | >1 x 10 14 | >1 x 10 14 | >1 x 10 11 | >1 x 10 11 | |
| 300ºC | 1 x 10 12 | 8 x 10 11 | 10 12 -10 13 | 1 x 10 10 | 1 x 10 10 | |
| 500ºC | 5 x 10 10 | 2 x 10 9 | 1 x 10 9 | 1 x 10 6 | 1 x 10 6 | |
| Insulation strength | KV/mm | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 20 |
| Dielectric constant(1Mhz) | (E) | 9.7 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 29 | 28 |
Manufacturing flow chart of advanced ceramic eyelet
We have in-housing comprehensive manufacturing types of equipment, including forming, sintering,
CNC machining, precision grinding, laser cutting, and so on, it helps us to control the quality very well.
Also, it greatly benefits cost control.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are a manufacturer of over 15 years of experience. You are welcome to visit our factory.
Q2: Do you send a sample to check?
A: Sure, the sample is free and freight collect.
Q3: When will you ship it?
A: If the products are in storage, we’ll ship within 48 hours
Q4: When can I get the price?
A: We regularly quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are in urgent need of getting the price.
Please call us or tell us in your email so that we will proceed with your inquiry as a priority.
Q5: Is it available to provide customized products?
A: We always support custom-made demand as per different materials, dimensions, and designs.
How to Fix a Faulty Drive Belt Tensioner
If you’re experiencing grinding, squeaking, or other unusual sounds from your car, your drive belt tensioner may be the culprit. In this article, we’ll discuss why a failed drive belt tensioner may need to be replaced and how to fix it. Once you have determined that your belt tensioner is faulty, you can use a Wrench to remove it and replace it with a new one. After you replace the belt tensioner, it will no longer be making noises.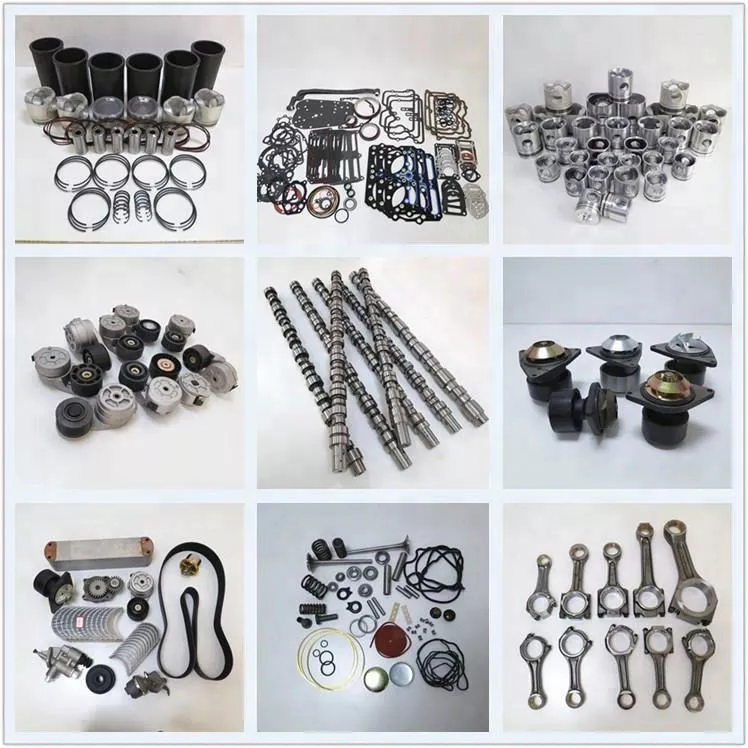
Problems with timing belt tensioner
Whenever your engine is making strange noises, it is likely that the timing belt tensioner is causing the problem. A bad timing belt tensioner is a big cause of such sounds, as the timing of the engine is critical. When the belt is moving properly, the camshaft and crankshaft are perfectly synchronized, and the valves work in perfect sync during the intake and exhaust strokes of each cylinder.
Other signs of a worn tensioner include rust bleeding and dripping. Usually, rust will appear at the mounting bolts and “stops” on the tensioner. Other symptoms of a worn timing belt tensioner are noise, resistance, and roughness. If any of these symptoms are present, it’s important to get the car fixed as soon as possible. Troubleshooting problems with timing belt tensioner is an easy process if you know the symptoms.
If your car starts making squeaking or grinding noises when you drive, it’s probably the timing belt tensioner. The timing belt can also cause problems with your engine’s valves. When the timing belt is too loose, the valves cannot fully combust the fuel-air mixture. If this problem is left undiagnosed, it could result in severe engine damage. To solve the problem, you must replace the timing belt tensioner.
The repair of the timing belt tensioner is not a difficult job if you’re experienced and comfortable with DIY car repairs. If you have a good knowledge of car repair, you can try to replace it yourself – but don’t forget that it is a complex repair job that requires a lot of skill. So, it’s best to hire a professional mechanic. And if you don’t have the necessary tools and training, you can always try the DIY method.
Other symptoms of a bad timing belt tensioner include an abnormal chirping noise, misfiring, and check engine light malfunction. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should replace the timing belt tensioner as soon as possible. Often, the belt is wearing out and can’t spin freely. You may have to replace the timing belt tensioner to avoid major damage to your engine. The best way to tell if the timing belt tensioner is failing is to check it regularly.
Cost of a new drive belt tensioner
A new drive belt can be expensive. Replacing 1 is usually a straightforward task that requires little knowledge, but some cars are more difficult than others. Replacing a drive belt by yourself may result in the replacement of parts you do not know. You may also encounter problems that cannot be resolved unless you have a mechanic check all the affected parts. You can save money by taking the car to a mechanic before trying to fix the problem yourself.
A drive belt tensioner should last at least 125,000 miles, but can break sooner. Most car mechanics will replace the tensioner after you notice the belt is slipping. It takes about 15 minutes to an hour to replace 1 of these parts, and you can do it yourself with the proper tools. You can also ask about the replacement of pulleys or sprockets. The price of a new drive belt tensioner depends on the make and model of your car.
The average cost to replace a drive belt tensioner is between $235 and $267. This cost includes labor and parts, but doesn’t include taxes or fees. Some vehicles may need related repairs as well, such as serpentine belts or tensioner housing. For a detailed estimate, use the RepairPal Fair Price Estimator. You can compare labor costs and shop for the best price. There are many options available online, and you can choose the most convenient 1 for your needs.
In addition to replacing the drive belt, you should also check the idler pulleys, which do not drive anything. If they have excessive movement, replace them. A failed drive belt tensioner can cause the belt to slip and affect other components of the car. You may also notice warning lights that indicate a problem with the alternator, water pump, or power steering. You should also check your vehicle’s air conditioning.
Replacing the tensioner pulley can be done yourself for about $50. Depending on the type of pulley and belt, you may need to replace other parts of the engine as well. You can save money by replacing a tensioner pulley yourself if you have the time and skills. It’s easy to replace a new drive belt tensioner if you’re a mechanically inclined individual.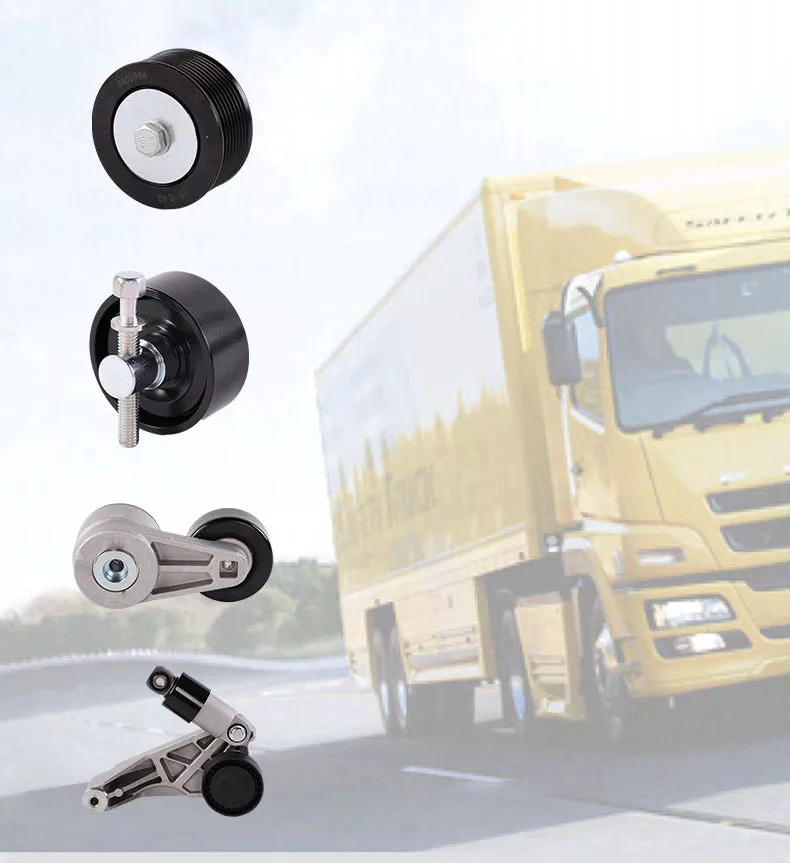
Repair options for a failed drive belt tensioner
A failed drive belt tensioner may have several symptoms. For instance, it can make a grinding or squealing sound, and it may emit a burning smell. The battery light on your car may also stay on. These are all signs that your drive belt has failed. However, these symptoms are not always indicative of the failure of the drive belt tensioner. Listed below are some common problems that can be caused by a failed drive belt tensioner.
To check for a failed drive belt tensioner, turn off the engine and examine the arm. If it doesn’t move, it’s time to replace the drive belt. A manual drive belt tensioner is easy to replace. A hydraulic or bad spring drive belt tensioner, however, will not be able to be fixed. If you can’t find a repair shop in your area, visit 1 of NAPA AutoCare locations, or a NAPA online store. They will be able to diagnose the failure and provide solutions for your car.
A spring tensioner is a type of drive belt tensioner that uses a spring-loaded pulley to apply the proper tension to the drive belt. However, spring tensioners can fail and seize if not properly maintained. A hydraulic tensioner uses hydraulic oil under pressure and can malfunction. In some cases, the tensioner can leak oil or lose its ability to tension the drive belt. It can also be damaged by excessive wear, which will cause the belt to break.
A failed drive belt tensioner can affect your car’s performance and functionality. In addition to making your car squeaky and jerky, a failed drive belt tensioner can cause the serpentine or v-belt to slip and wear out prematurely. Repairing a failed drive belt tensioner can also prevent your car from experiencing the same problems in the future. So, what do you do if you find your drive belt is slipping?
If your drive belt tensioner isn’t the problem, you’ll have to replace it. In some cases, a loose tensioner arm can lead to cracks in the tensioner housing. In the worst case scenario, the damaged tensioner can also lead to an overheated engine. Ultimately, a failed drive belt tensioner can cause your car to experience overheating, weak battery charging, and even a weakened power steering system.
Maintenance requirements for a drive belt tensioner
Drive belt tensioner maintenance begins with proper alignment of the pulleys. Misaligned pulleys or drives can wear a belt out too fast. Misalignment can occur if the component was recently replaced. A set of shims can restore the pulleys to the proper alignment. It is important to regularly check the tensioner to ensure proper function. Also, check the belt for cracks or wear.
Before performing any maintenance work, always turn off the drive to protect the motor. The belt should be in a safe position so that it will not fall on the workers. Lock down any moving parts and ensure the fans do not freewheel. When inspecting the drive belt tensioner, examine the belt guard for wear and debris. If the belt is damaged or has excessive heat, it is necessary to clean it or replace it.
It is important to maintain a proper fit between the belt and the drive belt tensioner. An incorrectly-sized drive belt will be difficult to install and adjust. An incorrect-rib count drive belt will fit, but will not last as long. Likewise, drive belts with too many ribs will not last as long. For these reasons, drive belt tensioners should be replaced when they are over 50,000 miles.
A drive belt tensioner is a pulley that rides on the outside surface of the serpentine belt. Its purpose is to maintain constant pressure on the pulleys that power car components. It is typically mounted on the front of the engine, bolted to the crankshaft, and rests against the serpentine belt. If the drive belt is cracked, it needs to be replaced immediately. If the arm is loose or bent, the bearings in the tensioner are probably worn.
The drive belt tensioner is an important part of the drive system, which is essential for smooth operation of the vehicle. However, it does wear out prematurely and should be replaced at a certain mileage. It should also be inspected for normal wear and tear as a result of road dirt, excessive heat, and oil leaks. However, it is important to remember that drive belts are highly sensitive to excessive heat, road dirt, and oil leaks.


China Best Sales Applied in Textile Machinery Ceramic Wire Guides Caged Ceramic Pulley with Great quality
Product Description
Applied in Textile Machinery Ceramic Wire Xihu (West Lake) Dis.s Caged Ceramic Pulley
1.Applicable for wire jump preventing during winding.
2. The precision ceramics circle inside has an ultra-fine polishing degree Ra0.2.
3. Hign-speed bearing in its’ porcelain circle controls the sliding distance between enameled wire and the circle under 0.2mm.
4.The structure protect the film and assure the beating of the enameled wire in a very small scope to stabilize the tension.
5. Being popular in the market for easy installation, low maintenance cost, robust construction and longer service life.
| Installation Specification Ø2 Series | ||||||||
| Nubmer | Model | specificationmm | ||||||
| L | L1 | D | D1 | d1 | d2 | H | ||
| 1 | RC0326-2-1006 | 26 | 6 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 2 | RC0326-2-0806 | 26 | 6 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 3 | RC0330-2-0807 | 30 | 7 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | N/A |
| 4 | RC571-2-571 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | N/A |
| 5 | RC571-2-1008 | 35 | 8 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | N/A |
| 6 | RC571-2.5-1411 | 35 | 11 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.8 | N/A |
| 7 | RC0336-2.5-1011 | 36 | 11 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 8 | RR 0571 -2-1610 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | N/A |
| 9 | RS571-2.5-1210 | 35 | 10 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | N/A |
| 10 | RC571-2-1208 | 30 | 8 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.6 | N/A |
| 11 | RS 0571 -2 | 30 | N/A | 2 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | N/A |
HARTAI TECHNOLOGY INDUSTRY Co., Ltd is professional manufacturer for coil winding pulley, We offer ceramic coated rollers, caged caramic pulleys, wire jump preventer and ceramic wire guides for coil winding machine at competitive price.
Types of V-Belts and Their Properties
A v-belt’s inside length and pitch are determined by measuring along the bottom side. The included angle of a v-belt is measured from its flanks when it is extended. Most v-belt sections are 40 degrees. There are different types of v-belts, and the dimensions of each are standardized by different organizations. This article will introduce the different types of v-belts and their properties.
Notched v-belts reduce bending stress
Notched V-belts reduce bending stress by reducing the axial length of the belt by 2 or more notches. These notches are characterized by different profiles, which differ in the pitch angle and the inside length. ISO and DIN standards are followed by the manufacturers of these belts. Notched v-belts are used on industrial machinery in countries other than the US.
Compared to the standard V-belts, notched ones are designed to resist bending stress better and offer better heat dissipation. They also last longer and run cooler than standard V-belts. Furthermore, they are about 2 percent more energy efficient than their standard counterparts. Therefore, notched V-belts are a viable replacement for standard V-belts.
Notched V-belts are commonly used in industrial applications because of their low price, ease of installation, and availability of many sizes. Another advantage of notched V-belts is that they provide more wedging force and higher load capacity. Notched V-belts have a wider v-groove than flat ones, which makes them more effective for heavy-duty applications.
Notched V-belts also provide better traction. They reduce bending stress, which is beneficial for preventing fatigue and tearing of v-belts. Additionally, v-belts can be installed in an existing equipment to add more performance. And with proper maintenance and installation, notched V-belts will provide trouble-free service for many years to come.
Ribbed v-belts reduce heat dissipation
Various kinds of v-belts are available for varying applications. The more popular types are the fractional horsepower and the double-V. Fractional horsepower v-belts are designed for light-duty applications, such as machine shop equipment and household appliances. The common sectional names are 2L, 3L, 4L, and 5L. The L in each of these belts refers to the top width of the belt, multiplied by 1 eighth inch.
Unlike conventional belts, ribbed v-belts are flexible, making them ideal for use in vibrating loads. They reduce heat dissipation and can be ordered in single or multiple sets to match your application. However, ribbed v-belts should not be mounted on deep-groove sheaves, as this can cause the belt to turn over. If you use deep-groove sheaves, the risk of rupture is very high. Deep-groove sheaves can also cut banded belts. Extremely worn sheaves can also cause the belt to rip.
The 2 types of ribbed v-belts differ in their construction and application. While both types have trapezium cross-sections, they are similar in that they are made of polyurethane or other durable materials. Ribbed v-belts have an additional layer of fabric on the elastomer core for reduced noise and better heat dissipation.
Ribbed v-belts are available in a variety of sizes, including trough v-belts. Their cross-sections are categorized by their top and bottom widths and depths. The included angle of most v-belt sections is approximately 40 degrees. Different types of v-belts have different cross-sections, and these cross-sections are standardized by various organizations.
As the load increases, a ribbed v-belt will wedge into the groove and decrease the amount of friction needed to maintain the correct torque. Flat belts can track off the pulleys due to friction. However, V-belts are more stable and require less width than flat belts. The main advantage of ribbed v-belts is their increased efficiency.
The global-local finite-element model is also used to calculate the maximum and minimum J-integrals during a belt’s running cycle. The data is then used to evaluate the durability of ribbed v-belts in various applications. The numerical models used for the calculations involve a ribbed V-belt with 5 full ribs.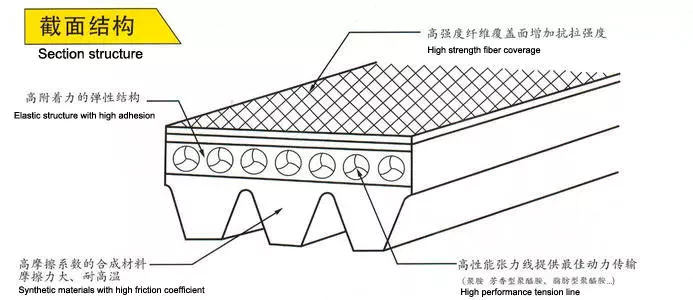
Cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip
Cogged v-belts are designed for maximum performance and durability on even the harshest drive systems. These belts are made from high-modulus polyester cords that resist hardening and stretch and provide superior balance and strength. They also feature raw-edge sidewalls to reduce slip and drive vibration. In addition, they have specially-formulated rubber compounds for oil resistance. CZPT Cog-Belt offers substantial savings in downtime, energy consumption and horsepower.
A double cogged v-belt combines the benefits of cogged and double vee-belts. Its bonded reinforced tie band offers enhanced flexibility and reduces belt whipping in multiple-belt drives. Double cogged v-belt dimensions vary depending on the standards of the manufacturer. Regardless of the type, you’ll want to use a belt that is aligned correctly.
Standard v-belts are also known as wrapped or raw edge v-belts. Wrapped V-belts feature fabric covers above and beneath the cord to increase lateral rigidity and reduce belt whip. Cogged V-belts also have fabric covers to prevent wear on the core and increase the belt’s operating temperature. They’re ideally suited for applications that require high-temperature operation.
Cogged V-belts can significantly decrease energy consumption and improve power transmission capabilities. They also have a bias-cut cover stock that provides axial and lateral stability while preserving the cord integrity. A fiber loaded cogged construction offers optimum flexibility while minimizing heat buildup. It can be installed on any type of drive, including chain conveyors and industrial-grade machines.
The two-layer tie-band permanently bonds multiple belts together. This provides maximum cord support, heavy shock absorption, and stability. The belts are also engineered with patented banding processes that eliminate belt turnover and distribute load evenly across the drive. CZPT Cog-Band Belts minimize belt whip and provide stability. They also minimize belt turnover and rollover in heavy-duty industrial applications.
A classic v-belt is the most common and economical belt. Its nominal dimensions are 1/2″ to 1-11/2″ wide and 16″ to 400 inches long. The width is usually 40 degrees. Different organizations use different cross-sections to classify v-belts. The following table provides a general comparison of the 2 types. The Cogged V-Belt is designed to reduce belt whip by increasing the lateral rigidity of the belt.
Cogged v-belts provide superior environmental resistance
The patented design of the Dayco V-Belt provides maximum power transmission while combining the benefits of a cogged belt and raw-edge construction. The belt’s top cogged design helps increase air flow around it, preventing deterioration and extending its useful life. The belt’s three-ply design features neoprene impregnated fabric for superior durability and a specially-formulated polyester cord for increased strength and stability.
A variety of v-belts are available, with cogged and notched versions presenting unique characteristics. Cogged V-belts are more flexible than uncogged versions and feature ‘X’-shaped grooves for enhanced heat dissipation. Cogged V-belts are interchangeable with conventional v-belts, although their ‘X’ design is most common. Hexagonal v-belts are a popular option for applications where traction is needed.
Another type of Cogged V-belt is designed specifically for outdoor power equipment. This v-belt is brown, with smooth clutching covers. Its aramid cord is very strong and provides superior durability in adverse conditions. Cogged V-belts can withstand severe shock loads and are therefore ideal for outdoor power equipment. Furthermore, they offer superior environmental resistance, minimal stretch, and a long service life.
A Cogged V-belt is composed of tensile cords that are supported by a rubber stock. Different manufacturers use different synthetic rubber stocks for this purpose. These materials help to extend the belt’s operating temperature range and resist premature failure. In addition to tensile cords, the belt’s body is covered with a fabric cover. The fabric is treated to form a chemical bond with the core materials, which allows it to withstand constant bending.

